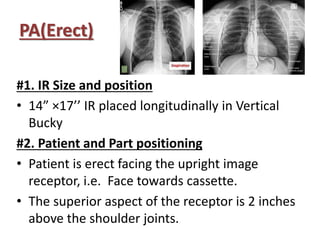
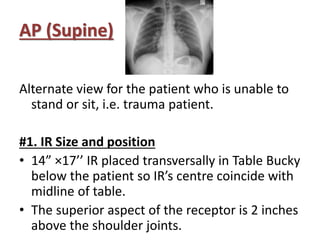
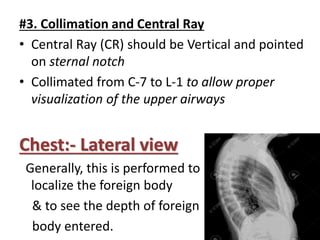
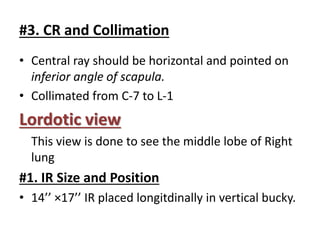
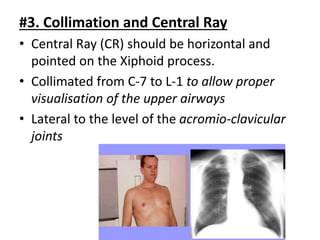
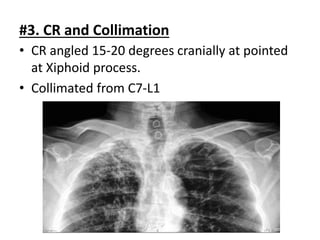
This document describes various chest radiography views including PA, AP, lateral, lordotic, and special views. It provides details on image receptor size and position, patient positioning, central ray direction, and collimation for each view. The views are used to evaluate conditions like pneumonia, tuberculosis, and fractures as well as localize foreign bodies.