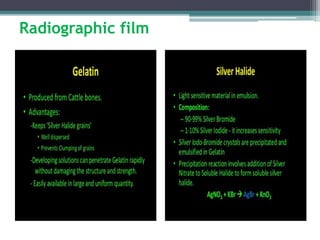
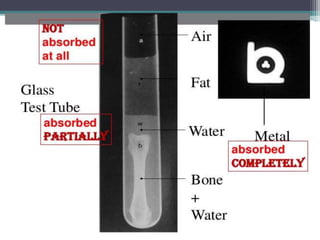
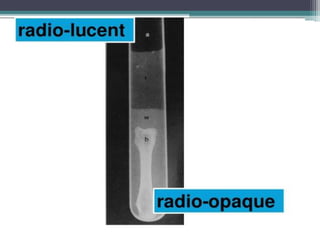
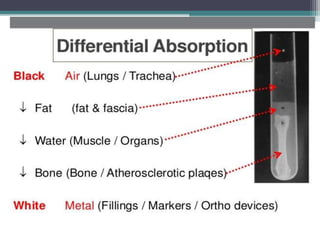
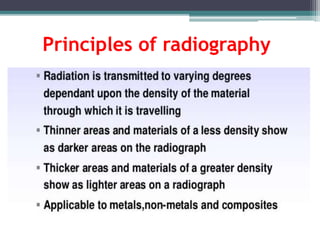
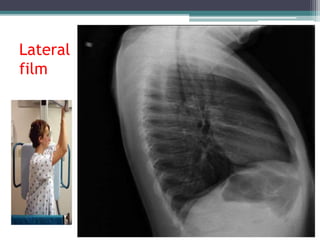
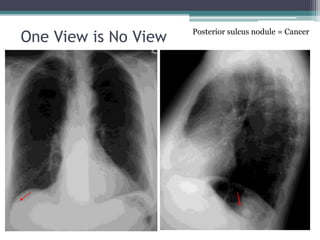
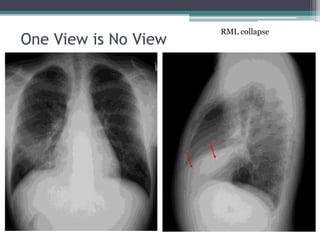
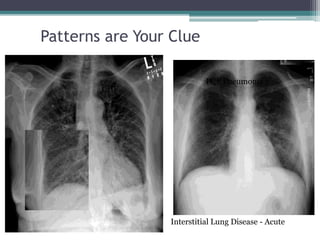
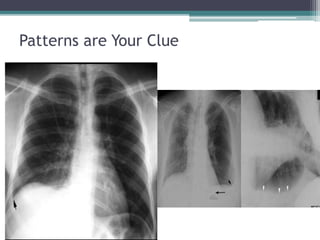
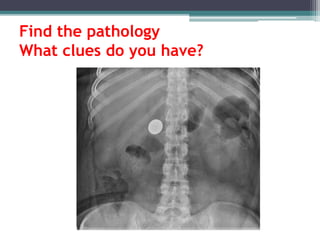
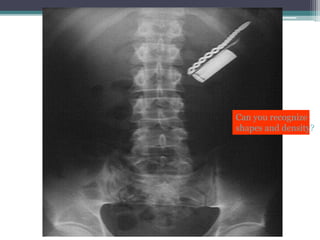
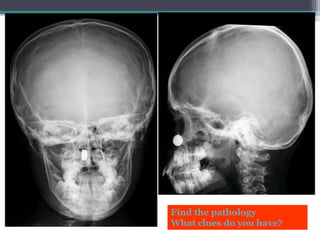
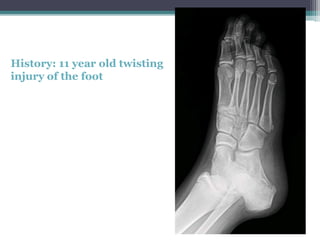
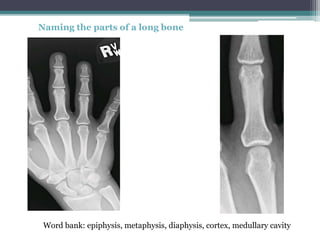
This document discusses x-rays and medical imaging technology. It covers:
1. X-rays are a form of ionizing radiation that can potentially damage DNA and increase cancer risk, though risk from medical imaging is generally small depending on dose, age, sex, and body region exposed.
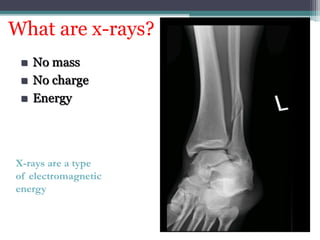
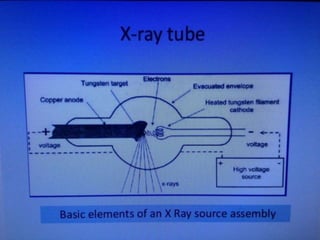
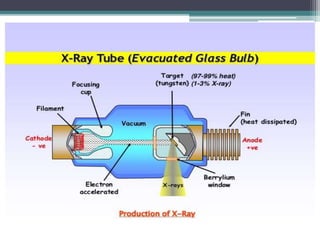
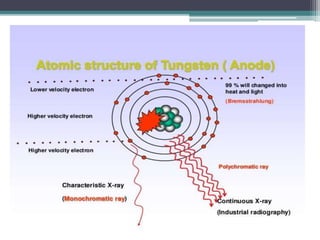
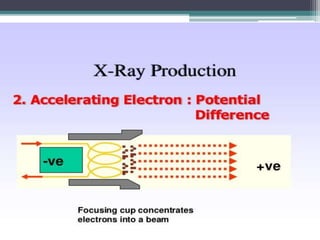
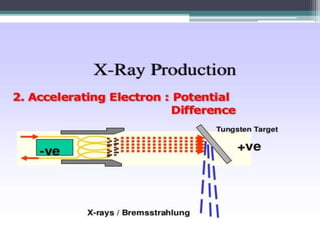
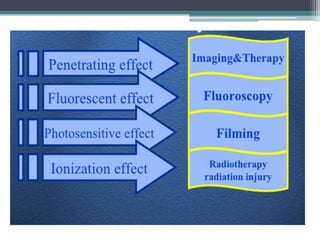
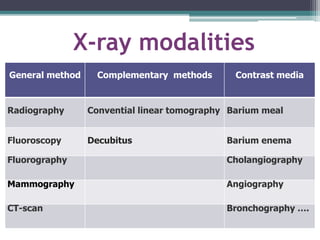
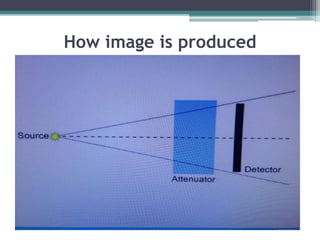
2. X-rays are used in medical imaging to non-invasively diagnose disease, monitor therapy, and guide procedures through techniques like radiography, fluoroscopy, and CT scans.
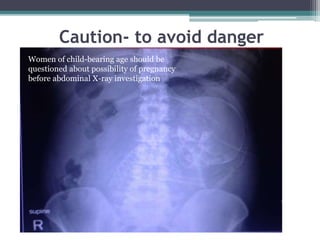
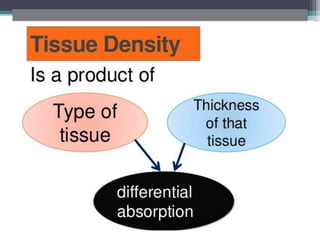
3. Principles of radiation protection include justifying exams based on medical need and optimizing techniques to use the lowest dose for adequate diagnosis. Risks include potential long-term cancer risk and rare tissue effects.