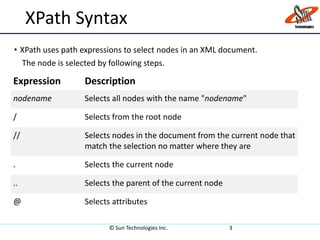
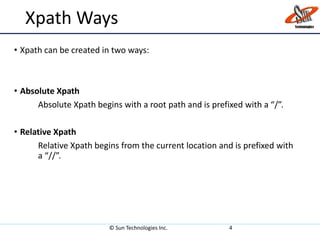
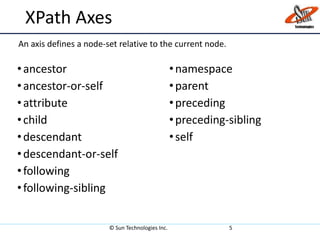
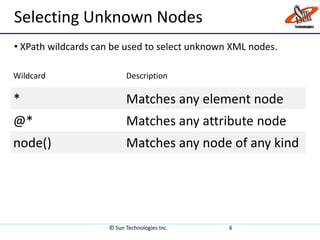
XPath is a language for selecting nodes in an XML document. It uses path expressions to navigate within elements, attributes, and nodes. XPath syntax includes nodename, /, //, ., .., @, and axes like ancestor, child, and descendant to locate nodes. XPath expressions can be absolute, starting from the root, or relative from the current location. It also contains functions to select unknown nodes, test strings, and check if a node contains, starts with, or ends with a value.


![XPath functions
XPath contains a number of functions on node sets, numbers, and strings;
here are a few of them:
• Contains: contains(arg1, arg2) tests if arg1 contains arg2
Example://img[contains(@src,’Profile’)]
• starts-with: starts-with(arg1, arg2) tests if arg1 starts with arg2
Example: //*[starts-with(name(), 'sec']
• ends-with: ends-with(arg1, arg2) tests if arg1 ends with arg2
Example: //*[ends-with(name(), ‘details']
© Sun Technologies Inc. 7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationonxpath-170313100532/85/XPATH-7-320.jpg)