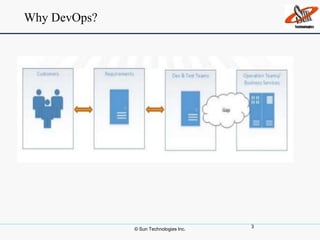
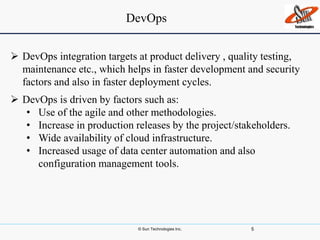
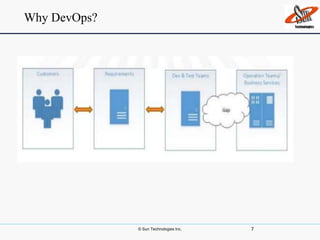
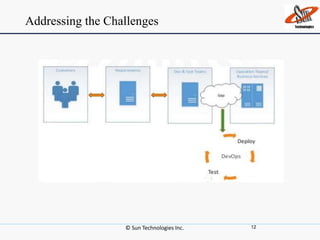
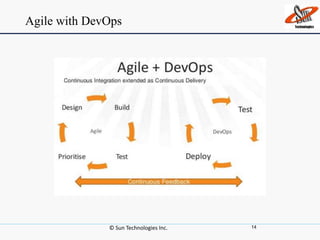
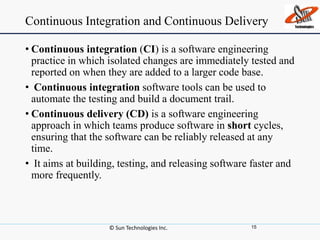
This document discusses DevOps, including what it is, its principles, challenges and benefits. DevOps aims to bridge the gap between development and operations through communication, collaboration and automation. It allows for rapid product evolution, improved quality and reduced costs and risks. DevOps principles include developing in similar environments to production and frequent, validated deployments. Challenges include release management and coordination, which DevOps addresses through continuous integration, delivery and automation tools. When to adopt DevOps includes ecommerce and websites, but not critical platforms like banking systems.