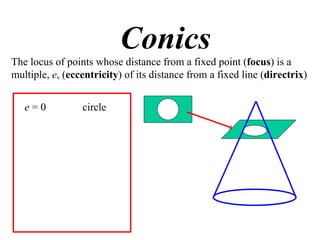
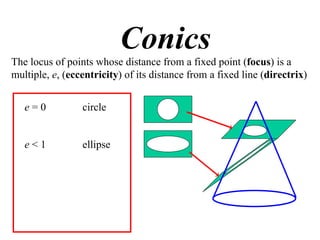
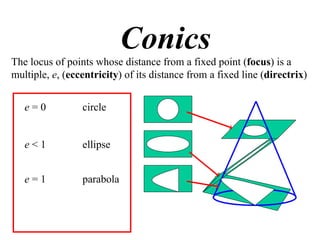
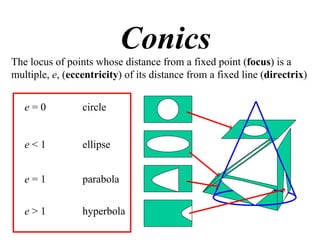
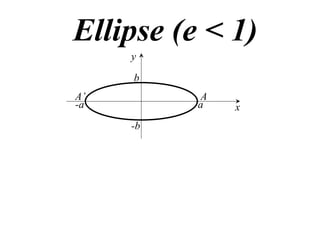
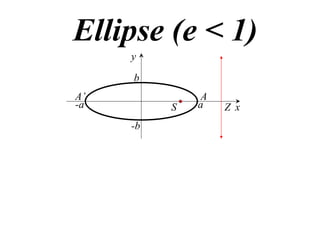
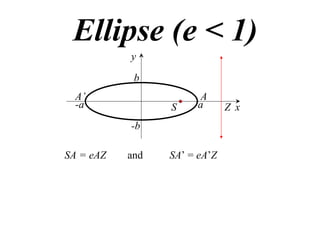
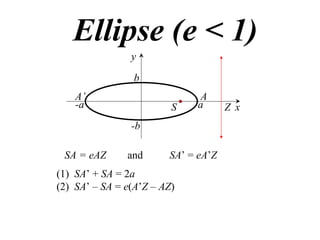
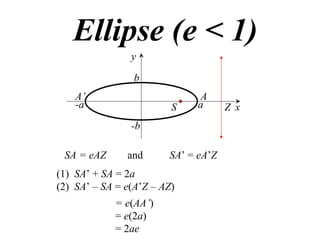
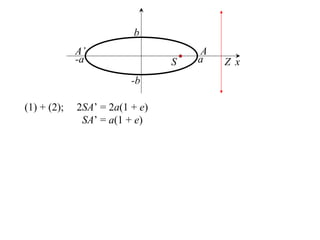
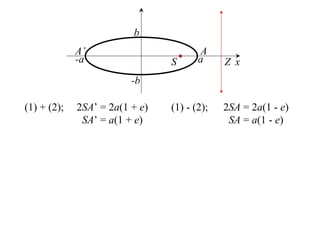
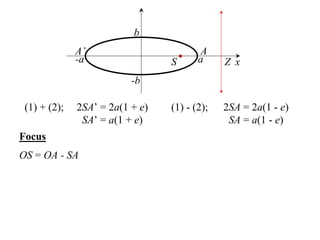
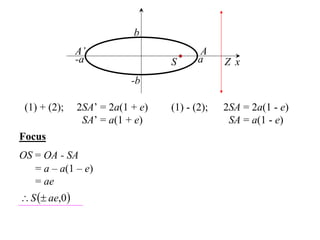
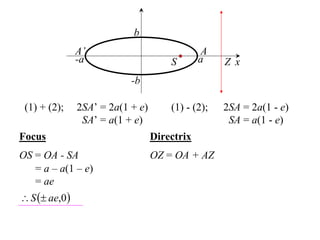
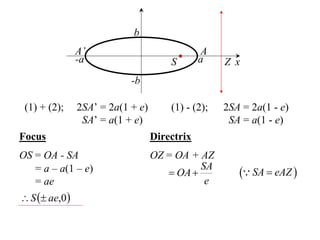
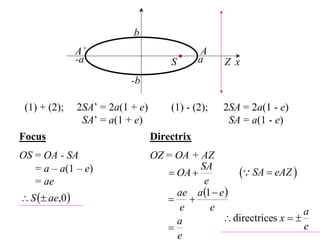
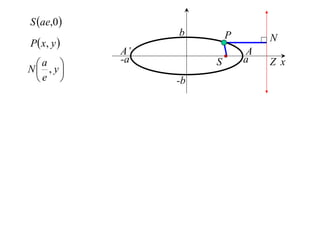
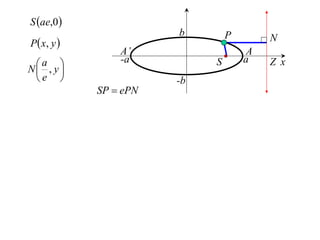
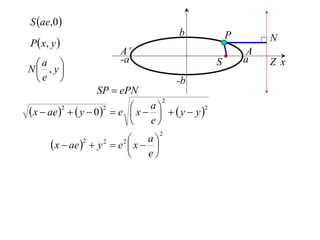
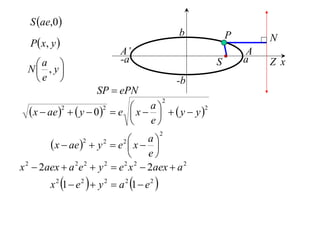
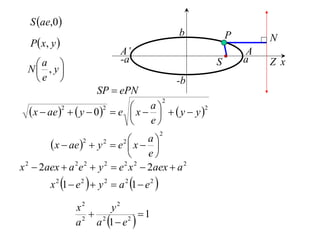
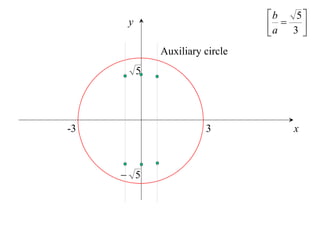
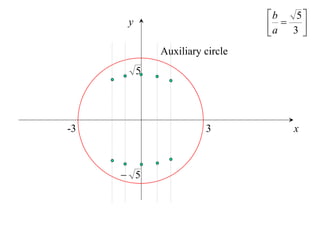
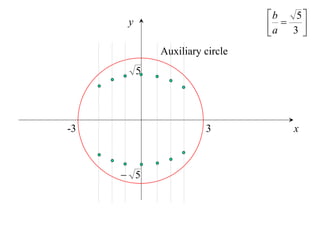
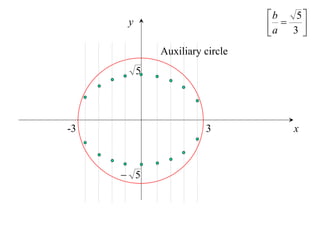
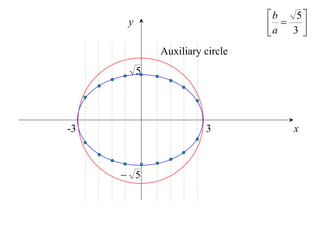
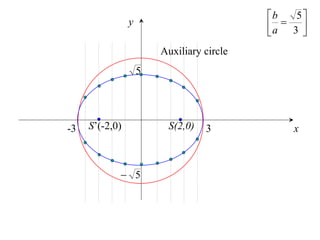
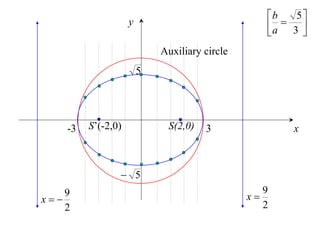
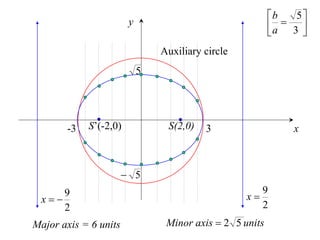
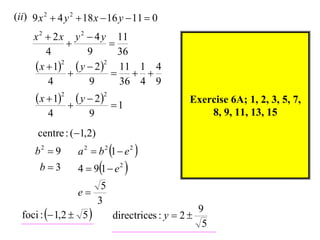
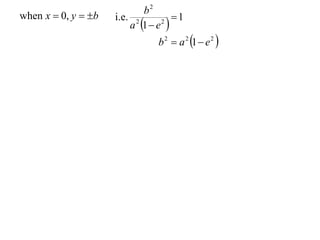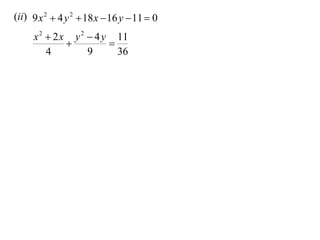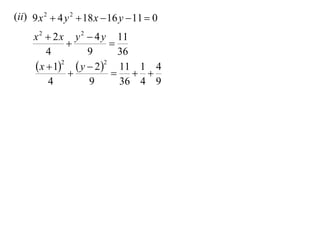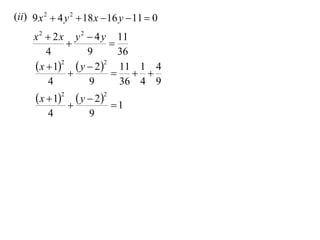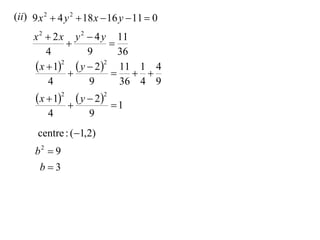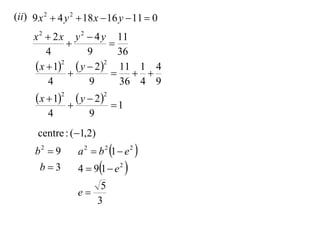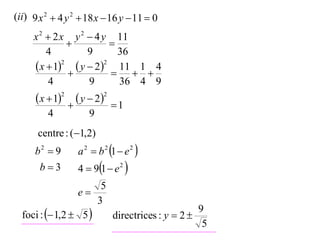The document discusses conic sections, specifically the ellipse. An ellipse is defined as the locus of points where the sum of the distances from two fixed points (foci) is a constant. For an ellipse, the eccentricity e is less than 1. The foci of an ellipse lie on the major axis, and the distance from each focus to any point on the ellipse follows the relationship d=ae, where a is the semimajor axis. The semiminor axis b is given by b2=a2(1-e2).