1. The document provides examples and explanations of key concepts in geometry including Cartesian coordinates, distance between points, types of triangles, area of triangles and polygons, division of line segments, slope and inclination of lines, and angle between two lines.
2. One example shows that the points (-2, 0), (2, 3) and (5, -1) are the vertices of a right triangle by applying the Pythagorean theorem.
3. Another example finds the area of the triangle with vertices (5, 4), (-2, 1) and (2, -3) to be 20 square units using the area formula.
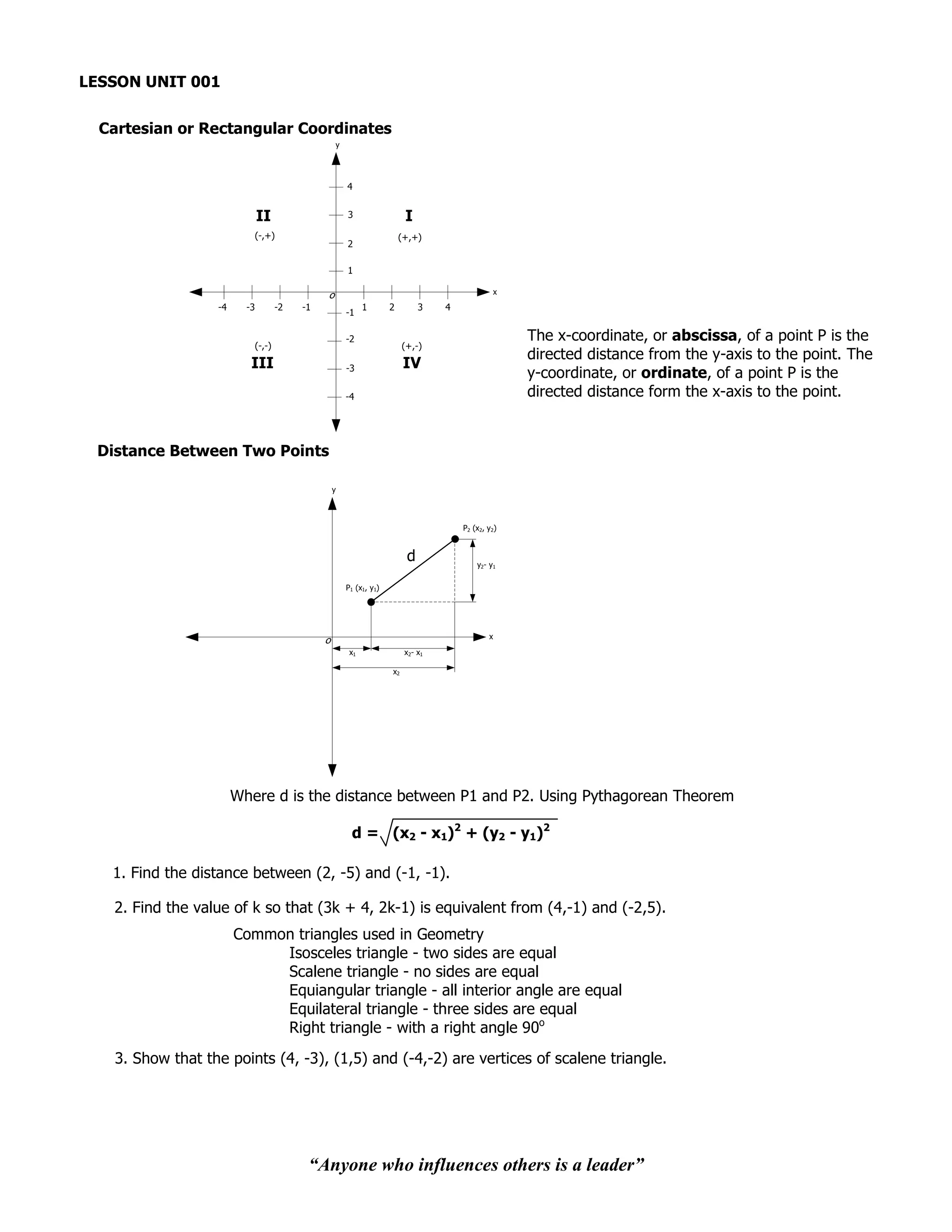
![4. Show that the points (5, 4), (-2, 1) and (2, -3) are the vertices of an isosceles triangle.
5. Show that the points (-2, 0), (2, 3) and (5, -1) are the vertices of a right triangle.
6. Show that (-1, 1), (0, -3), (5, 2) and (4, 6) are the vertices of a parallelogram.
Area of a Triangle
y
P1 (x1, y1)
P3 (x3, y3)
x
x1 x 2 x3
1
A= y1 y2 y3
2
1
A= [(x1y2 + x2y3 + x3y1) - (y1x2 + y2x3 + y3x1)]
2
P2 (x2, y2)
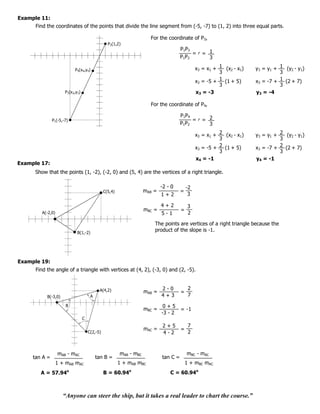
7. Find the area of the triangle with vertices at (5, 4), (-2, 1) and (2, -3).
8. Find the area of a parallelogram with vertices at (-1, 1), (0, -3), (5, 2) and (4, 6).
Area of a polygon of n-sides:
x1 x2 x3 ... xn
1
A= y1 y2 y3 ... yn
2
Division of Line Segment
y P2 (x2, y2)
P (x, y)
y2 - y1
y - y1
P1 (x1, y1)
Let P as the point that divides the line segment
x
from P1 to P2 such that: P1P
x - x1 =r
P1 P2
x2 - x1
Using similar triangles:
x - x1 y - y1
=r =r
x2 - x 1 y2 - y1
x = x1 + r (x2 - x1) y = y1 + r (y2 - y1)
1
If midpoint of the line segment from P1 to P2, if r =
2
x1 + x2 y1 + y2
x= y=
2 2
“Reputation is made in a moment. Character is built in a lifetime.”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/001basicconcepts-110917104853-phpapp01/85/001-basic-concepts-2-320.jpg)
![CARTESIAN COORDINATE
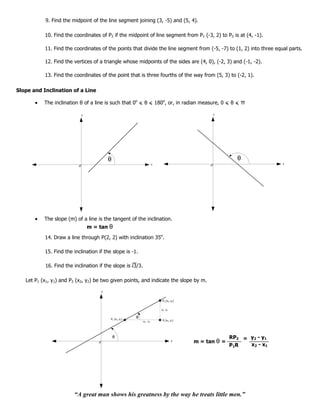
Example 5:
Show that the points (-2, 0), (2, 3) and (5, -1) are the vertices of a right triangle.
|AB| = (5 - 2)2 + (-1 - 3)2
B(2,3)
|AB| = 5 units
C(-2,0)
|BC| = (2 + 2)2 + (3 - 0)2
A(5,1)
|BC| = 5 units
|CA| = (-2 - 5)2 + (0 + 1)2
|CA| = 50 units
The vertices shows a right triangle because it satisfies the Pythagorean theorem.
Example 7:
Find the area of the triangle with vertices at (5, 4), (-2, 1) and (2, -3).
2 5 -2 2
1
P2(5,4)
A= -3 4 1 -3
2
1
A= [(8+5+6) - (-15-8-2)]
P3(-2,1) 2
A = 20 sq. units
P1(2,-3)
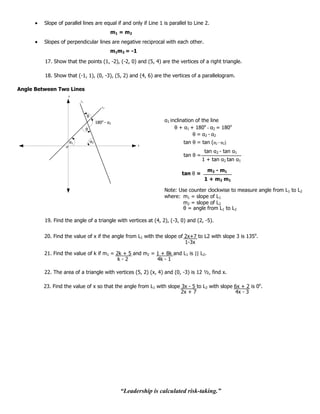
Example 10:
Find the coordinates of P2 if the midpoint of line segment from P1 (-3, 2) to P2 is at (4, -1).
x1 + x 2 y1 + y2
x= y=
2 2
-3 + x2 2 + x2
4= -1 =
P1(-3,2) 2 2
x2 = 11 y2 = -4
Mid point (4,-1)
P2(x2,y2)
“Unless you are faithful in small matters, you won't be faithful in large ones.” Luke 16:10a](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/001basicconcepts-110917104853-phpapp01/85/001-basic-concepts-5-320.jpg)