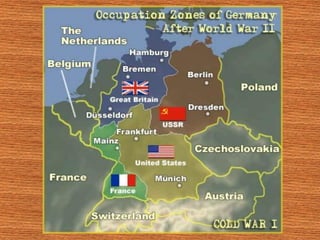
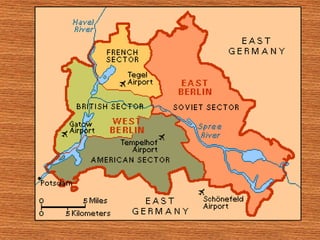
The Holocaust had a profound impact on Germany's image in the rest of the world. During WWII, Hitler systematically killed 6 million Jews through concentration camps and gas chambers. After Germany's surrender in 1945, the Allied powers divided Germany into Western and Eastern sectors, with the Western powers controlling West Germany and the Soviet Union controlling East Germany.