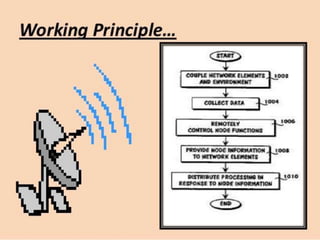
This document discusses wireless integrated network sensors (WINS) for border security. WINS were developed in the 1990s by DARPA to allow distributed sensor networks to operate using very low power. The key points are:
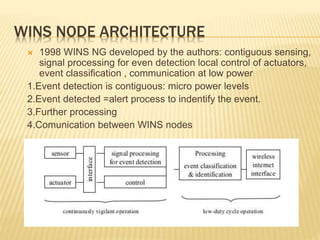
1. WINS nodes can detect intrusions using very little power (microwatts), making them cheaper than conventional radar systems.
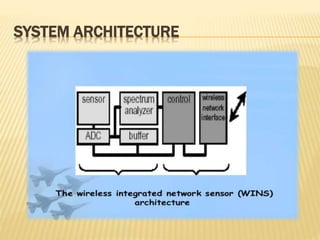
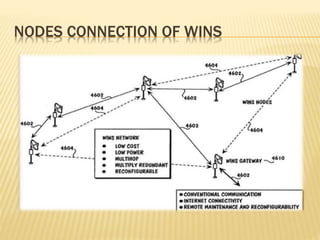
2. A typical WINS network architecture involves distributed sensor nodes that detect events, process signals locally, communicate with each other, and transmit alerts.
3. WINS applications include environmental monitoring, infrastructure monitoring, and border security due to their low-cost, distributed nature.