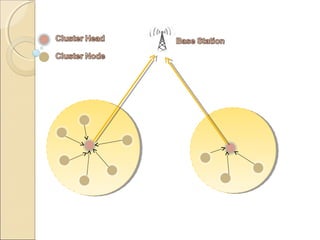
This document discusses generating sensor nodes and clustering for energy efficiency in wireless sensor networks (WSNs). It describes how sensor nodes are organized into clusters with a cluster head that communicates with the base station. The presentation proposes an algorithm for selecting the cluster head based on the node's distance to the base station and other nodes, with the goal of increasing network lifetime by optimizing energy consumption. Clustering helps reduce energy usage through data aggregation and limiting transmissions to cluster heads only.