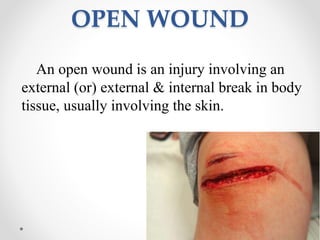
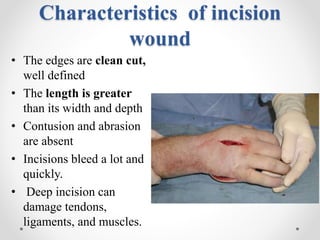
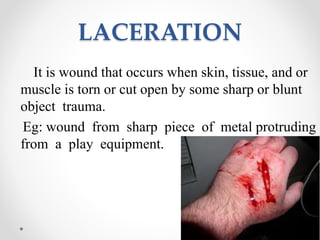
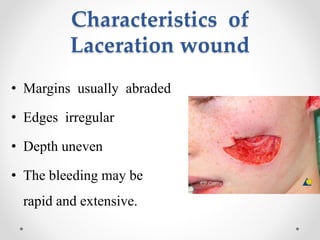
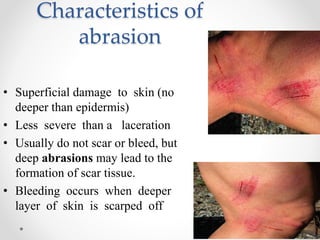
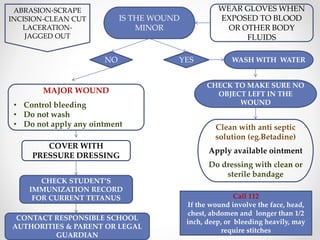
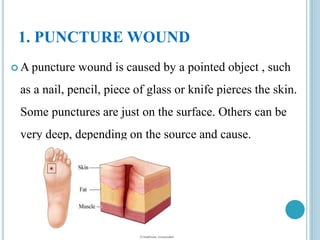
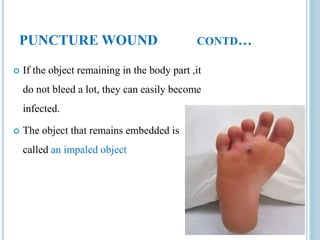
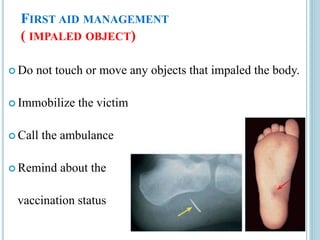
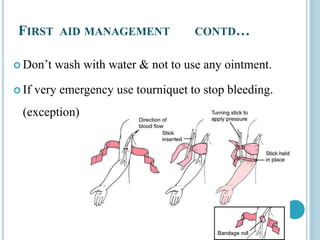
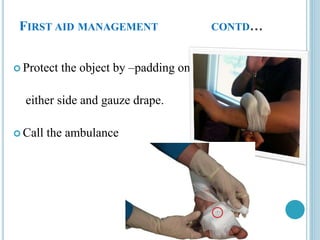
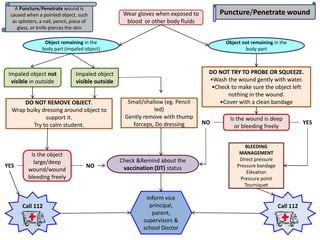
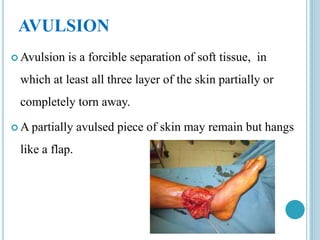
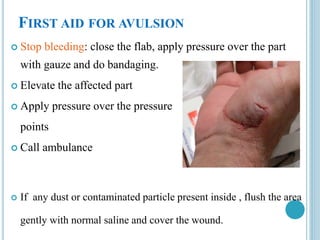
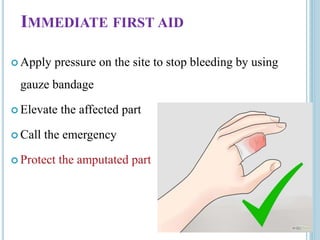
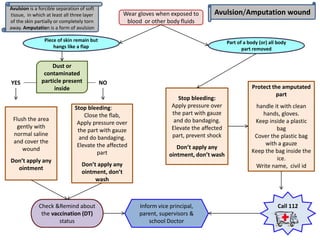
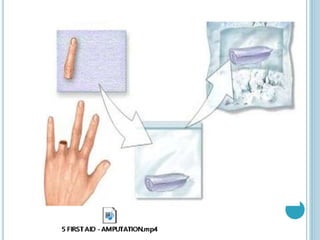
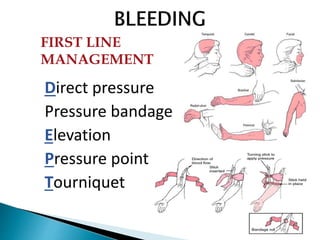
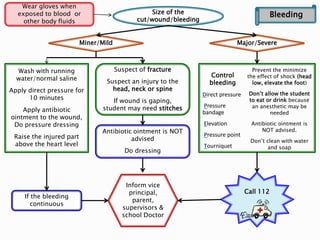
This document provides information on different types of wounds, including open wounds, incisions, lacerations, abrasions, puncture wounds, penetrating wounds, avulsions, and amputations. It describes the characteristics and signs of each type of wound and outlines the appropriate first aid response, which includes controlling bleeding, preventing infection, cleaning and dressing the wound, elevating the injured area, and determining whether to apply antibiotic ointment or seek further medical attention. The key steps for all wound types are to control bleeding, prevent shock, avoid contaminating or removing any embedded objects, and call emergency services for serious or uncontrolled bleeding.