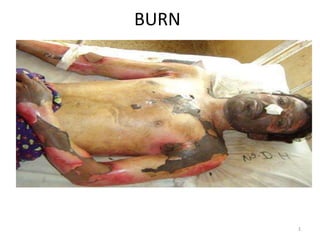
This document discusses the management of burn injuries. It begins with an introduction noting that scalds are the most common burn in children from accidents with hot liquids. Classification of burns is then described based on percentage of total body surface area burned and depth of burn. Pathophysiology involves inflammation, hypovolemia, and potential inhalation injury. Assessment involves determining burn size, depth, and severity. Management involves stabilizing the airway, providing fluid resuscitation, controlling the environment, and considering surgery depending on the depth and extent of the burn. Complications can include shock, renal failure, and infection.