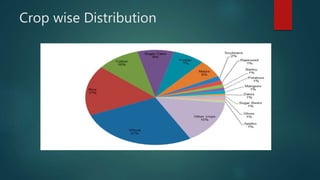
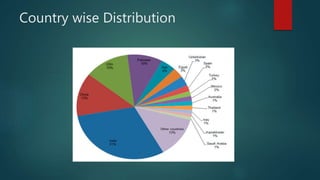
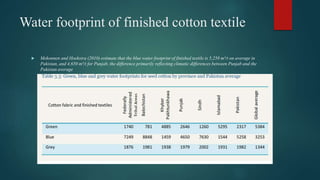
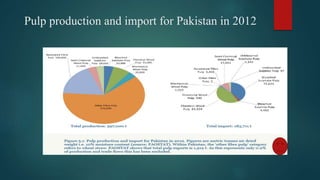
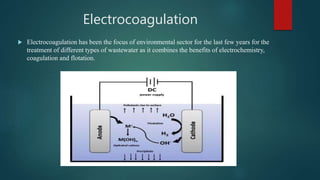
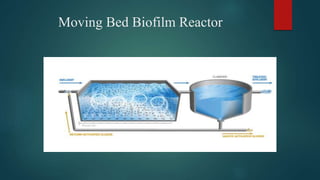
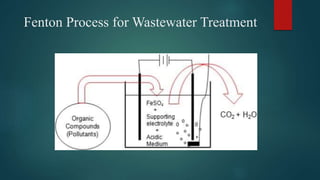
The document discusses the industrial water usage and its pollution impact in Pakistan, highlighting that while industry uses only 2-3% of fresh water resources, it contributes significantly to pollution. It emphasizes the importance of understanding the water footprint in various sectors, particularly in the food and textile industries, and outlines water management solutions provided by Water Care Services. Key points include the need for efficient wastewater management, water conservation technologies, and the significance of water recycling and reuse in promoting sustainable development.