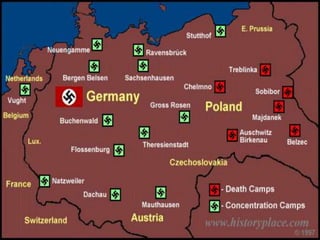
The document summarizes key events leading up to and during World War II. It discusses the rise of fascist dictators like Hitler in Germany and Mussolini in Italy in the 1930s. It also discusses the policy of appeasement by Britain and others to Hitler's expansionism, which ultimately failed. It then outlines major military campaigns and turning points of the war, including Germany's invasion of Poland starting the war, the Battle of Stalingrad, D-Day, and the dropping of atomic bombs on Hiroshima and Nagasaki that led to Japan's surrender.