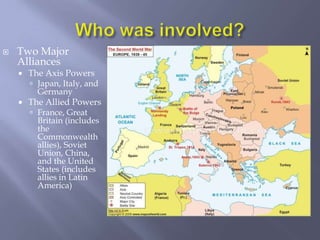
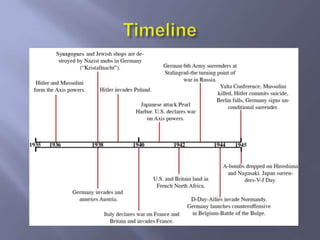
World War II involved two major alliances - the Axis powers of Germany, Italy, and Japan against the Allied powers of France, Britain, the Soviet Union, China, and the United States. Key figures included Adolf Hitler of Nazi Germany, Franklin Roosevelt and Harry Truman of the US, and Joseph Stalin of the Soviet Union. Major events of the war included Germany's blitzkrieg across Europe, the Holocaust, Pearl Harbor, and the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki. By 1943, German forces lost momentum against the Soviets, and Allied forces invaded from North Africa and Italy, culminating in Germany's surrender in 1945.