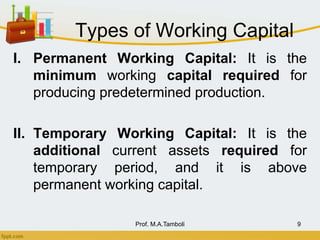
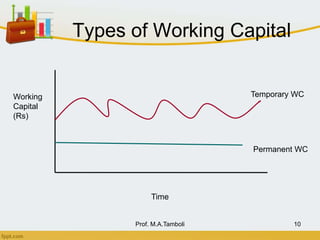
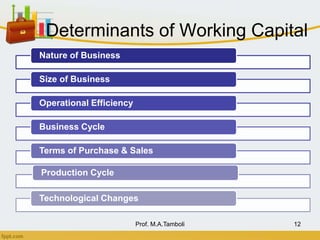
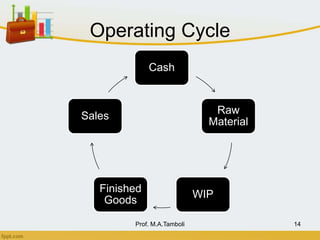
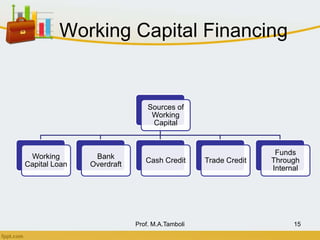
This document discusses working capital management. It defines working capital as short-term funds used to meet operating expenses and keep a business running. There are two concepts of working capital: gross working capital, which is the sum of all current assets, and net working capital, which is current assets minus current liabilities. The document also covers the nature, scope, components, determinants, and financing of working capital.