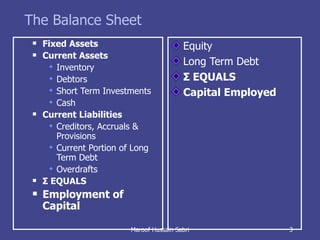
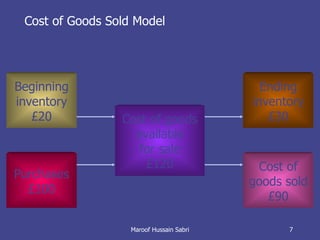
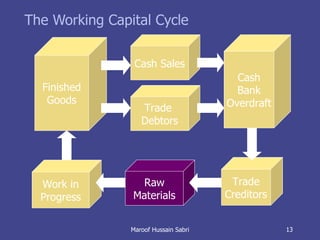
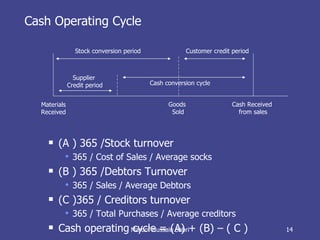
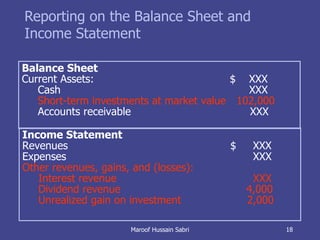
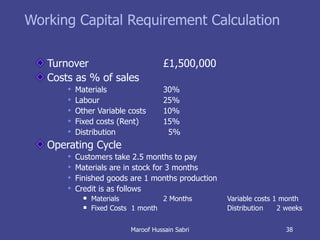
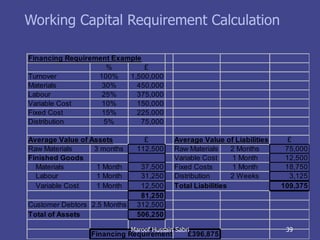
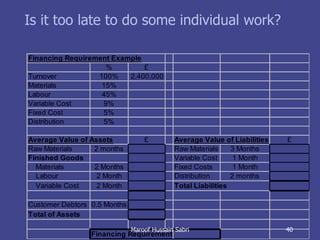
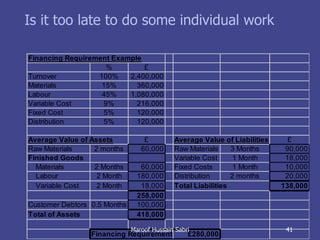
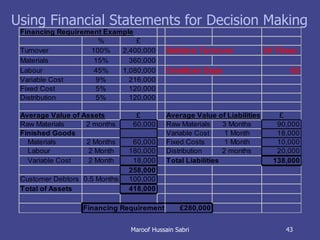
The document discusses key concepts related to working capital management including current assets, current liabilities, and calculating working capital requirements. It defines working capital as current assets minus current liabilities and describes key current asset and liability line items such as inventory, accounts receivable, accounts payable, and accrued expenses. The document also discusses calculating working capital needs based on factors like a company's operating cycle, credit terms, and inventory turnover.