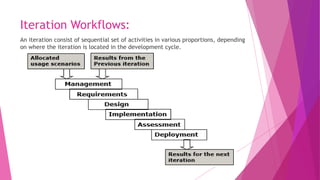
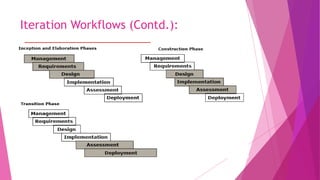
The document discusses 7 top-level workflows for software project management: management, environment, requirements, design, implementation, assessment, and deployment. It also outlines 4 key principles: having an architecture-first approach, using an iterative life-cycle process, practicing roundtrip engineering, and taking a demonstration-based approach. Iterations consist of sequential activities from the various workflows in different proportions depending on the life cycle phase.