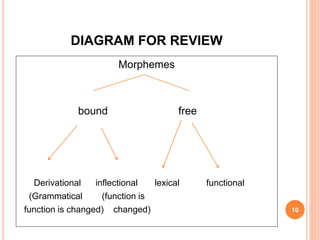
This document discusses descriptive syntax and word formation processes. It defines words and their components, called morphemes. There are two types of morphemes: free morphemes, which can stand alone as words, and bound morphemes, which cannot. Words are formed through processes like affixation, blending, clipping, and compounding. The document also outlines the eight parts of speech in English and provides examples of each.