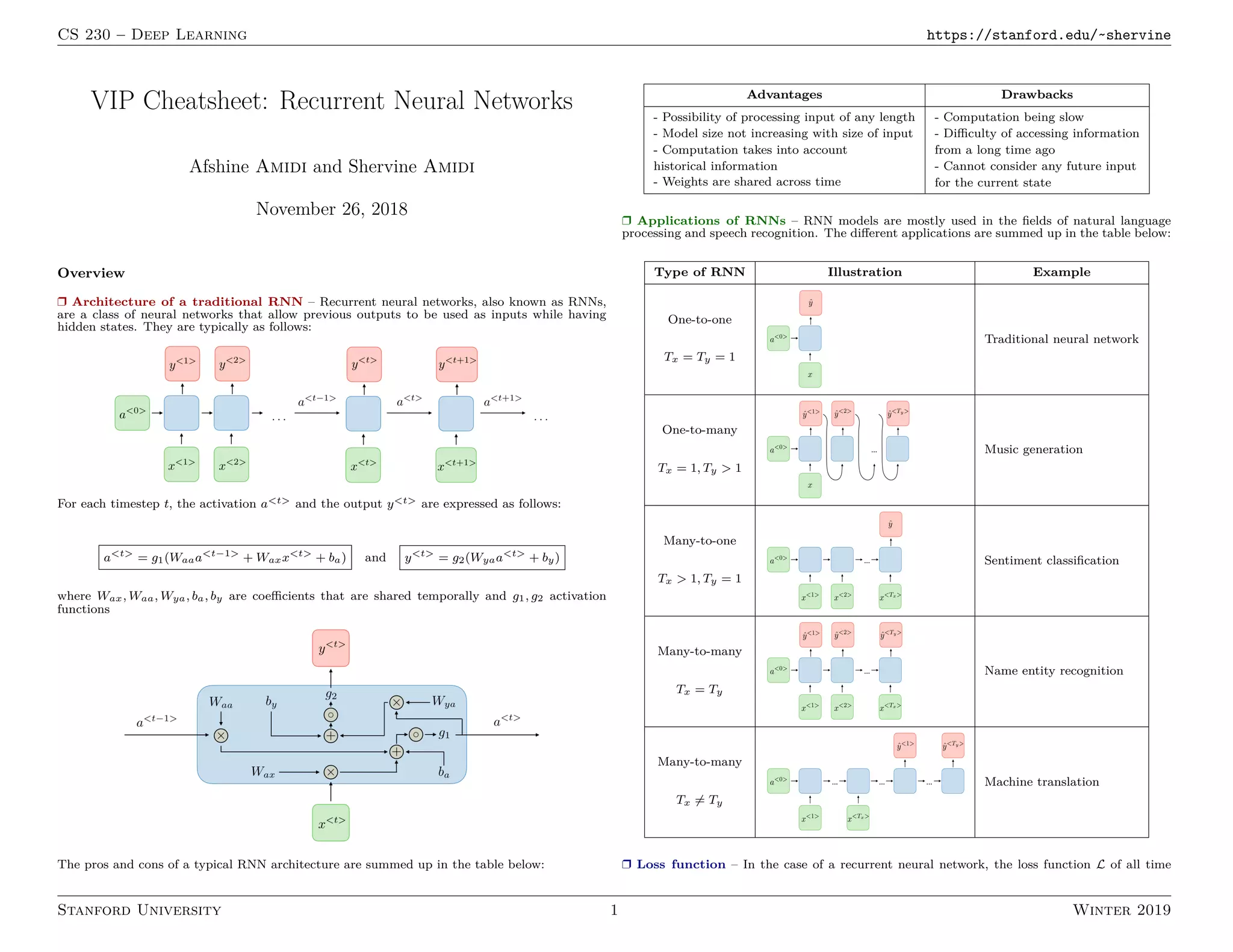
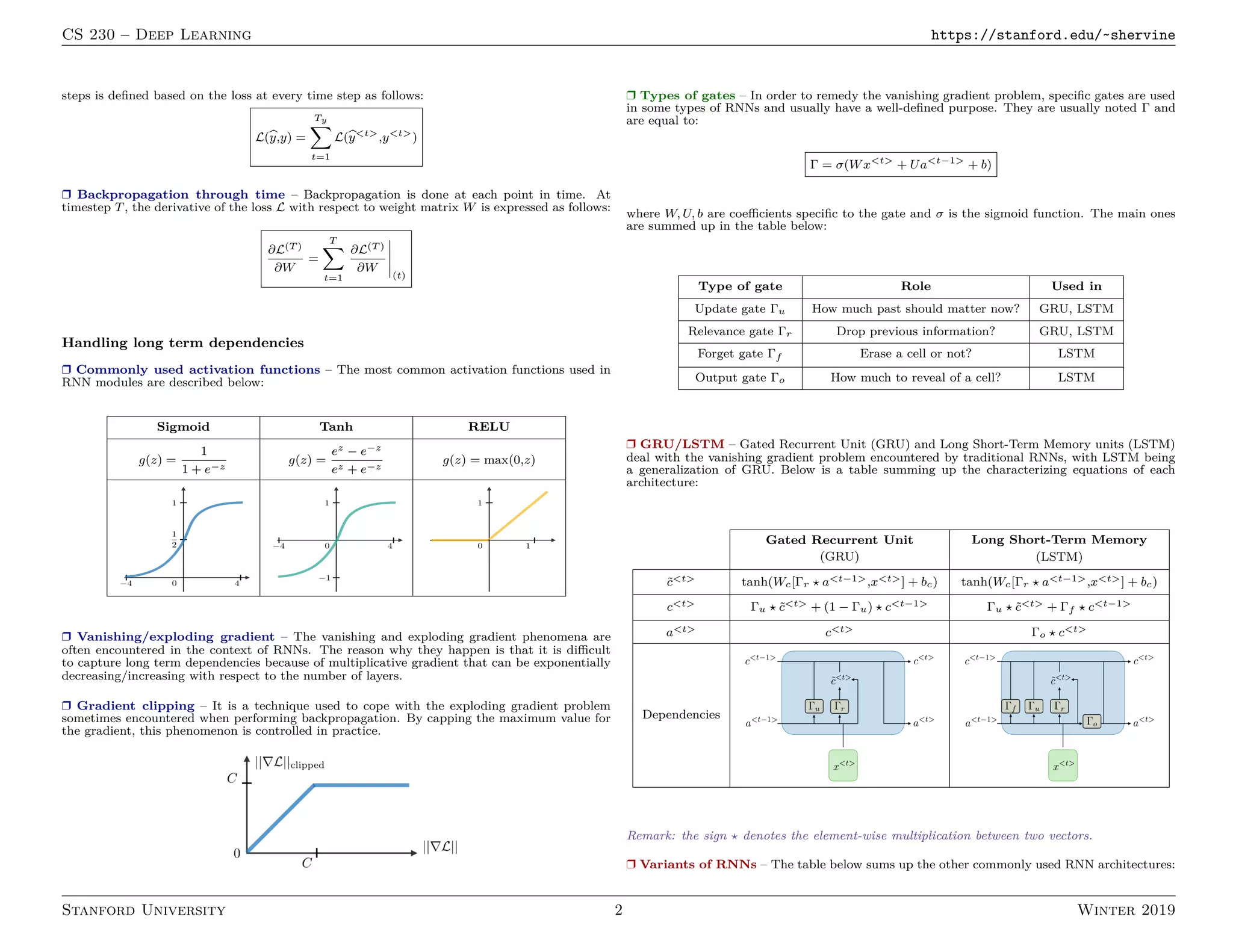
1. Recurrent neural networks (RNNs) allow information to persist from previous time steps through hidden states and can process input sequences of variable lengths. Common RNN architectures include LSTMs and GRUs which address the vanishing gradient problem of traditional RNNs.
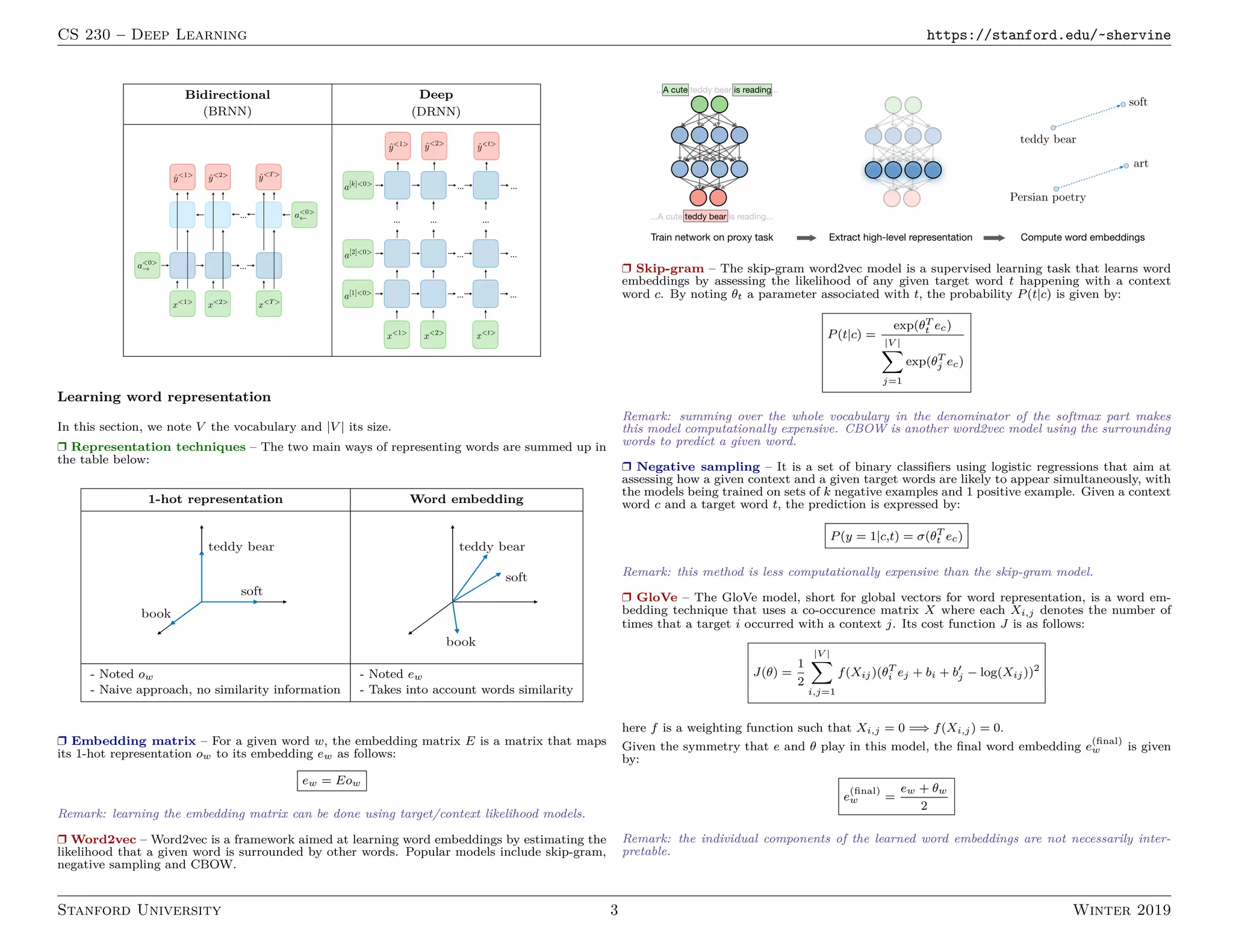
2. RNNs are commonly used for natural language processing tasks like machine translation, sentiment classification, and named entity recognition. They learn distributed word representations through techniques like word2vec, GloVe, and negative sampling.
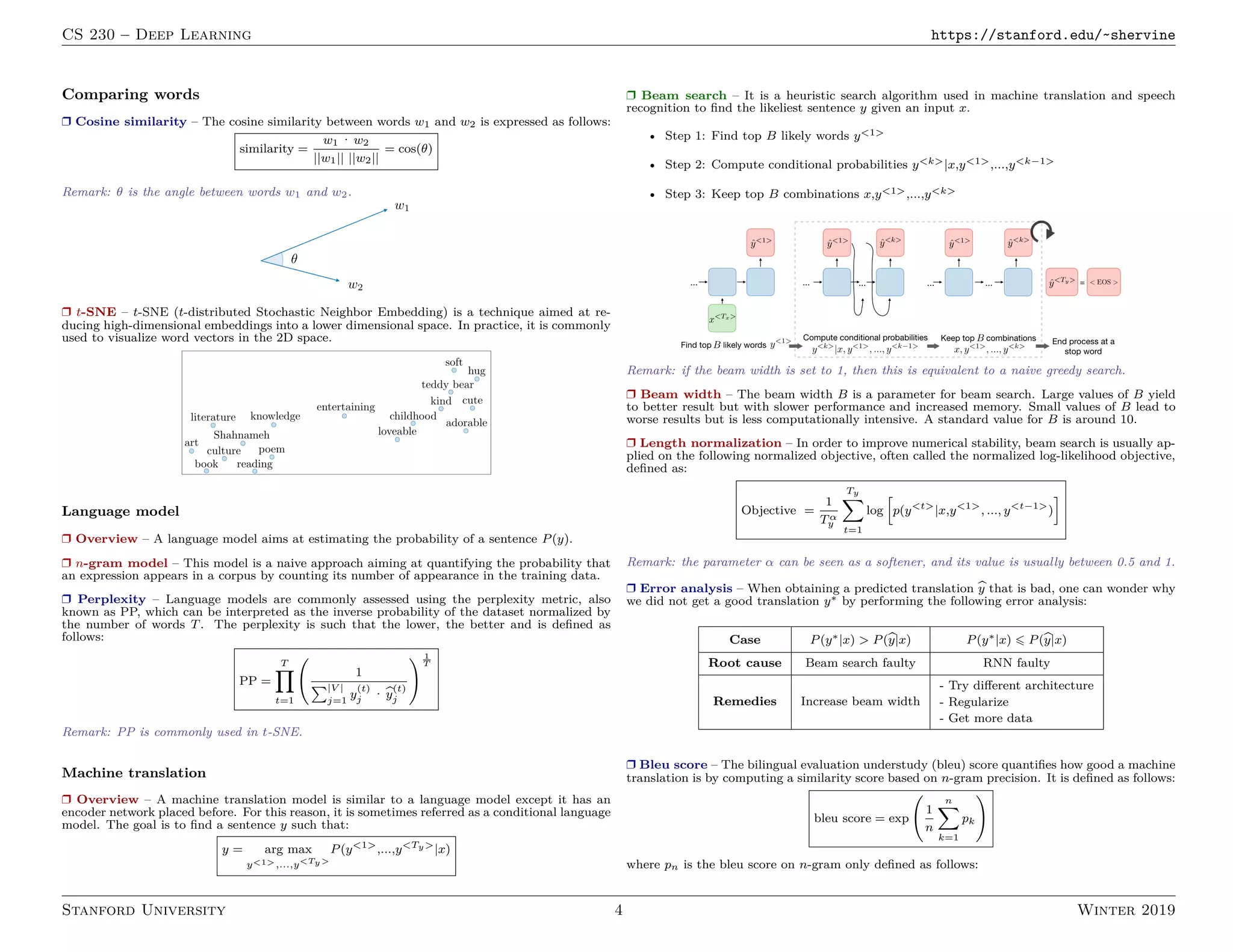
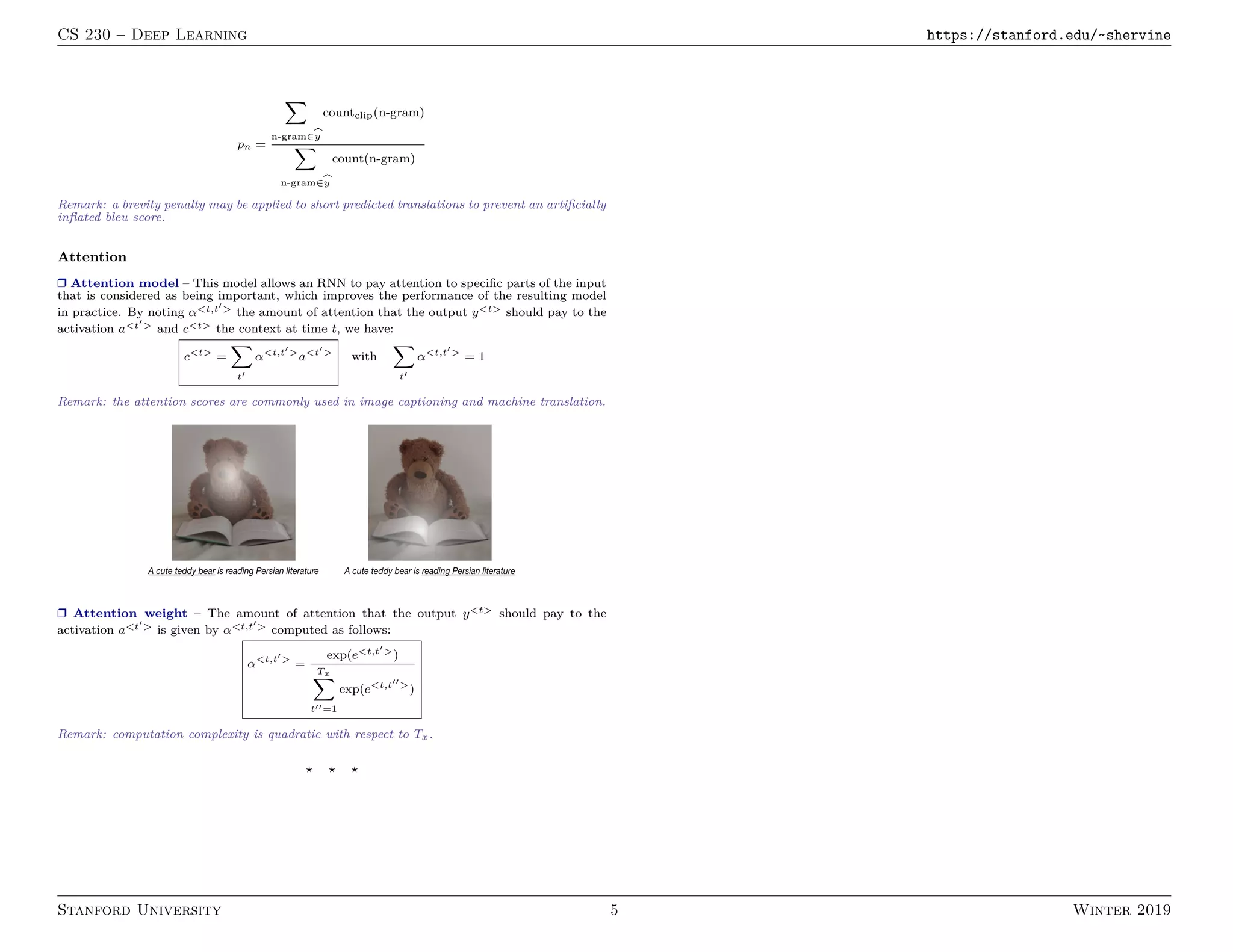
3. Machine translation models use an encoder-decoder architecture with an RNN encoder and decoder. Beam search is commonly used to find high-probability translation sequences. Performance is evaluated using metrics like BLEU score.