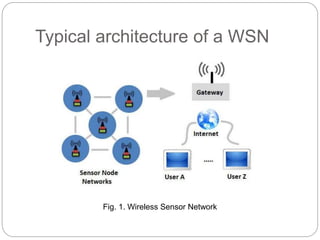
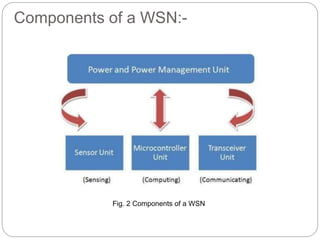
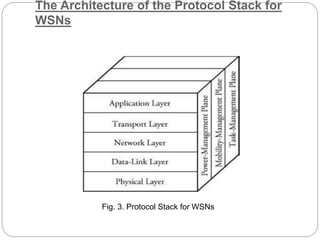
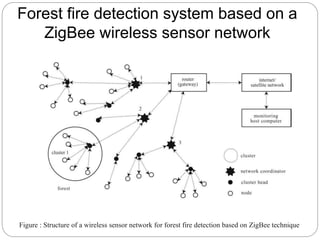
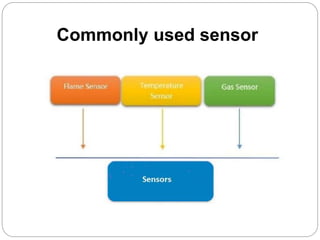
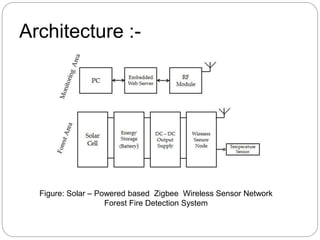
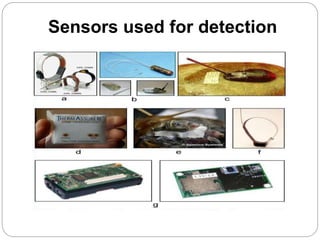
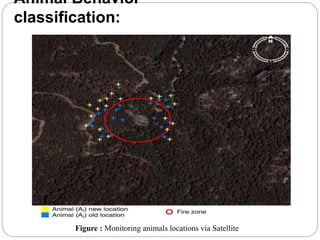
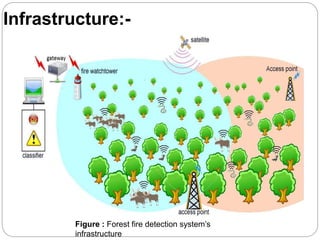
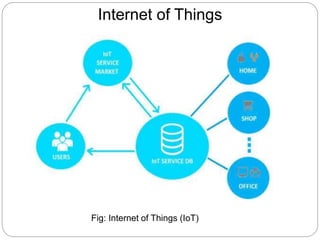
The document provides an overview of wireless sensor networks (WSNs) and their role in the Internet of Things (IoT), emphasizing their use in sensing, computation, and communication. It discusses the history, architecture, components, applications, and future scope of WSNs, particularly in areas like environmental monitoring and military applications. The document also highlights the integration of WSNs with IoT and the anticipated impact of micro-electromechanical systems (MEMS) on sensing technologies.