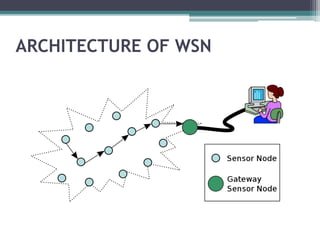
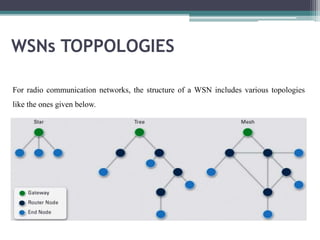
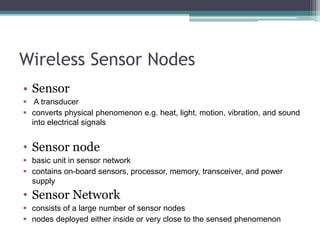
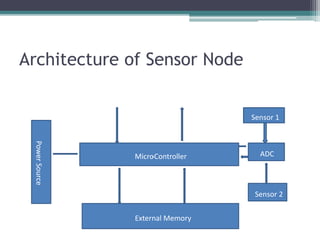
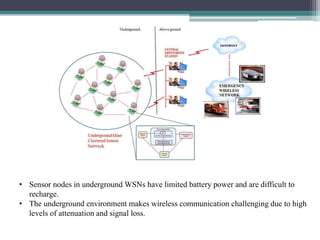
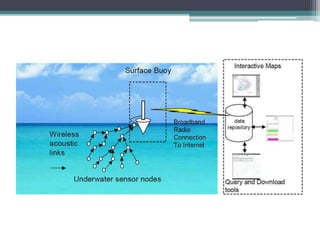
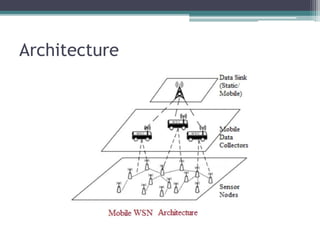
This document provides an overview of wireless sensor networks (WSNs). It describes the architecture of WSNs including sensor nodes, transceivers and controllers. It discusses different types of WSNs such as terrestrial, underground, underwater, multimedia and mobile WSNs. It also covers WSN topologies, characteristics, applications and limitations. The key aspects of WSNs are that they are made up of spatially distributed sensors to monitor environmental conditions and wireless connectivity is used to transmit sensor data to a central location for processing.