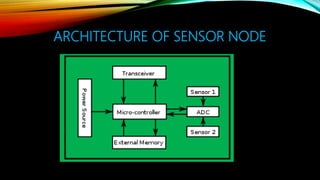
Wireless sensor networks (WSNs) refer to spatially distributed sensors that wirelessly transmit data about the environment such as temperature, sound, and pollution levels. A WSN consists of sensor nodes that contain sensors, processors, memory, transceivers, and power supplies. Sensor nodes form a multi-hop ad-hoc network to send data to a central location. WSNs have applications in military surveillance, environmental monitoring, healthcare, home automation, and more. However, designing WSNs poses challenges related to limited node resources, energy efficiency, scalability, and operating in harsh environments.