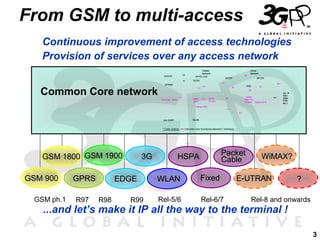
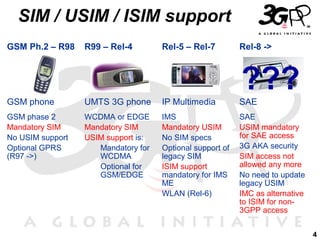
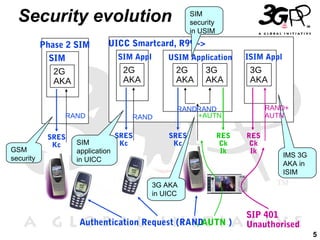
1) The document discusses the evolution from GSM networks to multi-access IP networks including 3G, LTE, WiFi and other technologies.
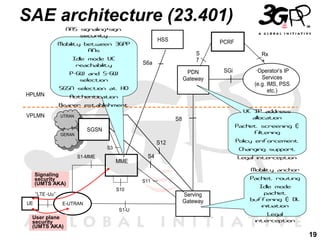
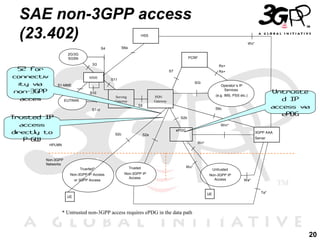
2) A key part of this evolution is the System Architecture Evolution (SAE) which defines an IP-based core network that can support both 3GPP and non-3GPP access technologies in a seamless manner.
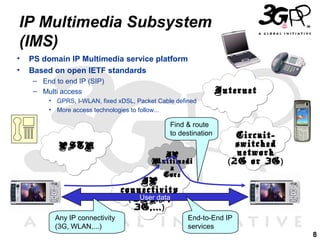
3) The IMS (IP Multimedia Subsystem) plays an important role as well, providing all-IP multimedia services across different access networks in a standardized way.