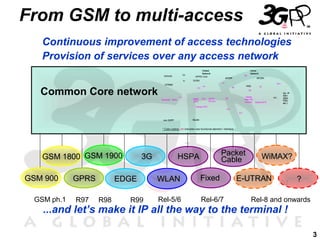
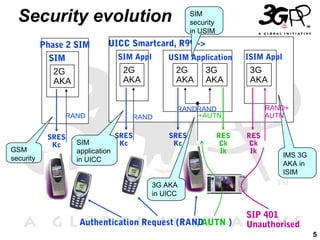
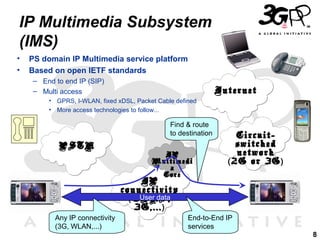
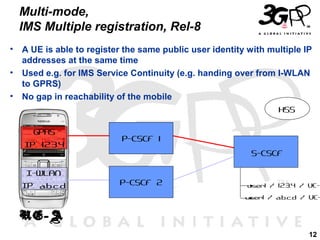
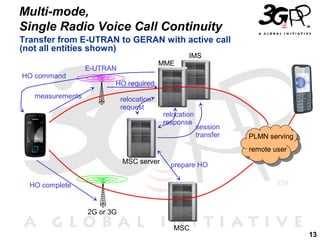
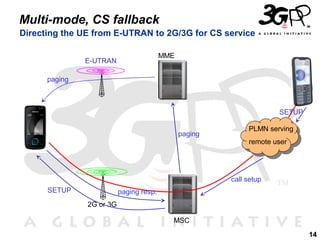
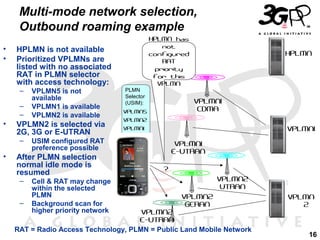
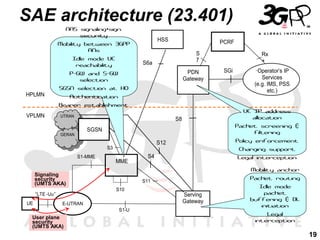
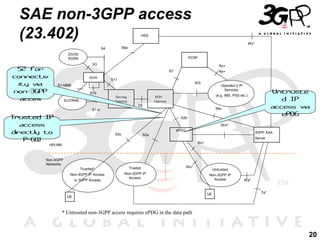
This presentation discusses 3GPP's System Architecture Evolution (SAE) which aims to provide services over any access network through a common IP-based core network. It covers migration from GSM to a multi-access system using SAE/LTE, including support for SIM/USIM/ISIM, security evolution, and interworking of multi-mode terminals and networks through service continuity, multiple registration, and voice call continuity. IMS is also discussed as the service platform for multimedia services in 3GPP networks.