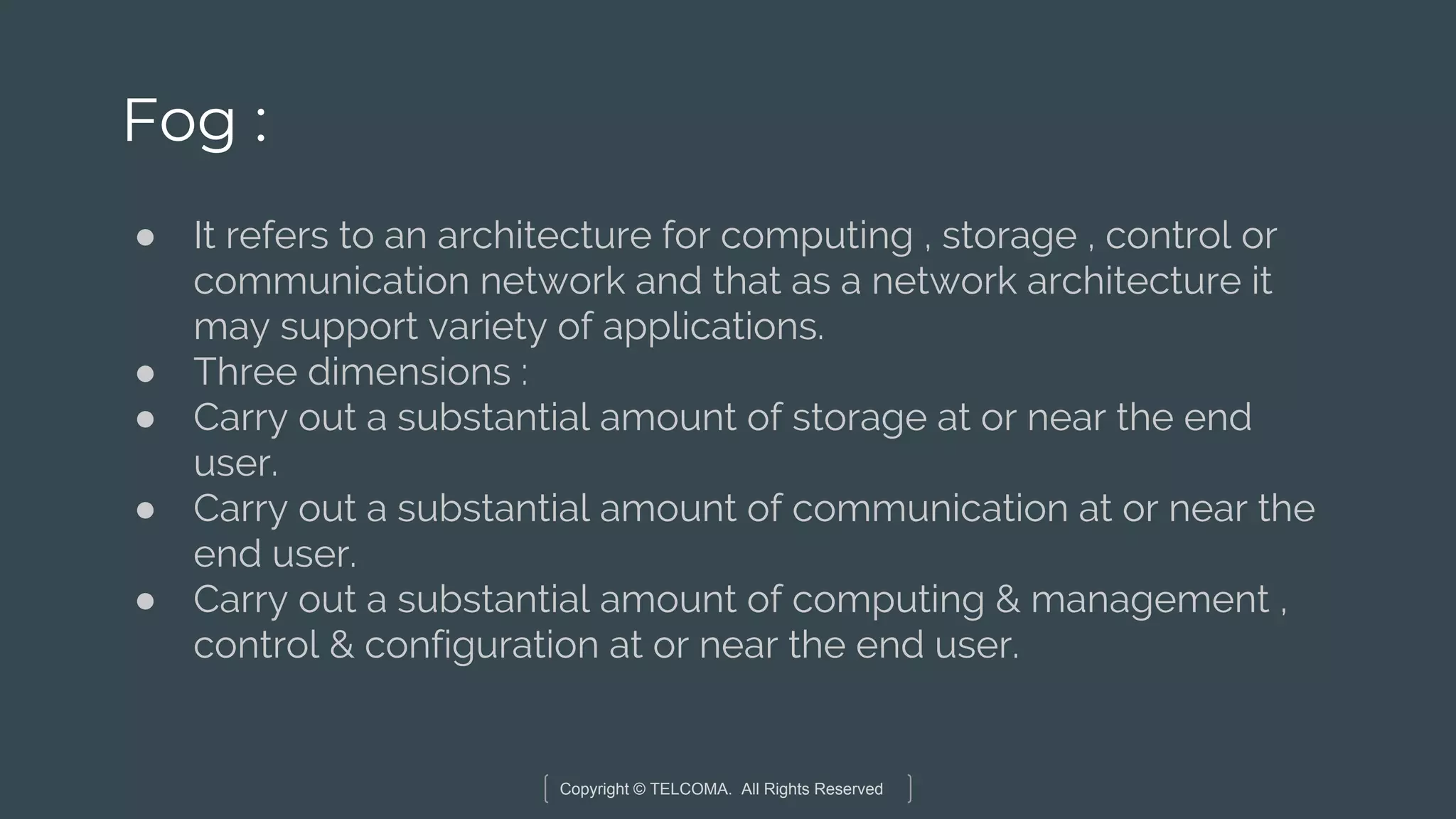
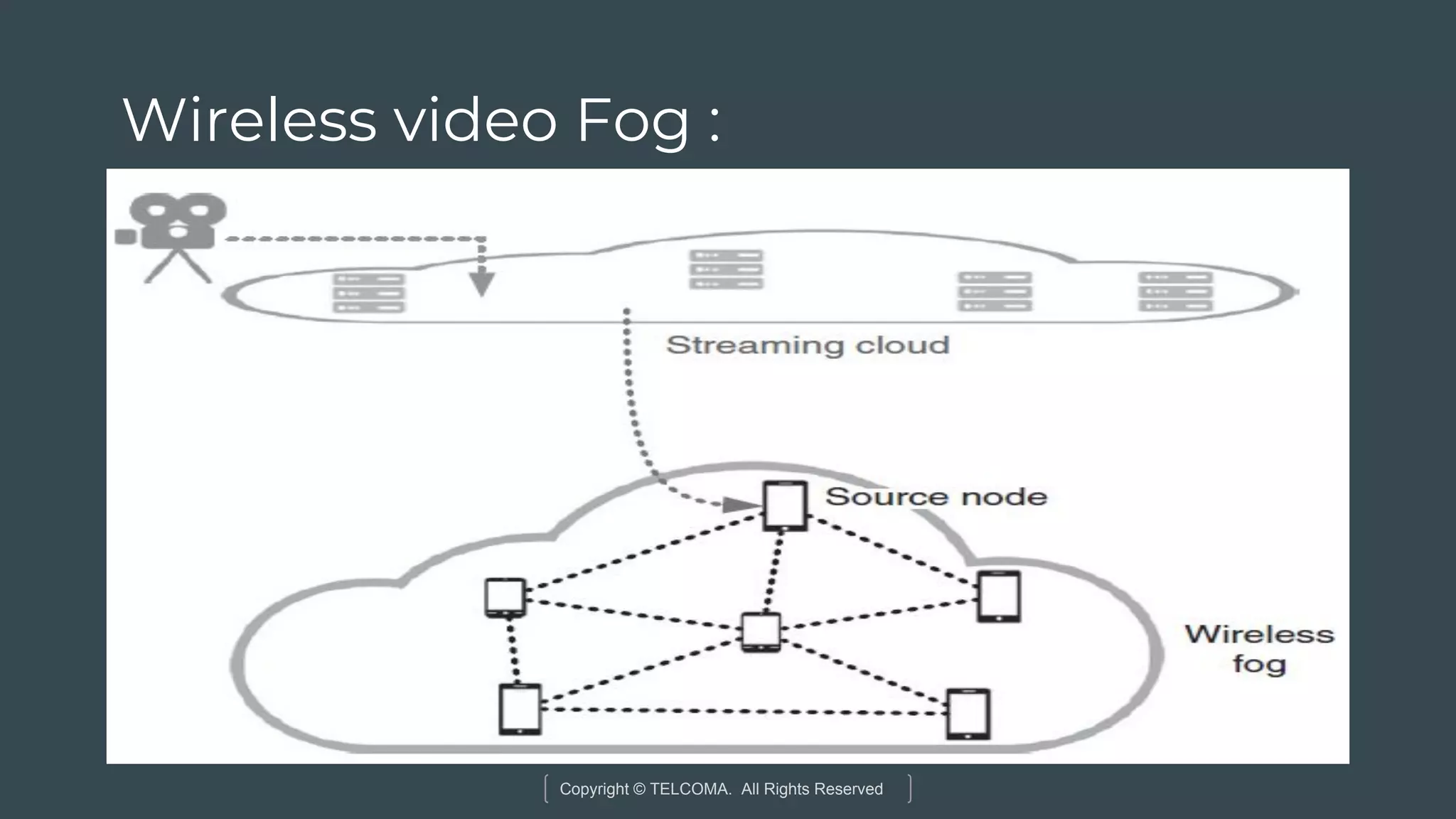
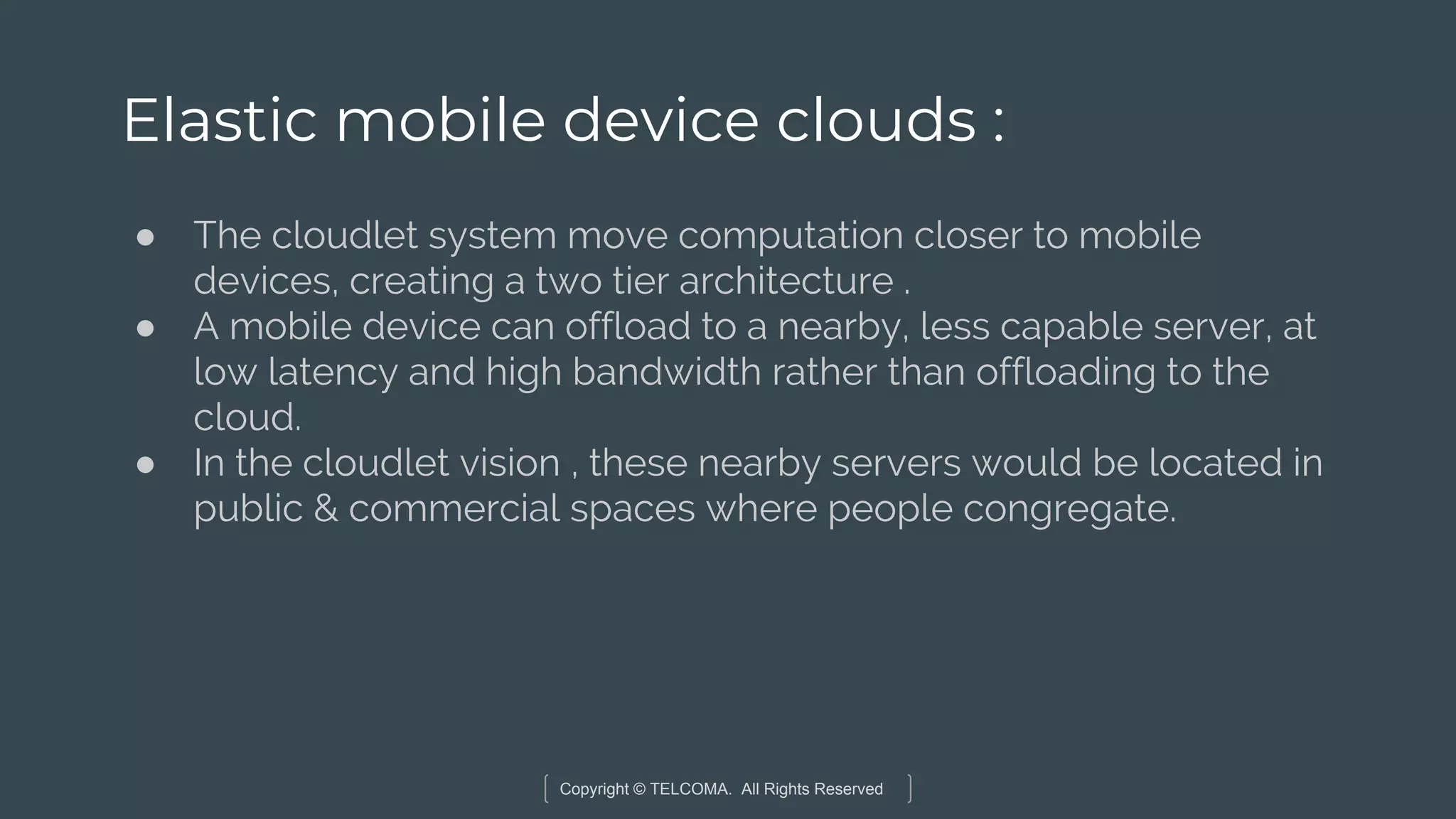
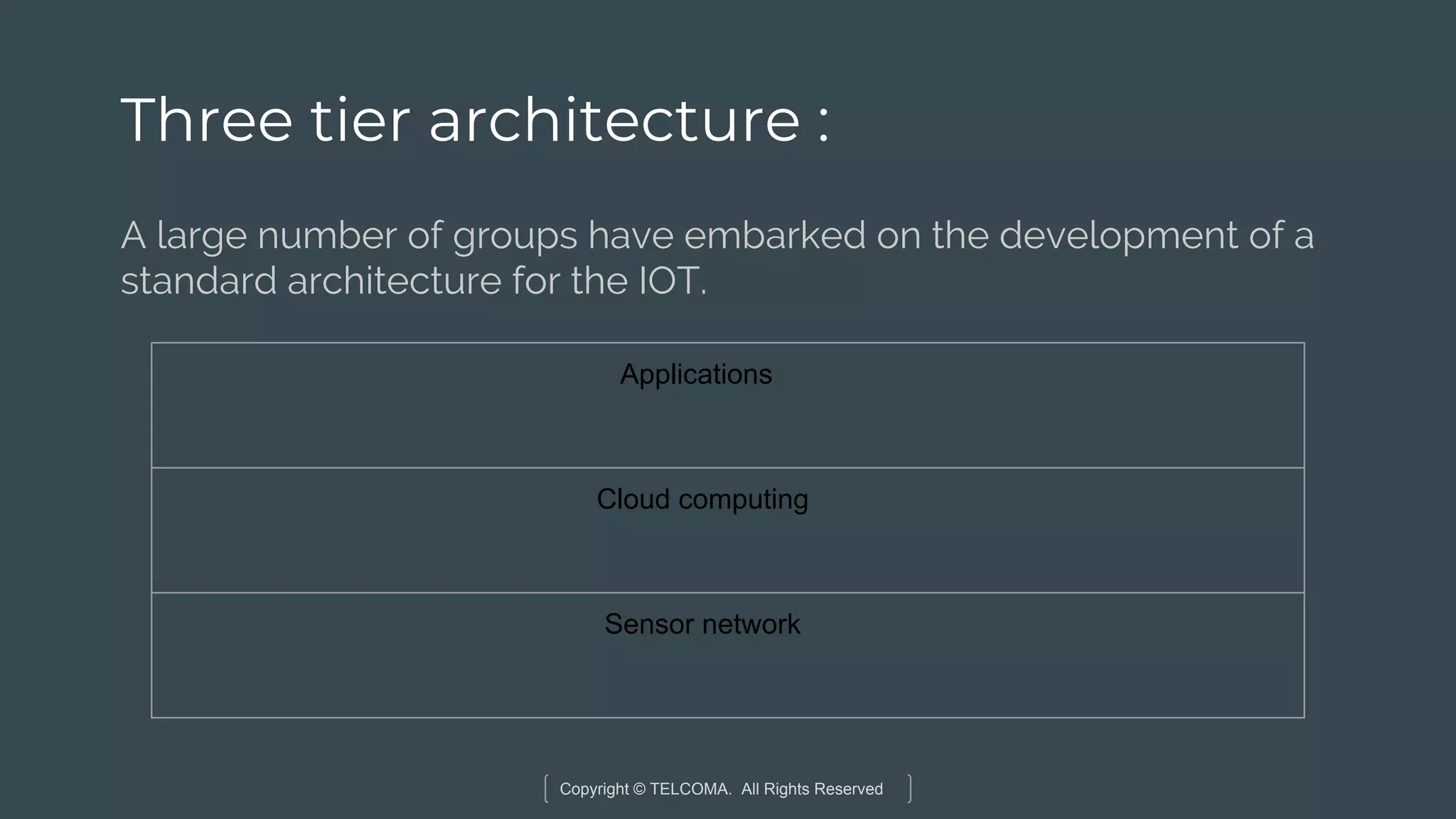
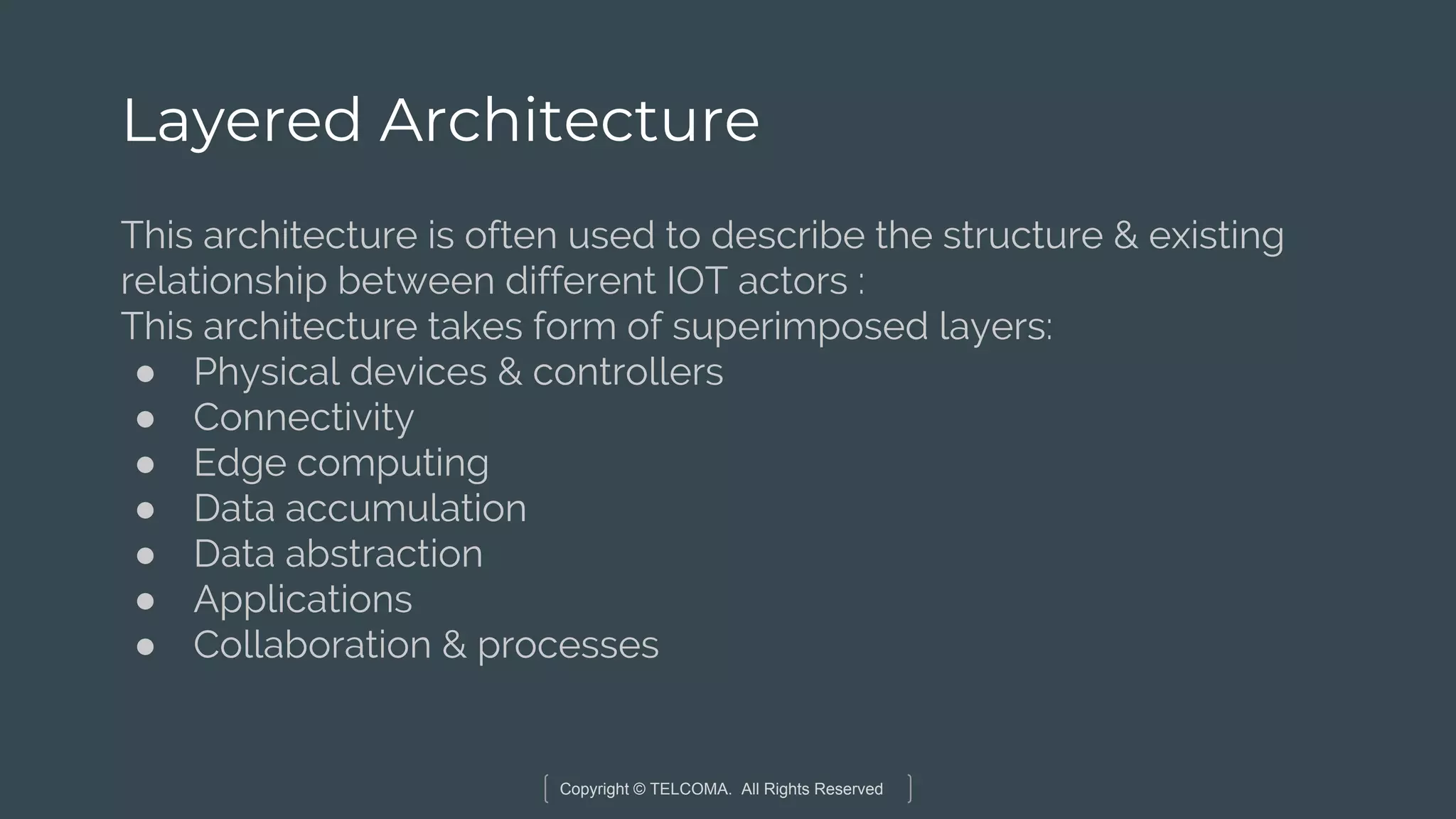
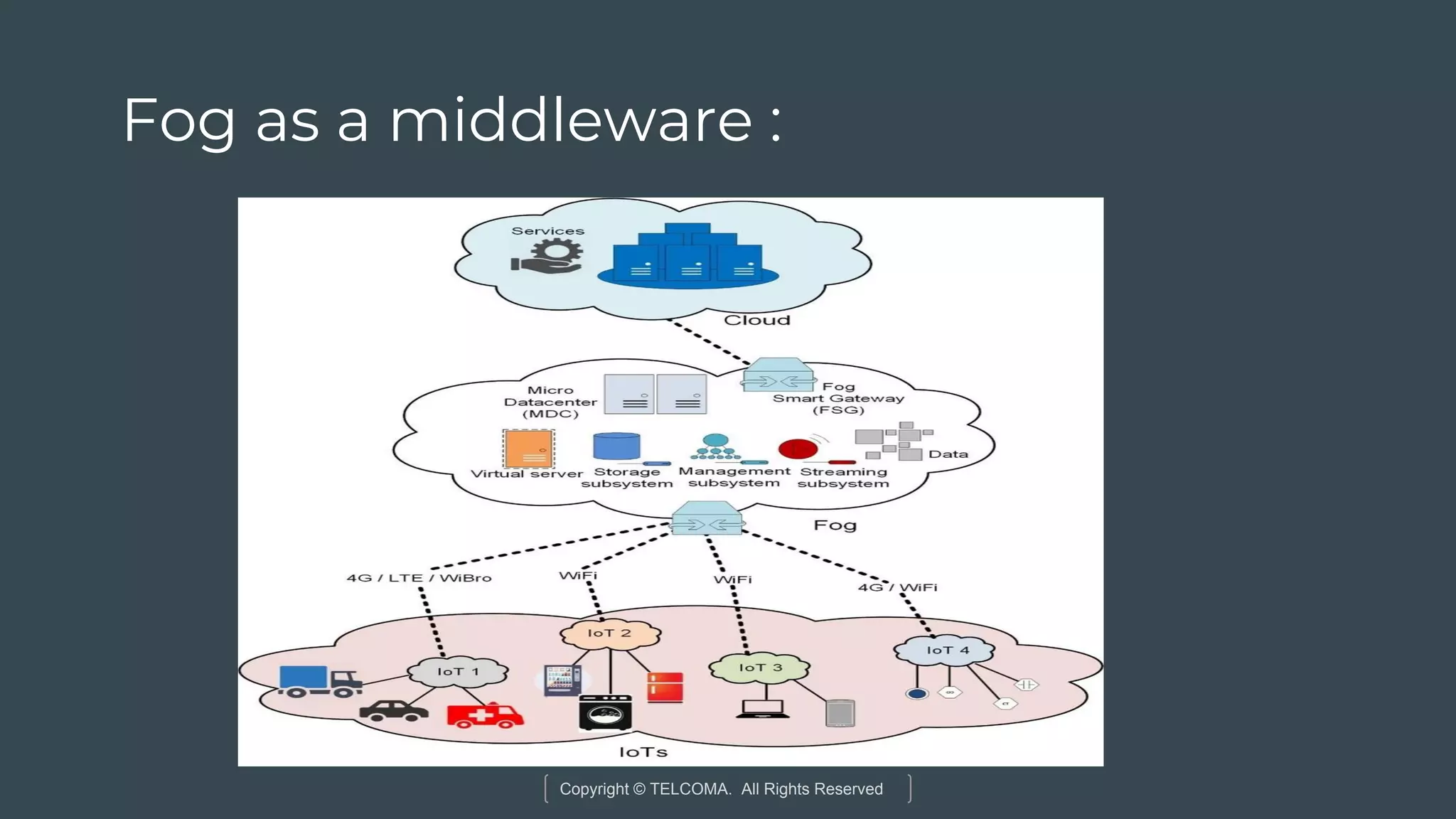
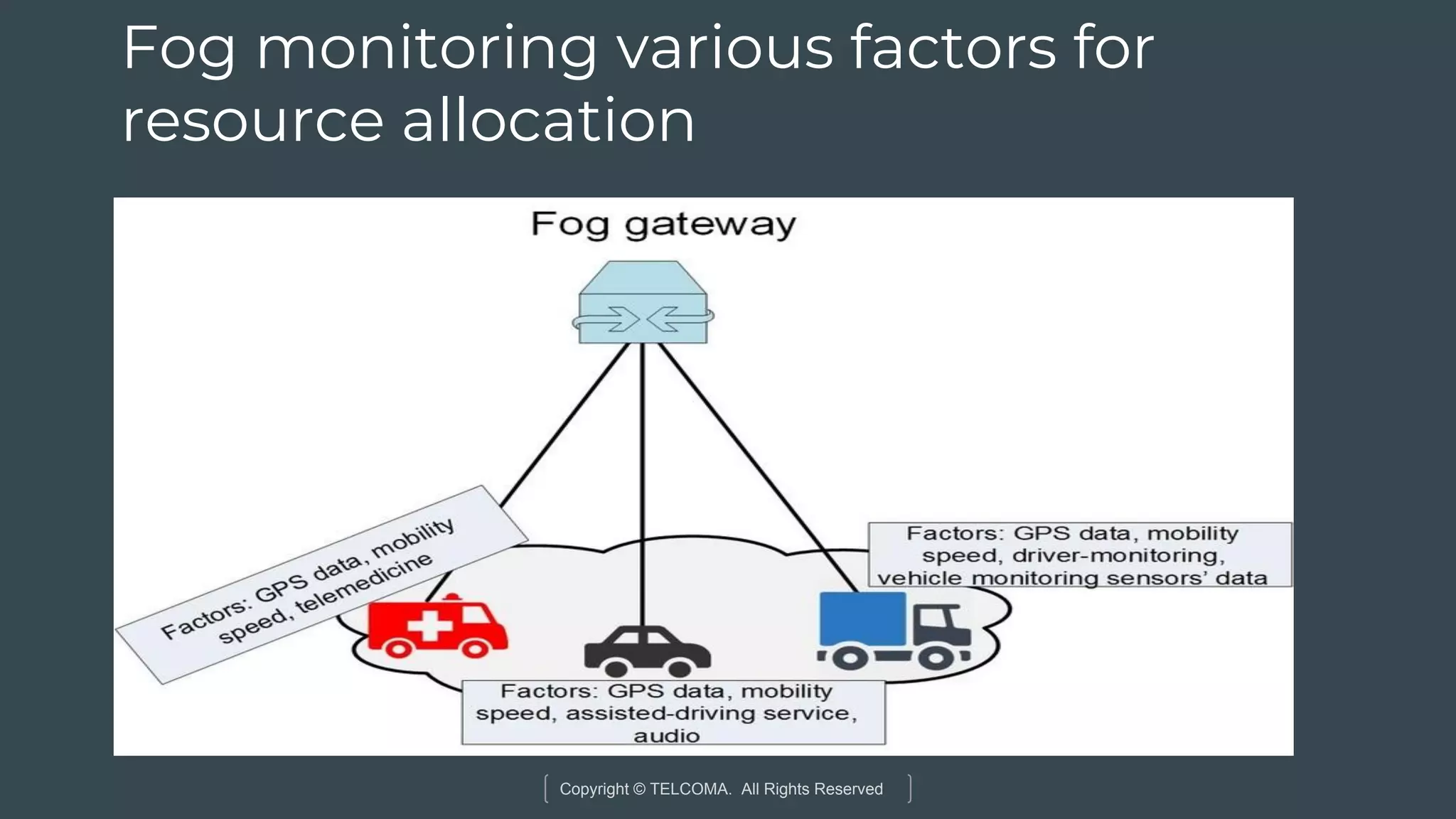
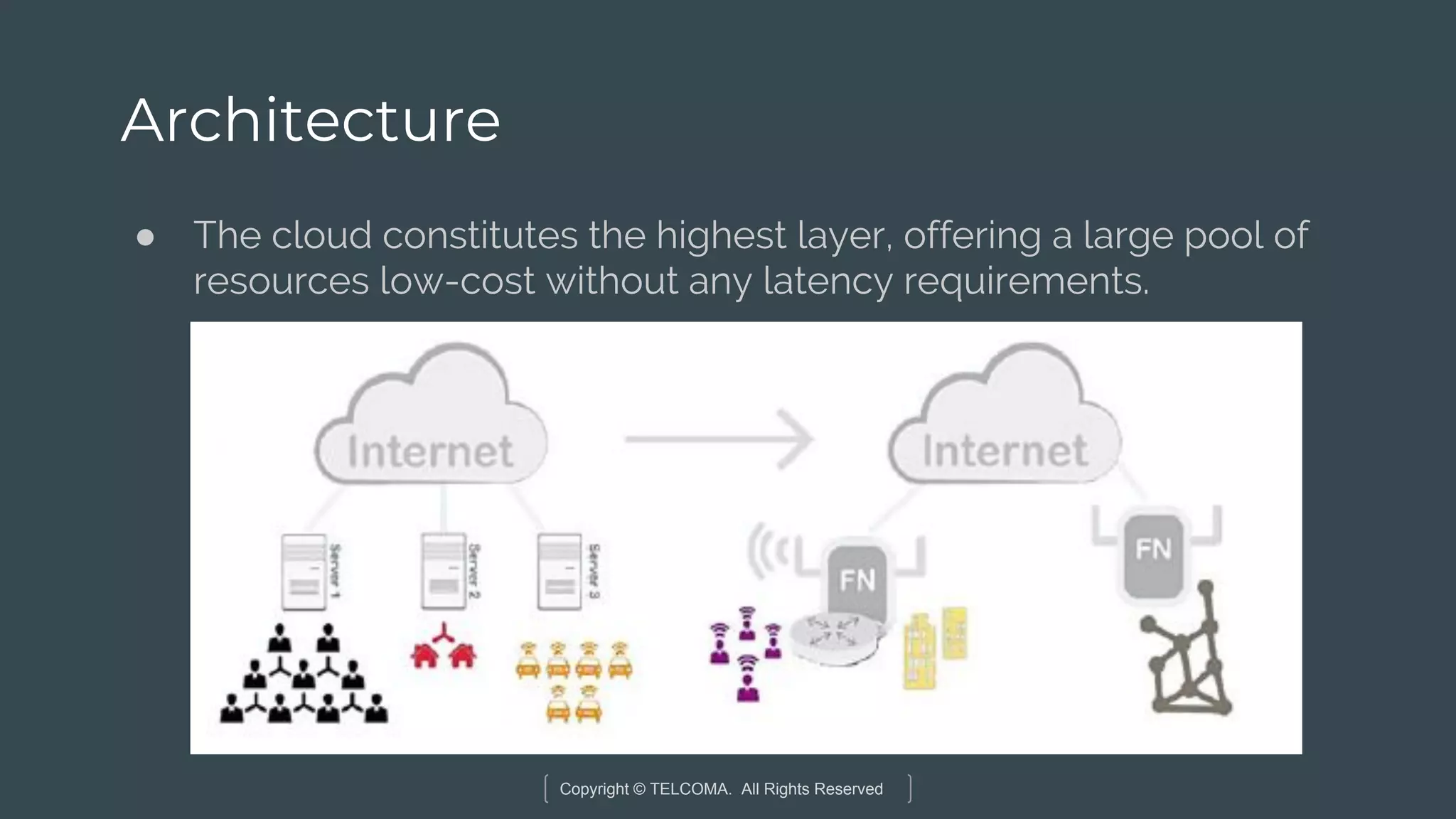
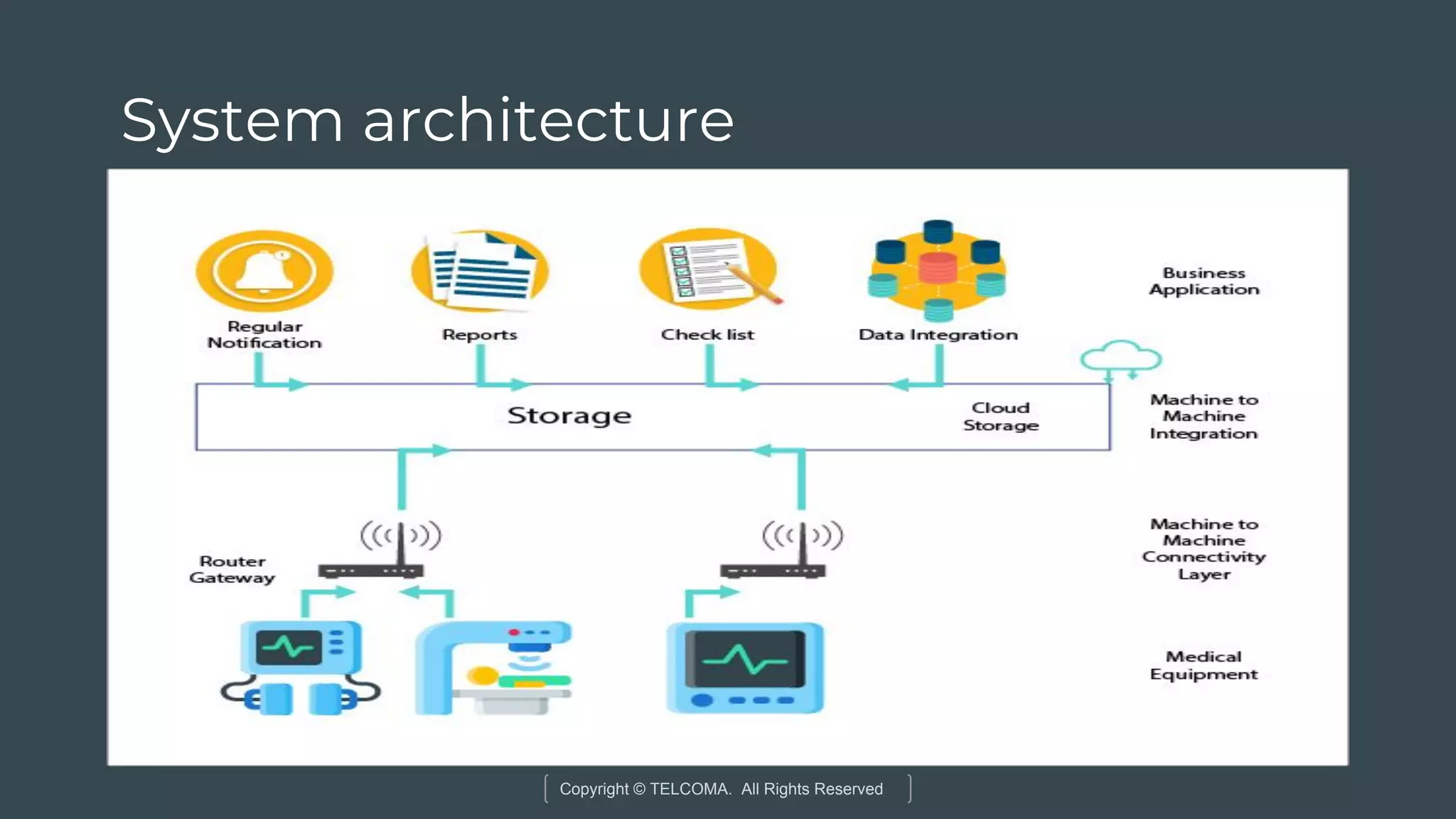
The document discusses the integration of Internet of Things (IoT) and 5G technology, detailing various computing architectures like fog computing and edge computing. It outlines the benefits of these architectures, including improved data management, low latency, and resource optimization, particularly in home gateways and distributed systems. Additionally, it emphasizes the role of cooperative communication and caching methods in enhancing efficiency within IoT networks.