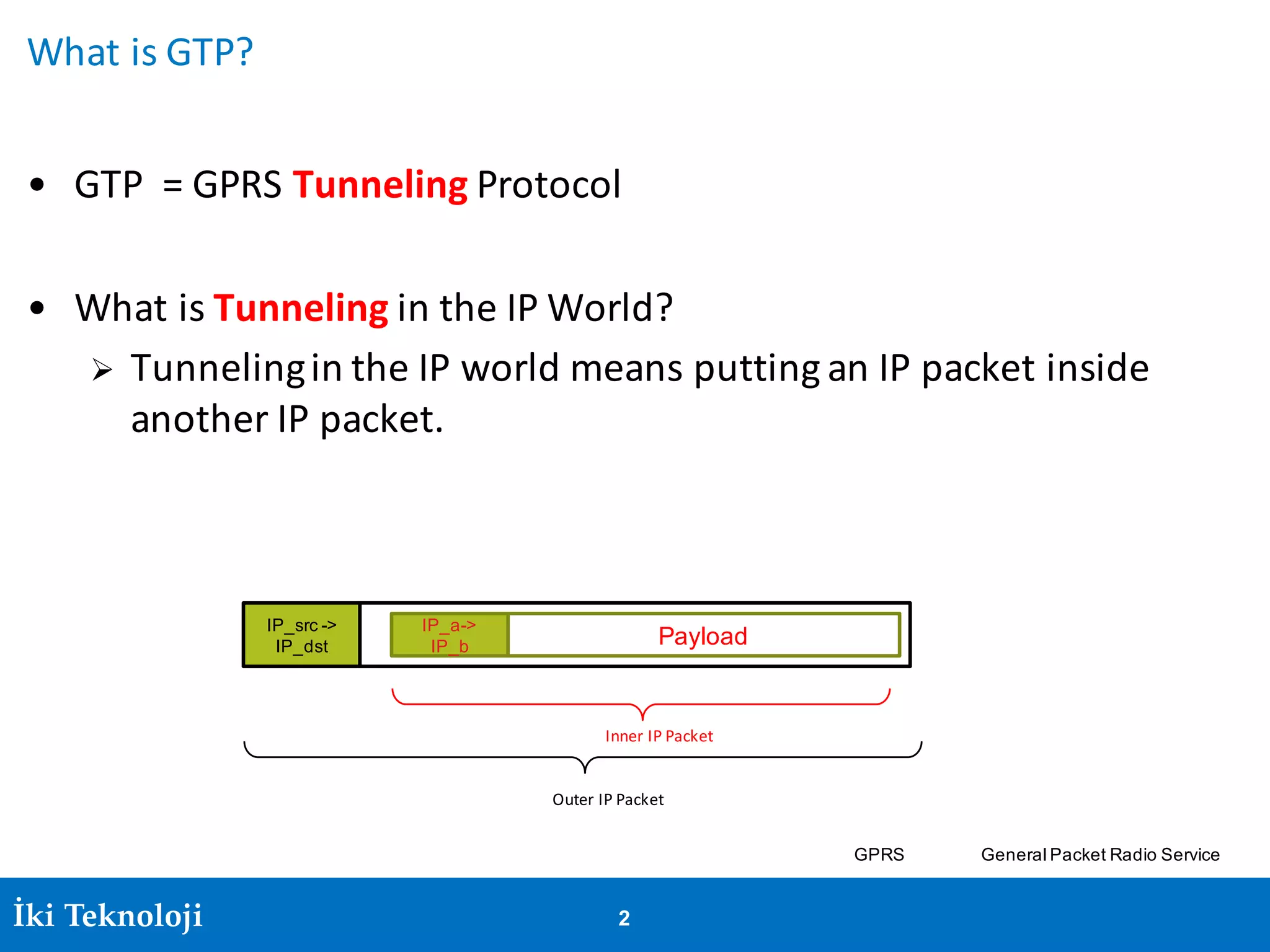
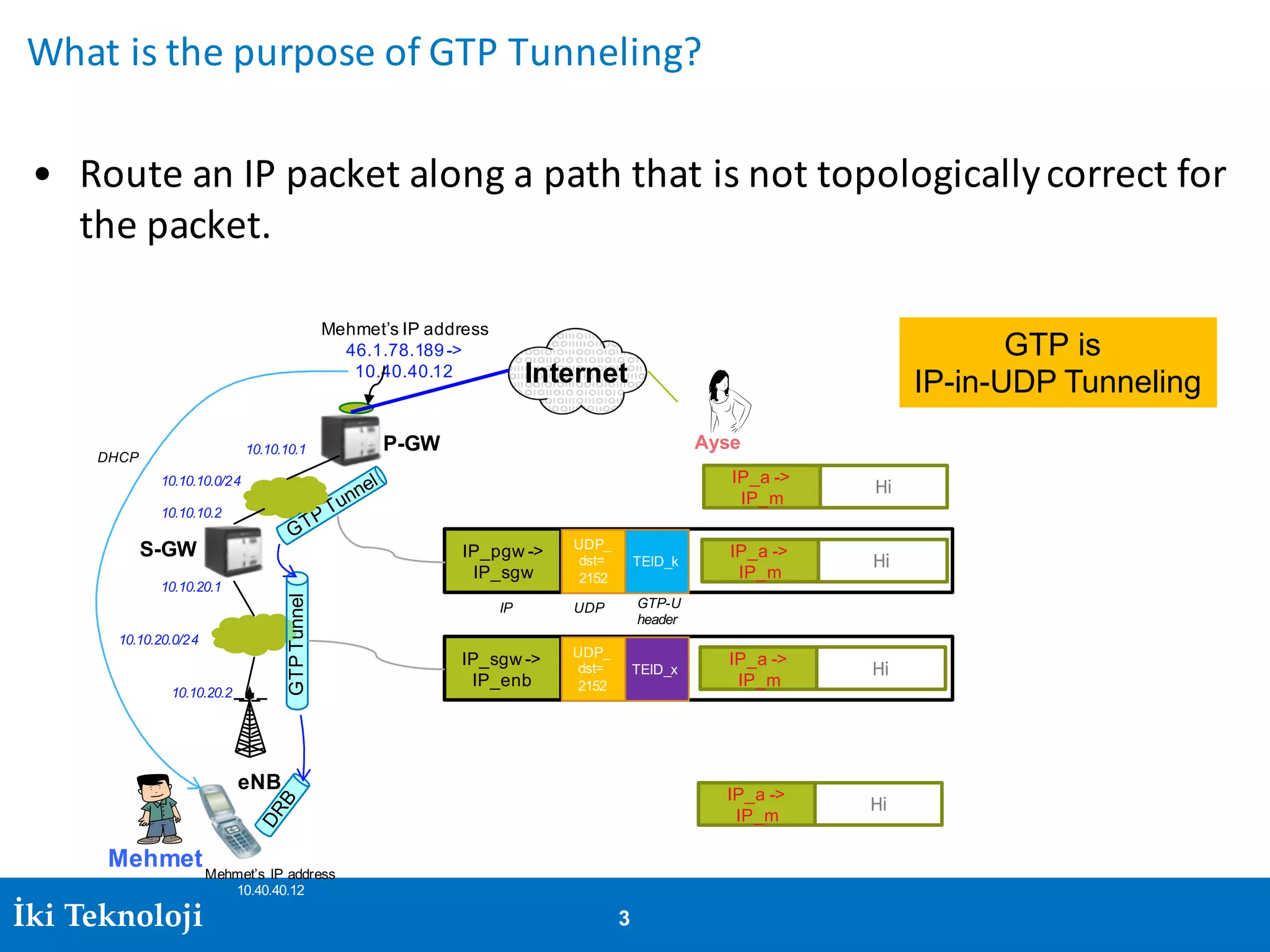
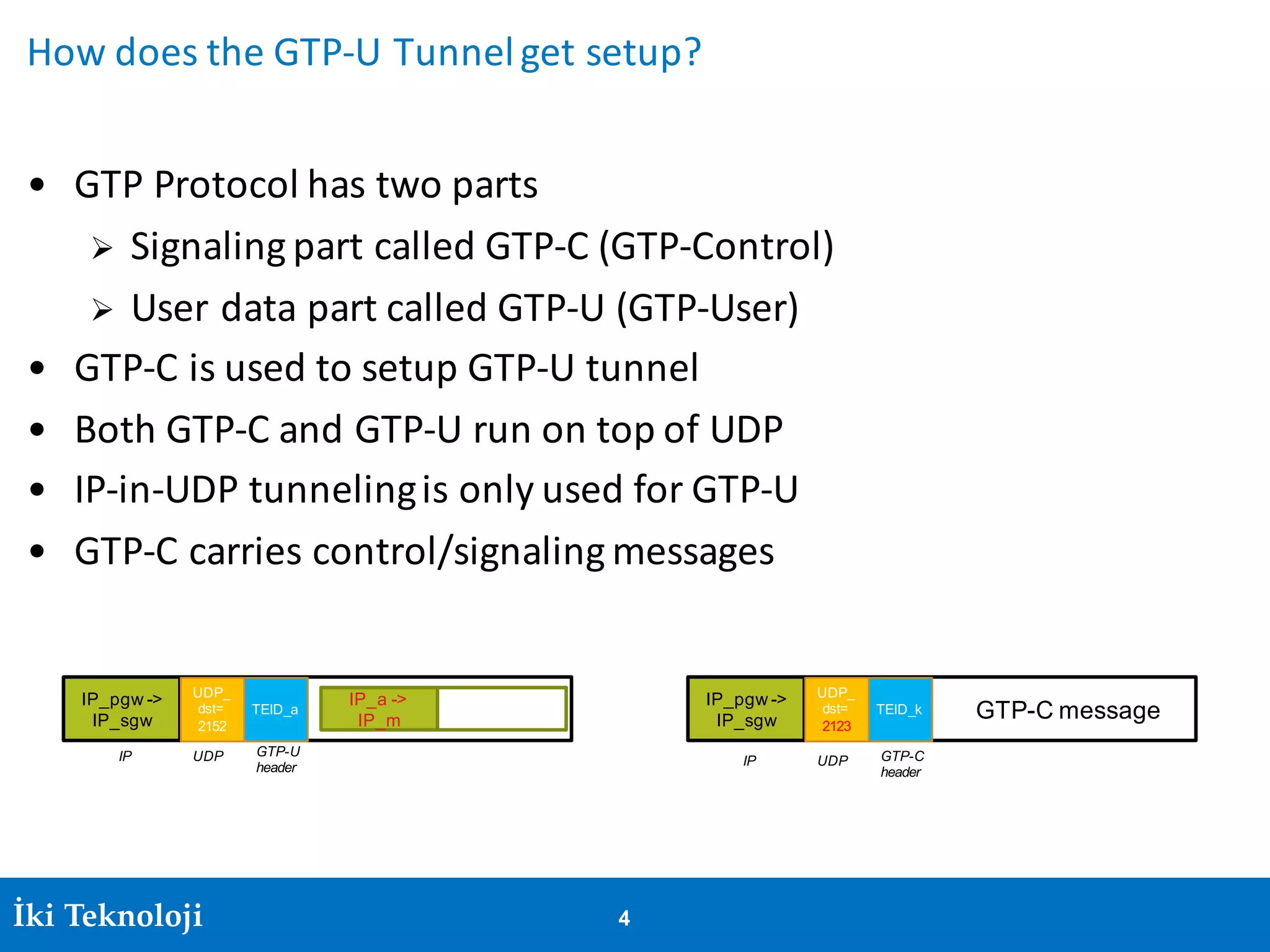
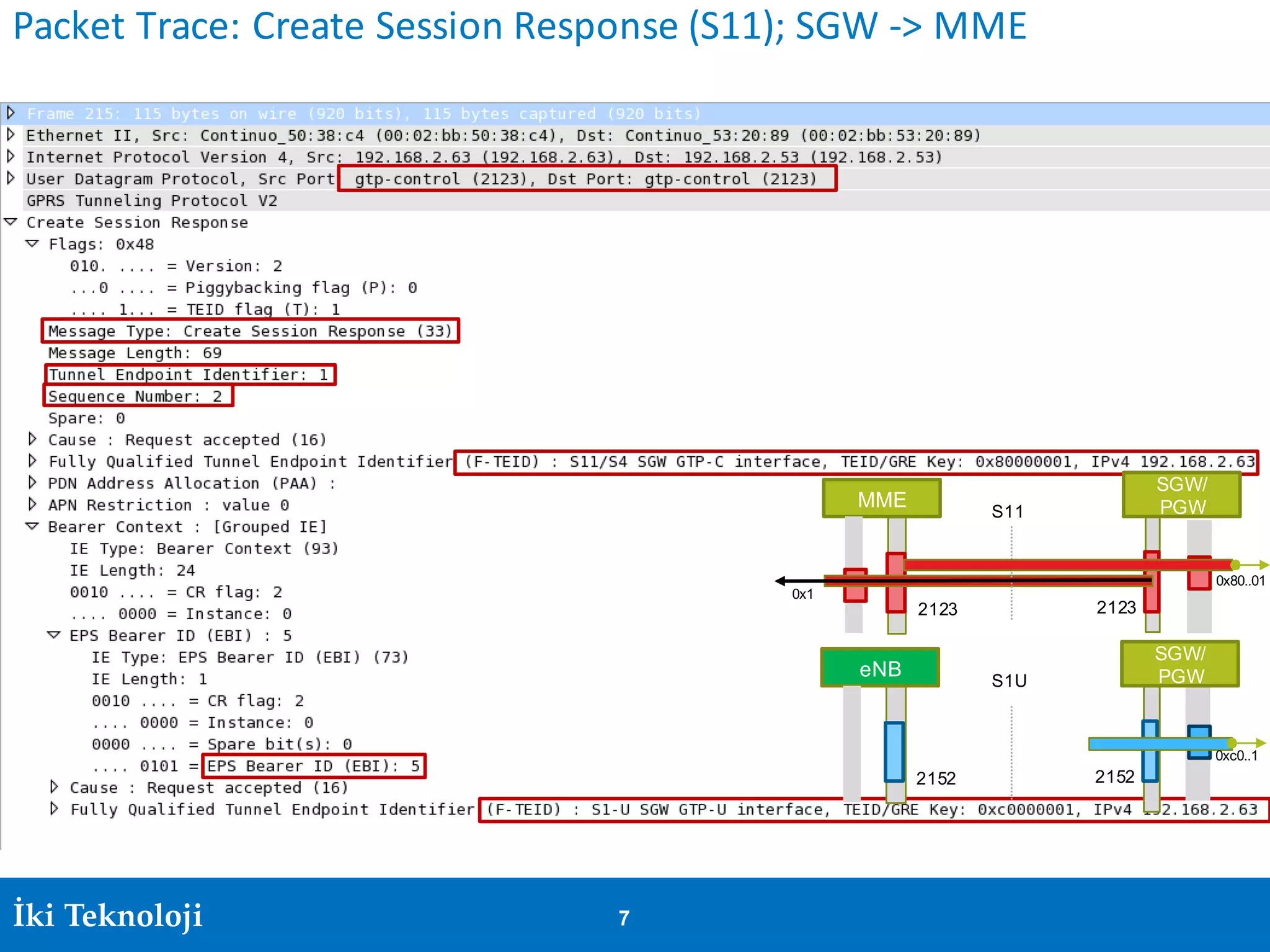
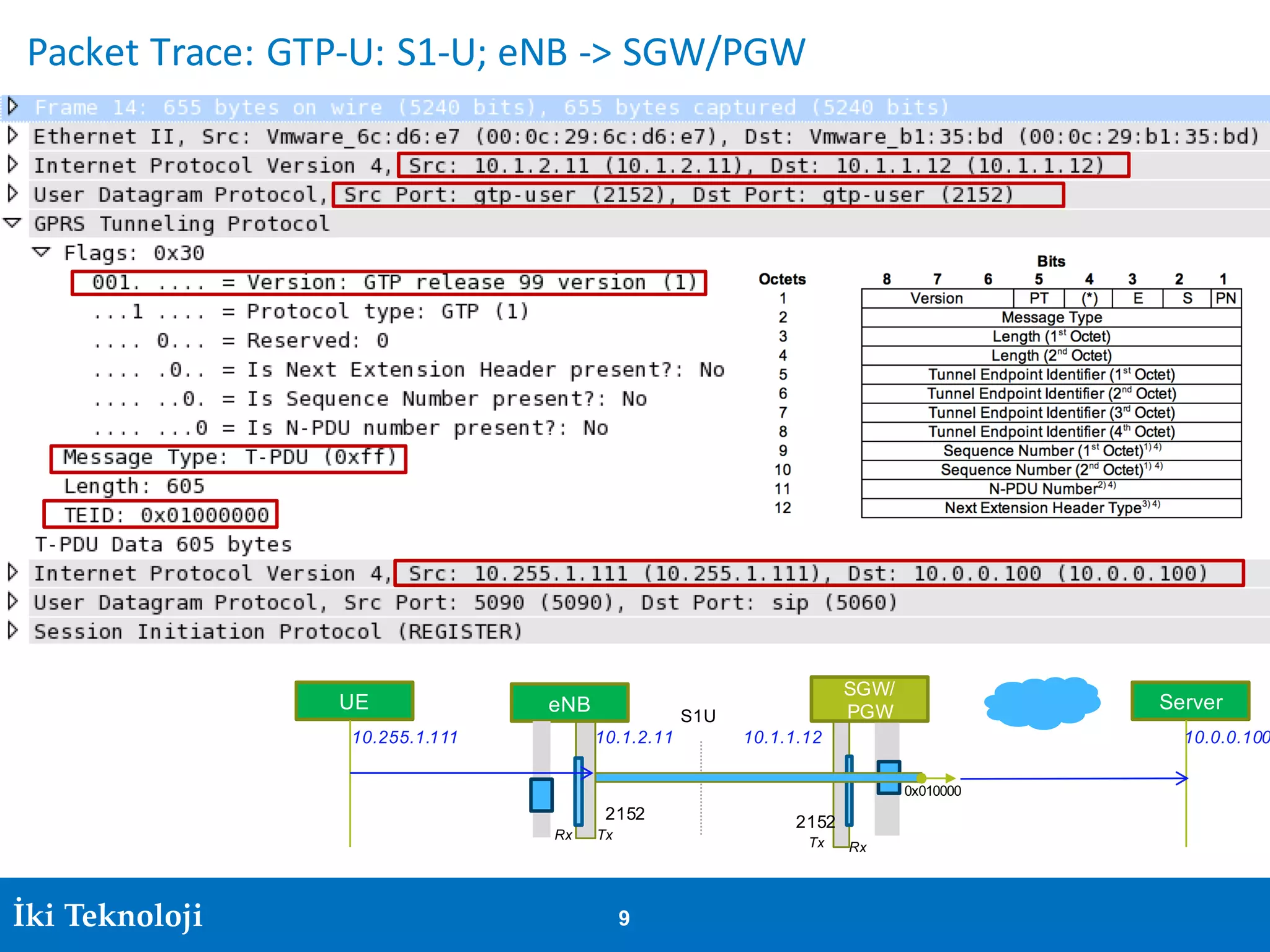
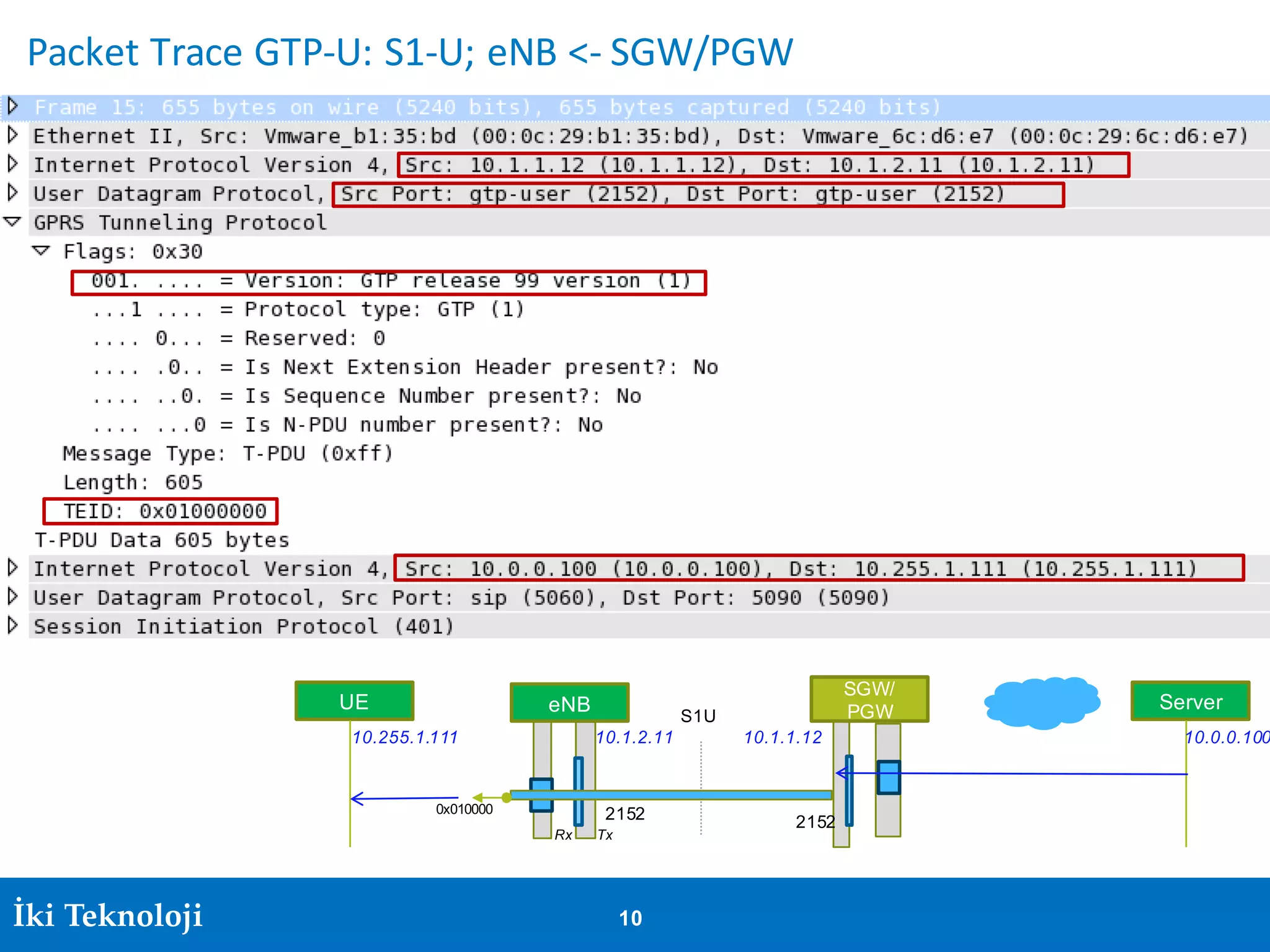
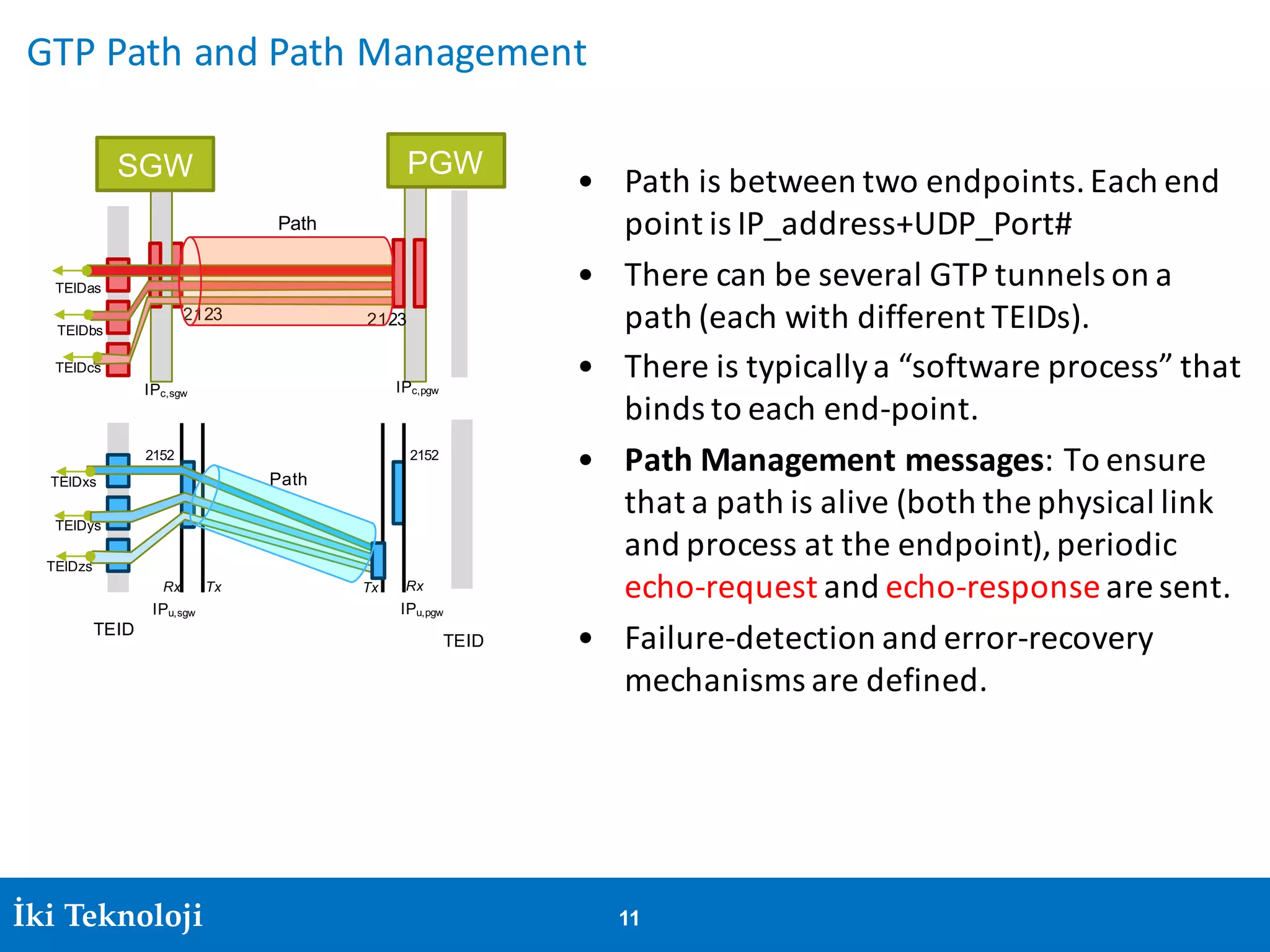
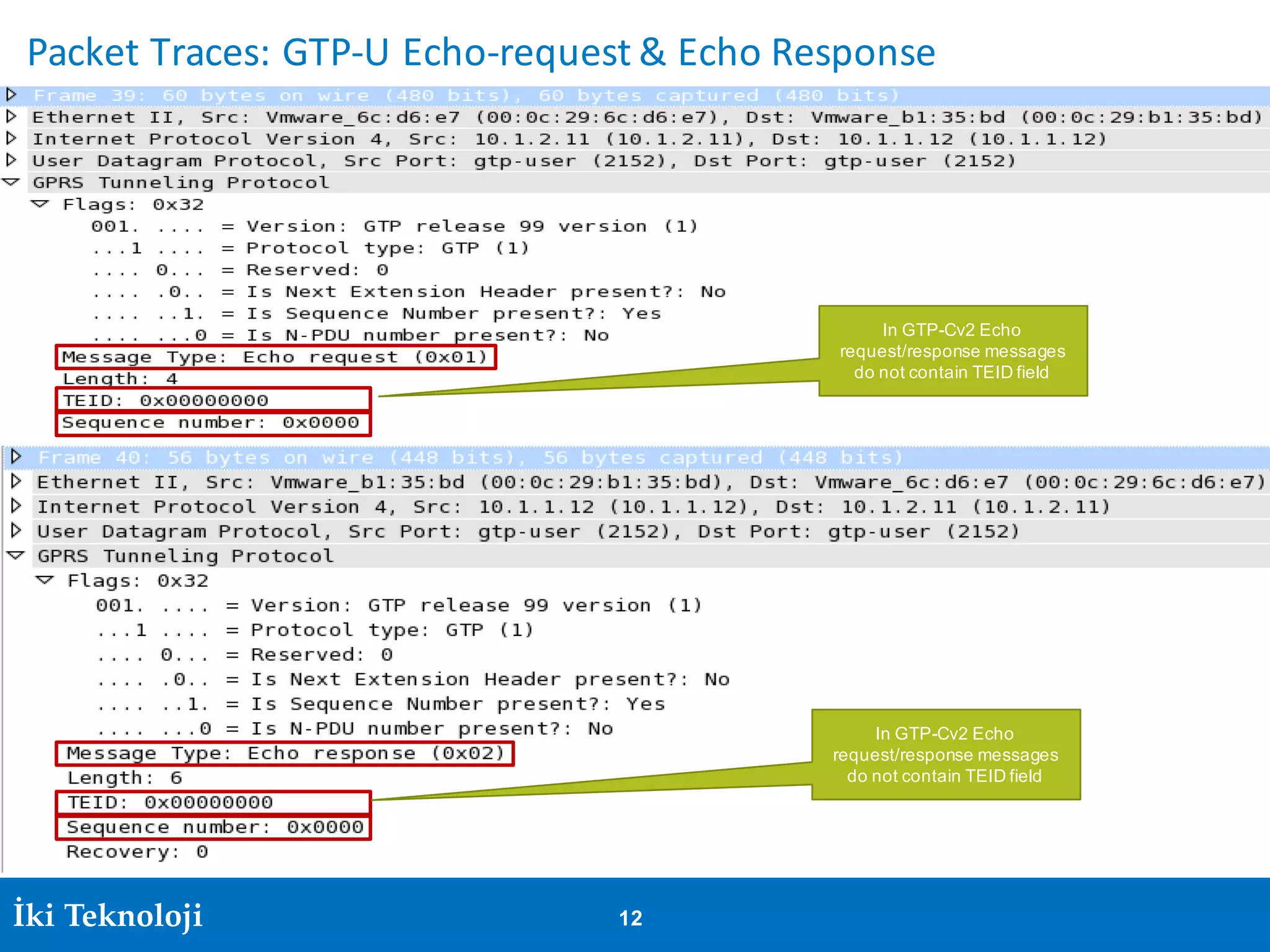
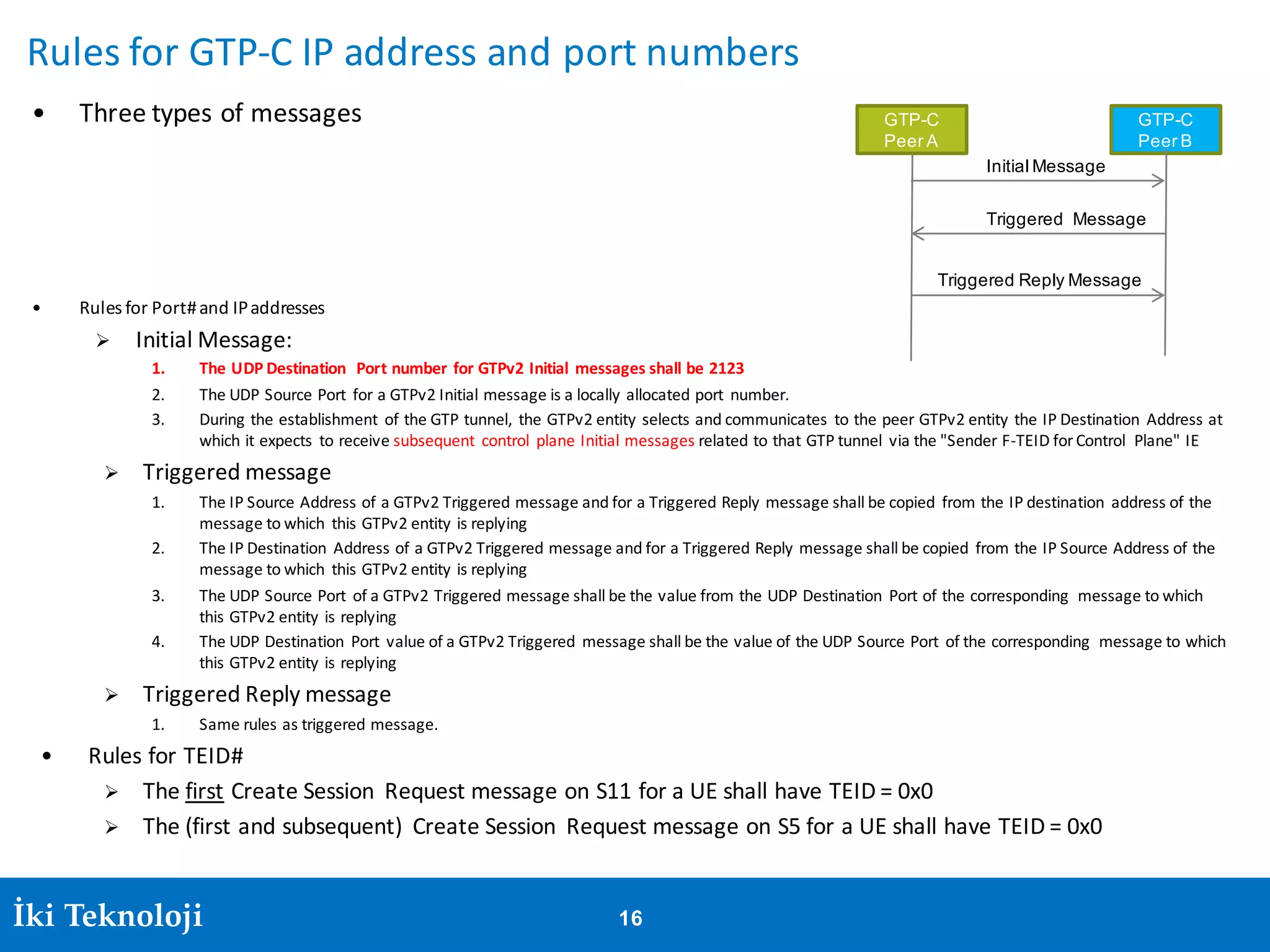
The document provides an introduction to the GPRS Tunneling Protocol (GTP), including its two main parts, GTP-C for control signaling and GTP-U for user data transmission. It details the tunneling process, setup of GTP-U tunnels, packet traces for sessions, and specifies rules for IP addresses and port numbers used in GTP communication. Additionally, it outlines path management and the specifications relevant to GTP versions.