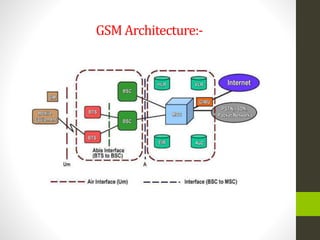
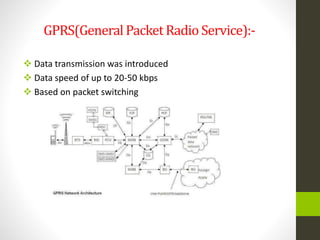
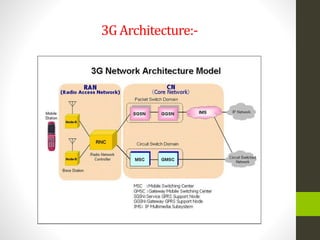
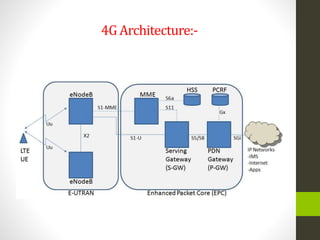
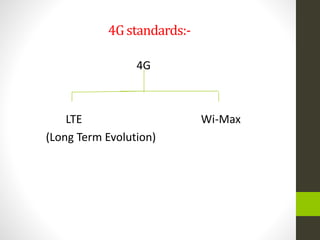
The document is a summer training presentation by Mohit Kumar Singh on wireless communication, covering base transceiver systems, network optimization parameters at MSC level, and the evolution of mobile cellular systems from 1G to 4G. It details the technologies and architecture for each generation, including GSM, GPRS, EDGE, and LTE, along with their respective data transmission speeds and modulation schemes. The presentation emphasizes advancements in wireless communication, such as the move to packet-switched networks in 4G and the introduction of MIMO technology.