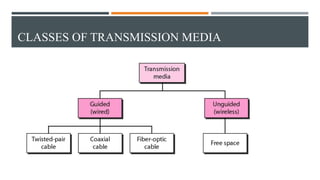
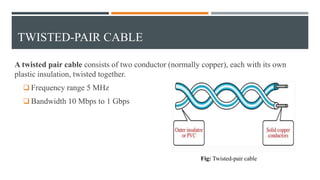
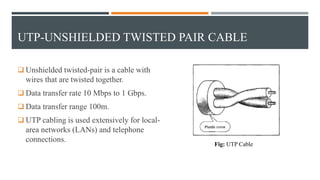
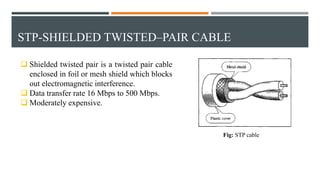
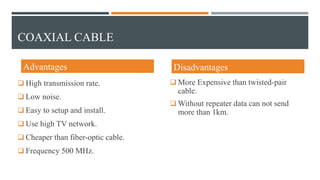
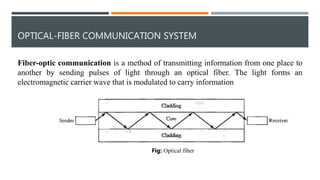
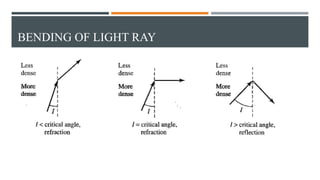
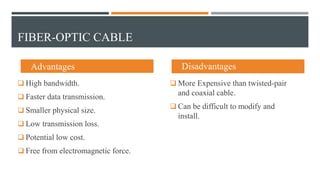
This document discusses different types of wired transmission media, including twisted-pair cable, coaxial cable, and fiber-optic cable. It describes their basic components and properties, such as maximum data transfer rates and distances. Twisted-pair cable comes in shielded and unshielded varieties. Coaxial cable uses a central conductor surrounded by insulation and shielding. Fiber-optic cable transmits data using pulses of light through glass cores. Each type has advantages like speed and disadvantages like cost.