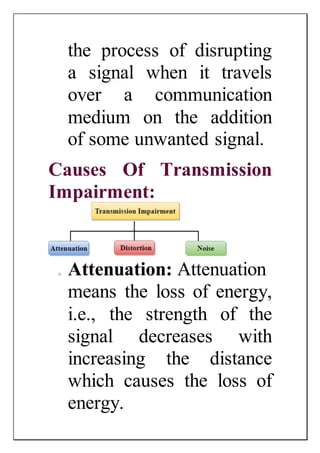
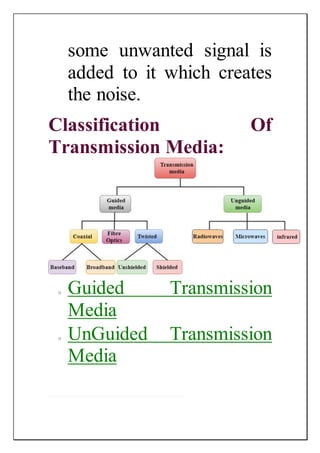
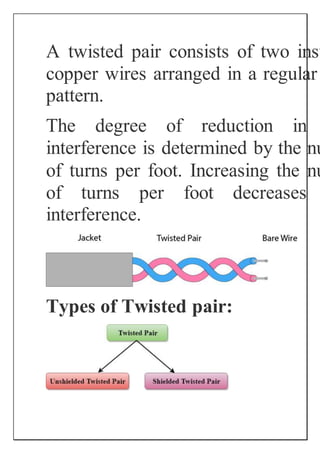
The document discusses different types of transmission media used in data communication including wired and wireless media. It provides details on various wired media such as twisted pair cable, coaxial cable, and fiber optic cable. It explains their characteristics and advantages/disadvantages. The document also discusses wireless or unguided transmission media like radio waves used for applications such as radio, television, and cellular networks. It notes that radio waves can cover a large area and penetrate walls, providing high transmission rates for wide area networks.