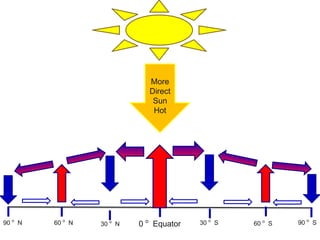
Winds are caused by differences in air pressure resulting from uneven heating of the Earth's surface by the sun. Warm air at the equator rises and cooler air from the poles moves in to replace it, creating global convection currents. These convection currents form circular wind patterns called prevailing winds, with easterly winds near the equator and westerly winds at mid-latitudes blowing toward the poles. The rotation of the Earth causes these winds to curve due to the Coriolis effect.