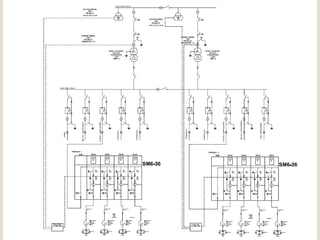
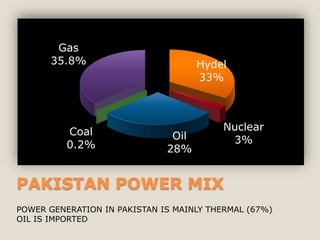
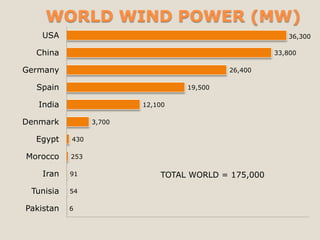
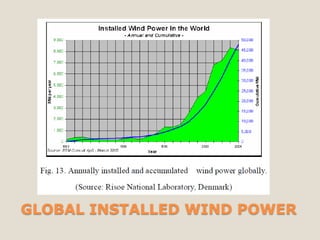
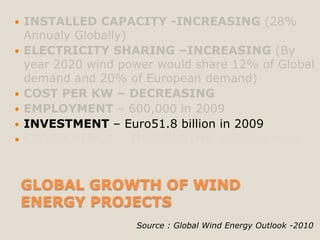
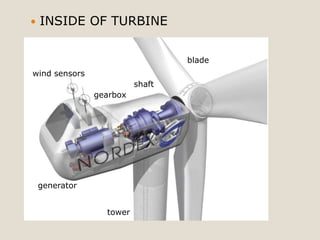
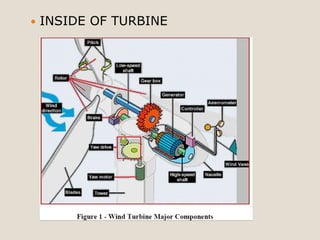
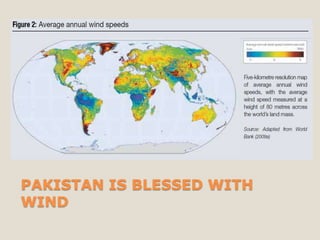
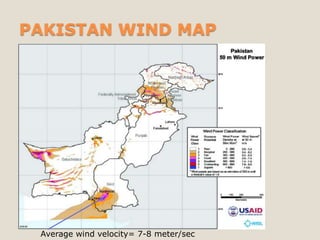
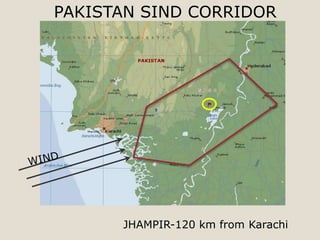
The document discusses renewable energy and wind power. It notes that climate change and oil conflicts pose major crises. Renewable energy from sources like wind can help address these issues. Wind power in particular is growing rapidly around the world and decreasing in cost. Pakistan has significant wind power potential due to its wind resources. Several proposed wind power projects in Pakistan are highlighted, including a 49.5 MW project by FFC Energy. Advantages of wind power are outlined. Common myths about wind energy are addressed.















































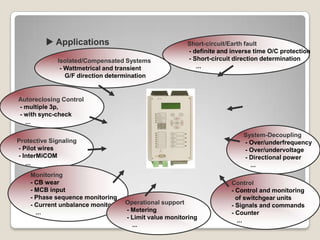
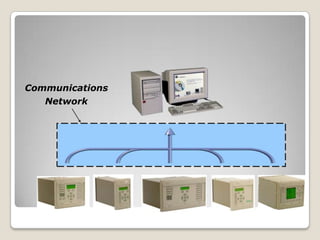
![ Operating state recognition and tripping characteristics
t [s]
Start-up
1.000 Load Overload
logarithmic t = 20 s
6Iref
m =0
500
reziprocally
Motor protection squared
k I > I/I
0,1 1,0 2,0 stup 3,0 ref](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/growingwiththewindli-130423115425-phpapp01/85/Wind-Farm-design-and-Construction-64-320.jpg)
![ Overload memory and start-up counter
m [%] Overload memory
100
80
60
40
20
t
Start-up counter Reclosure blocked
3
2
Motor protection
1
t](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/growingwiththewindli-130423115425-phpapp01/85/Wind-Farm-design-and-Construction-65-320.jpg)