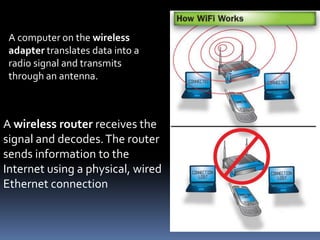
Wi-Fi allows devices to connect to the Internet and form local area networks wirelessly. The term Wi-Fi was coined in 1999 and resembles older "hi-fi" audio terms. Devices within range of a wireless network can connect to the Internet through an access point. Early plans for city-wide Wi-Fi networks proved difficult to implement at a large scale. Wi-Fi reduces network deployment and expansion costs compared to wired networks and operates in many public and private locations. Encryption has improved security but wireless networks still have limited range compared to wired networks. Common hardware for Wi-Fi includes routers, access points, and wireless adapters.