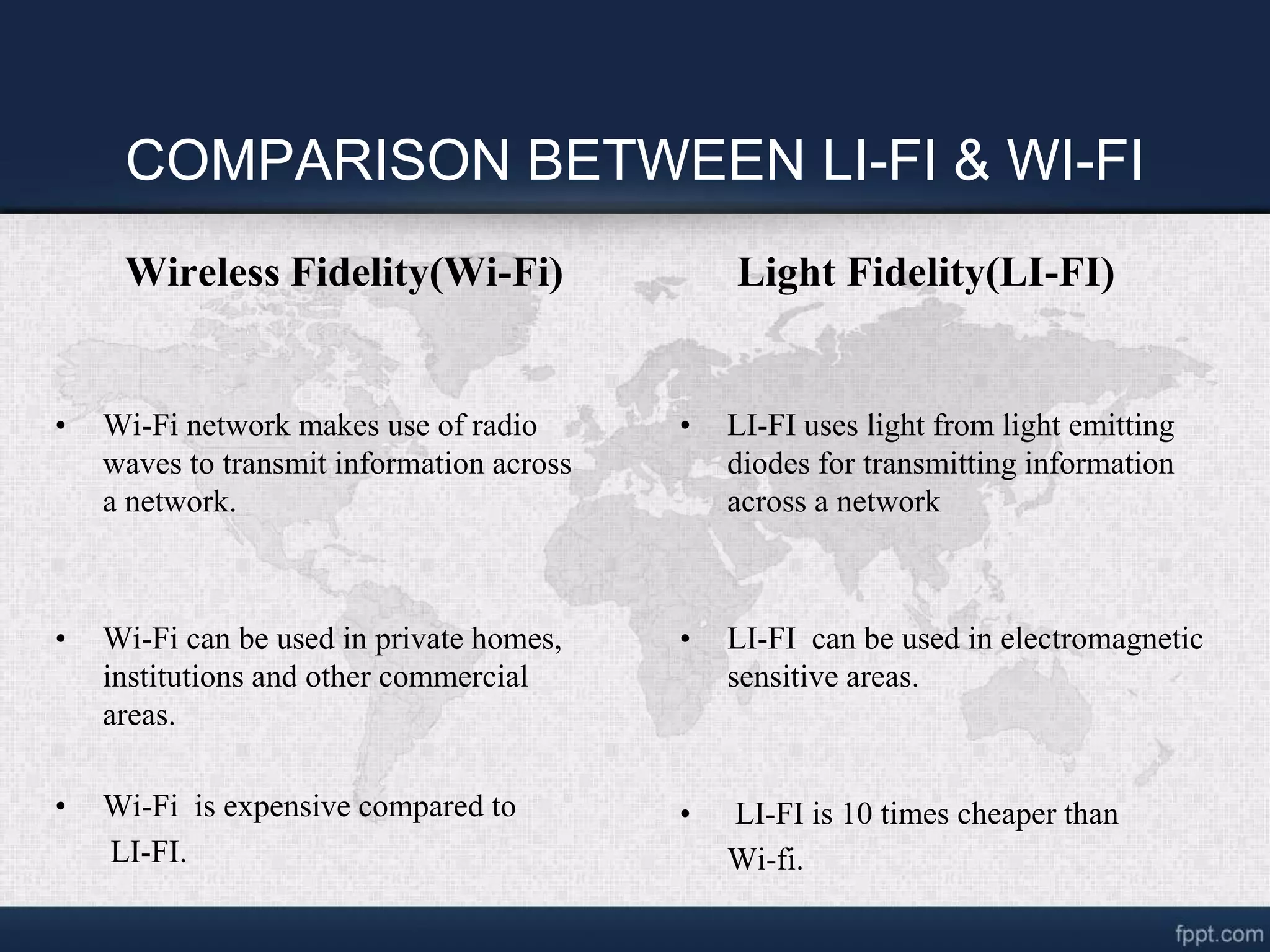
LI-FI technology uses visible light communication and light-emitting diodes to transmit data wirelessly. It was invented by Harald Haas at the University of Edinburgh. LI-FI is expected to be faster, more energy efficient, and more secure than existing Wi-Fi technology. It could be used in places where Wi-Fi poses issues, like hospitals, nuclear power plants, and aircraft. Challenges include the need for direct line of sight and developing effective bidirectional transmission. Potential applications include use in traffic lights, street lamps, and smart power plants.