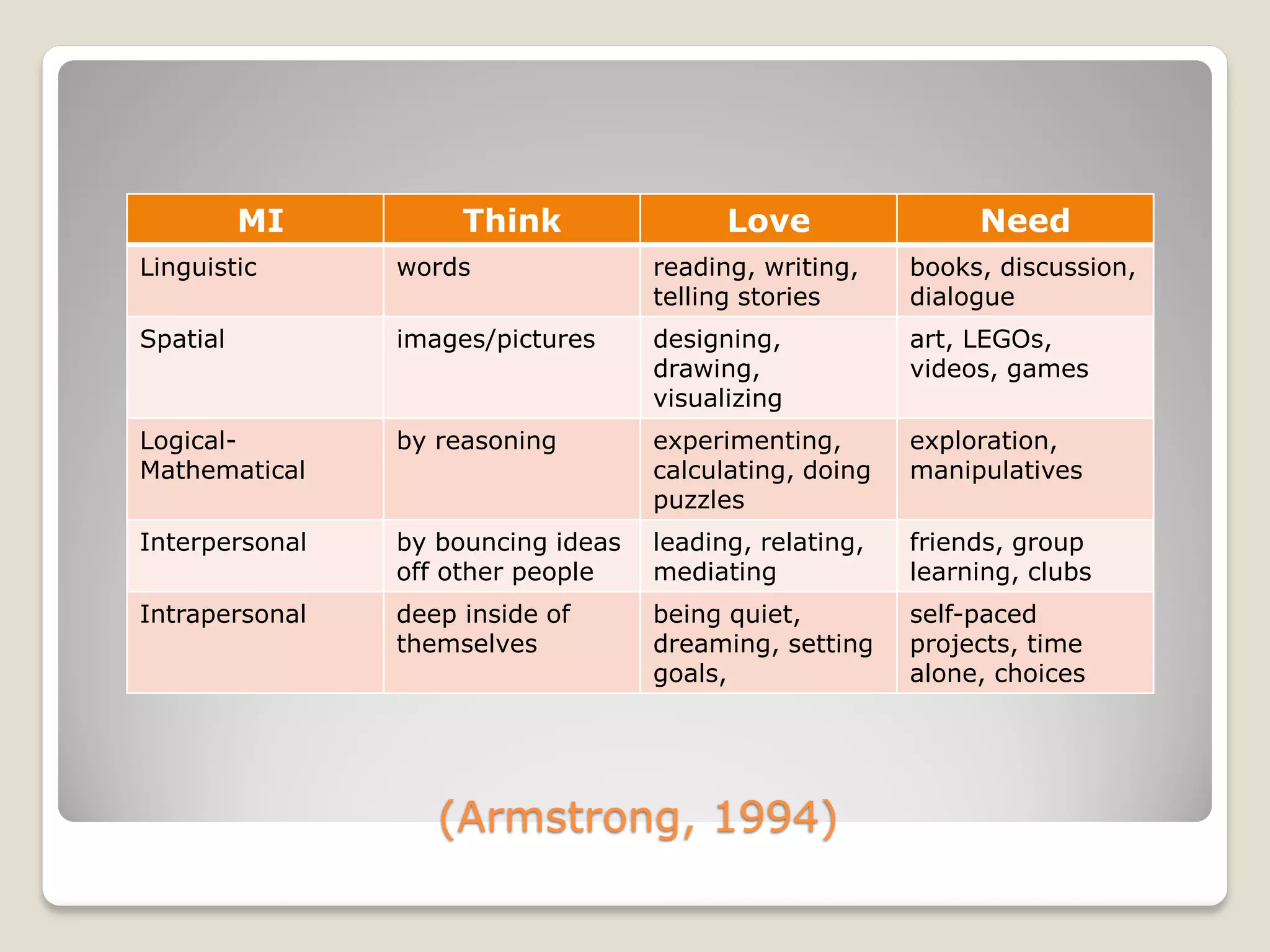
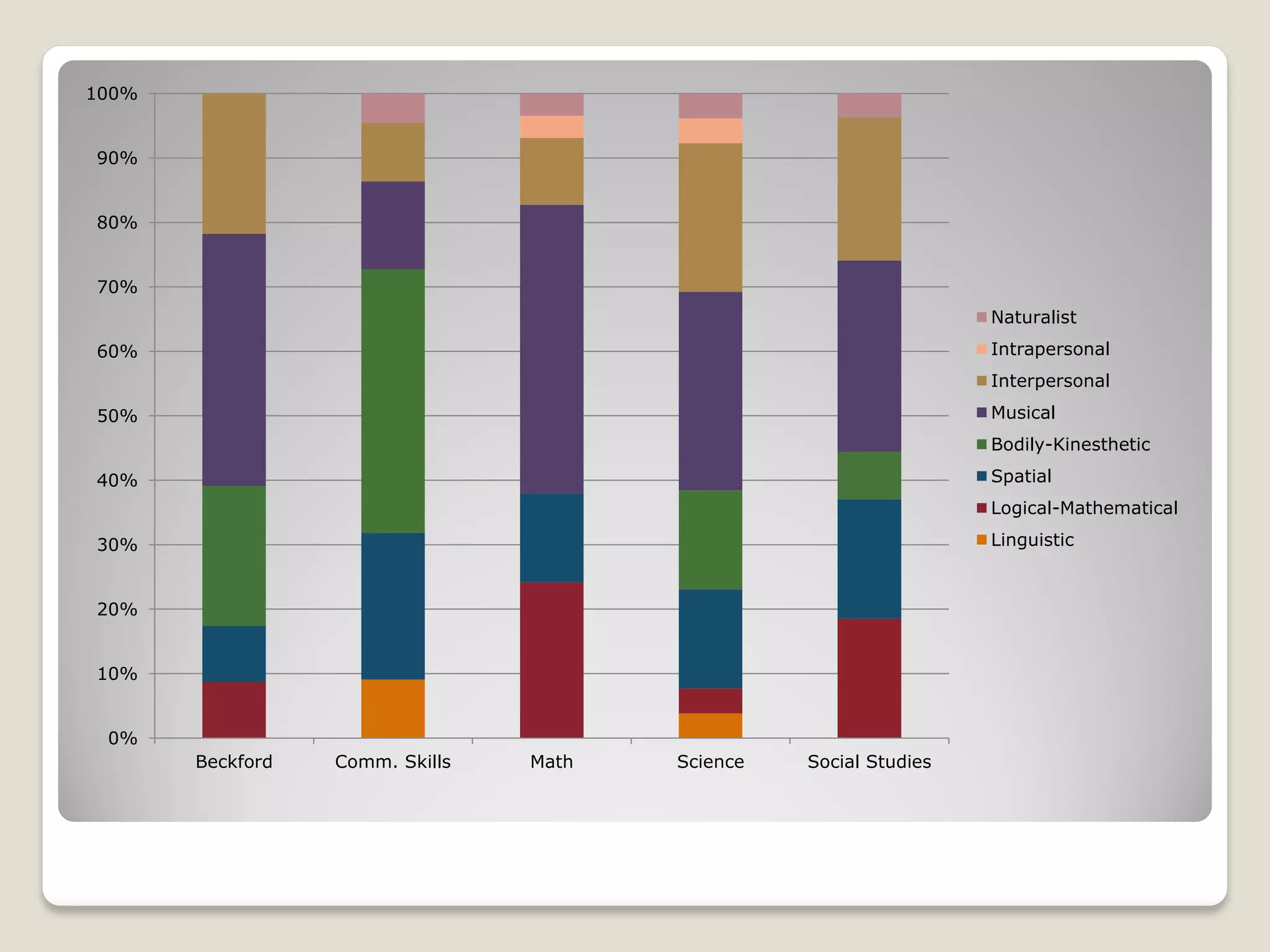
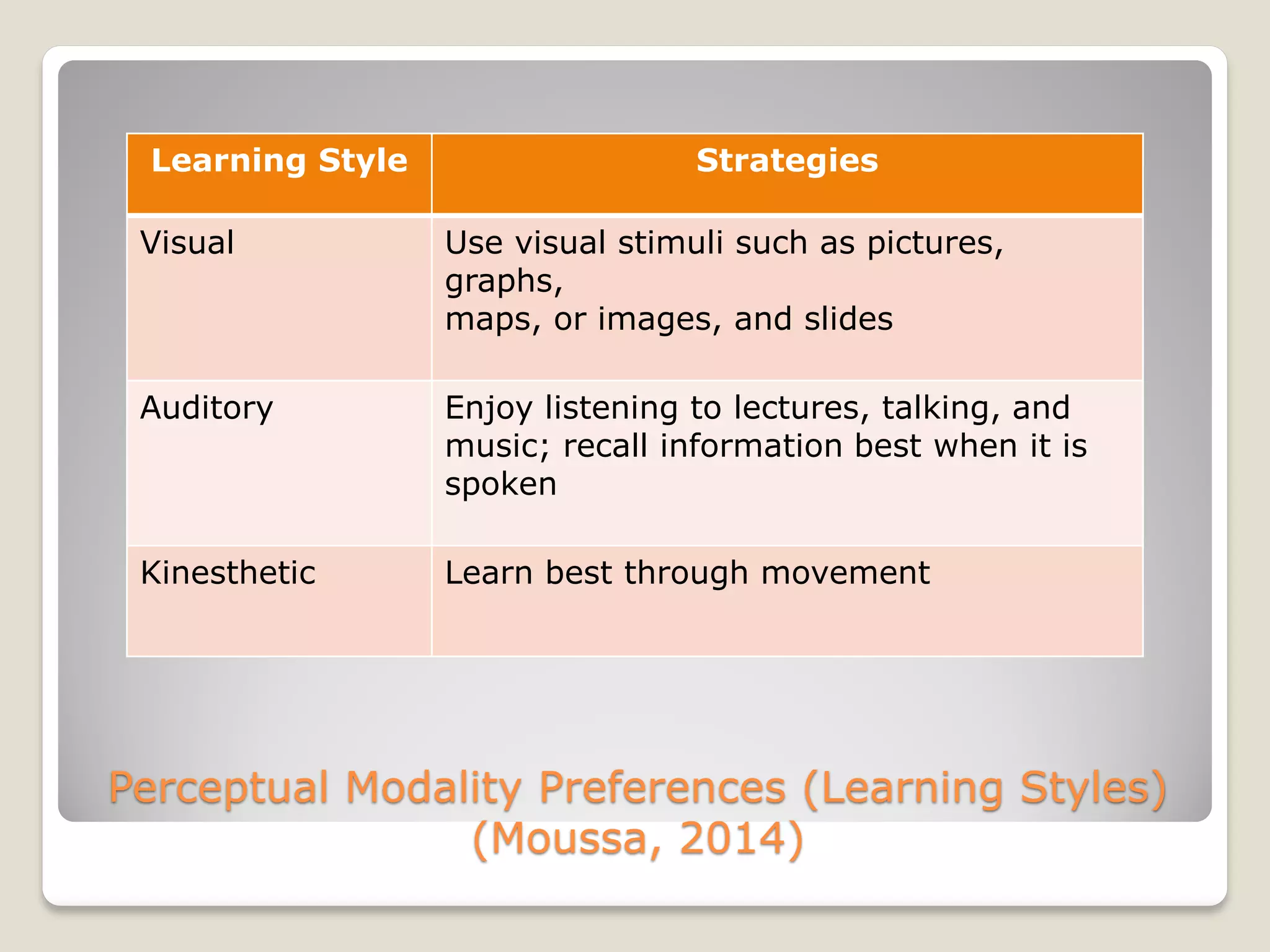
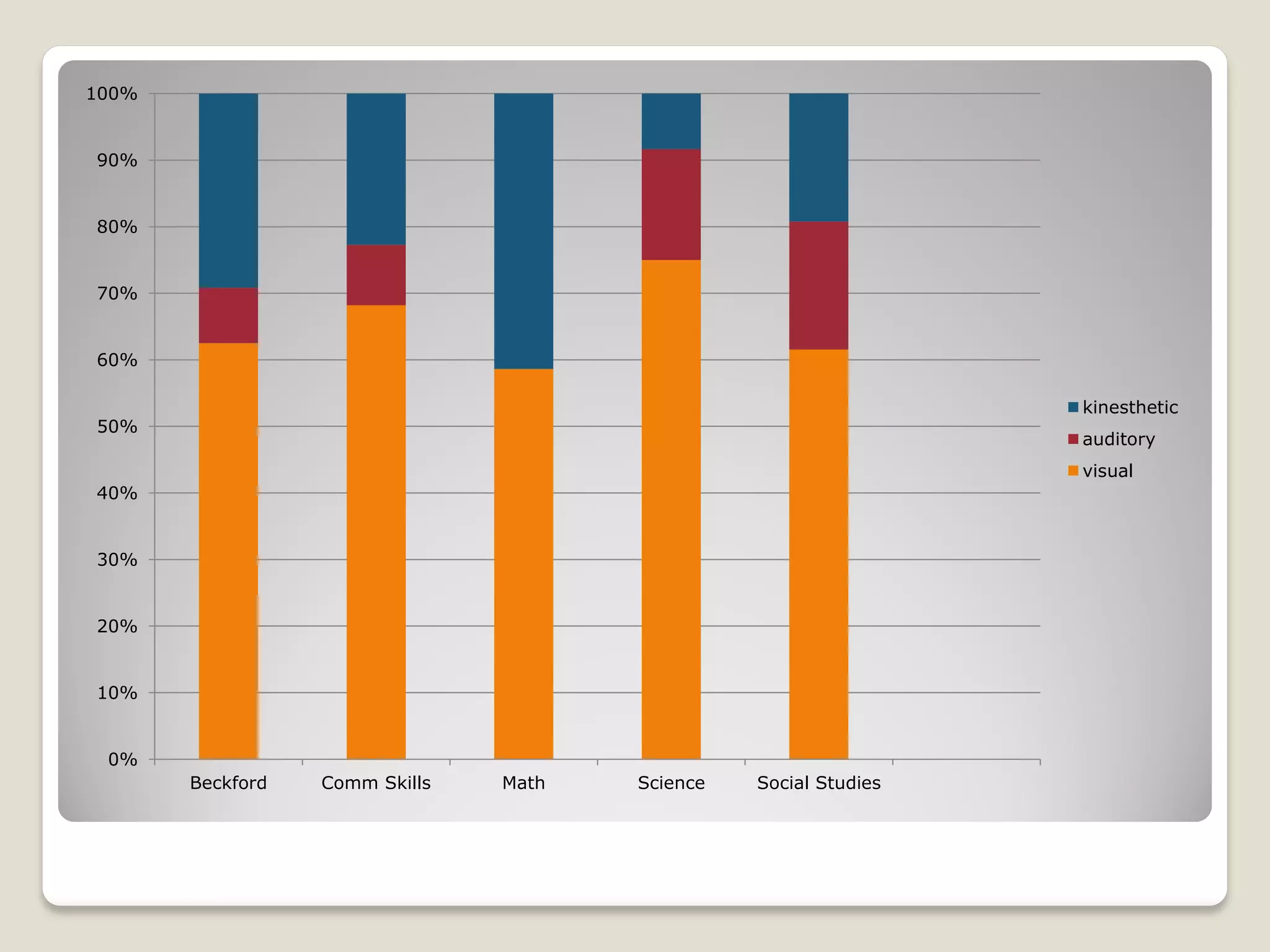
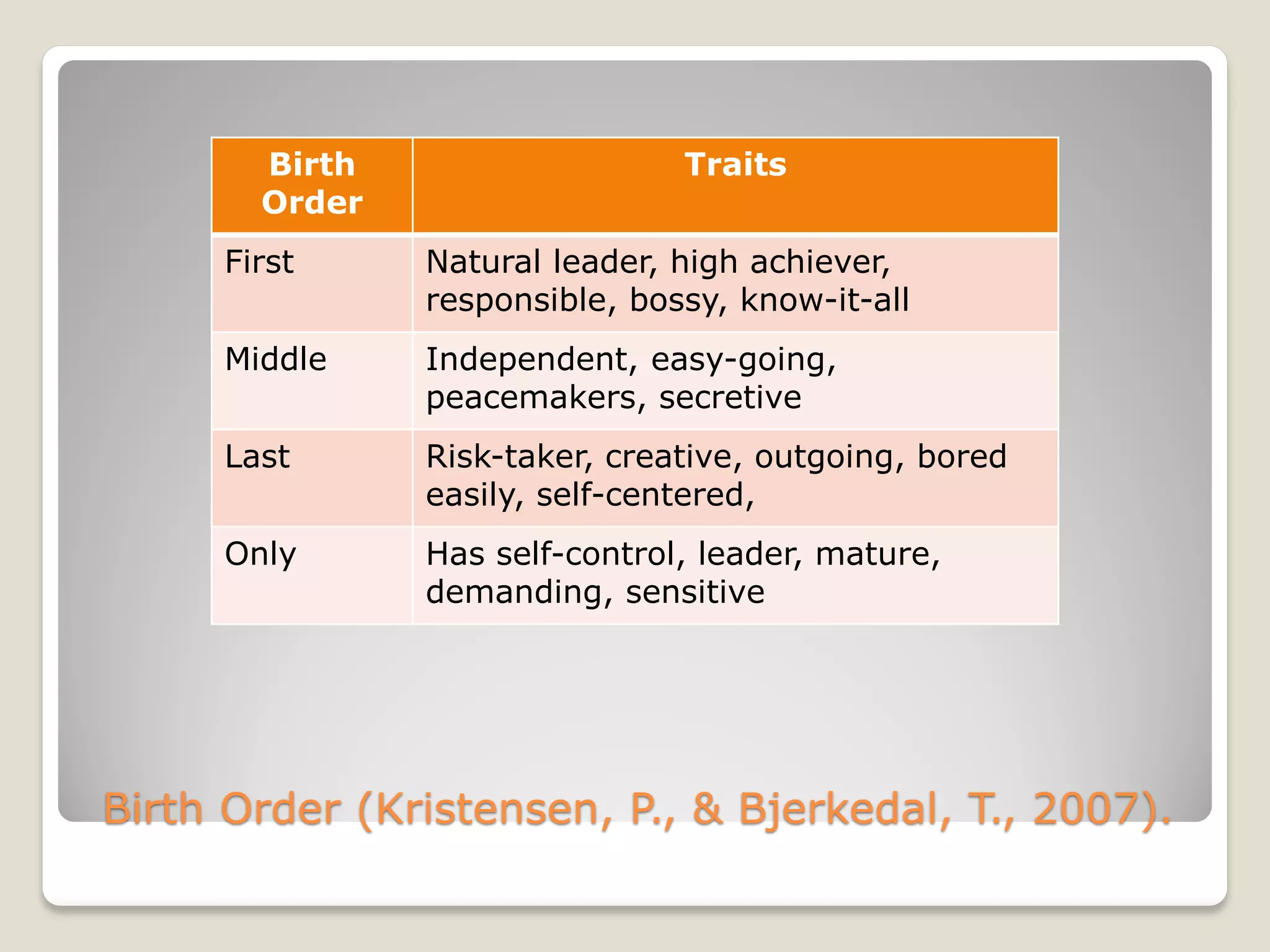
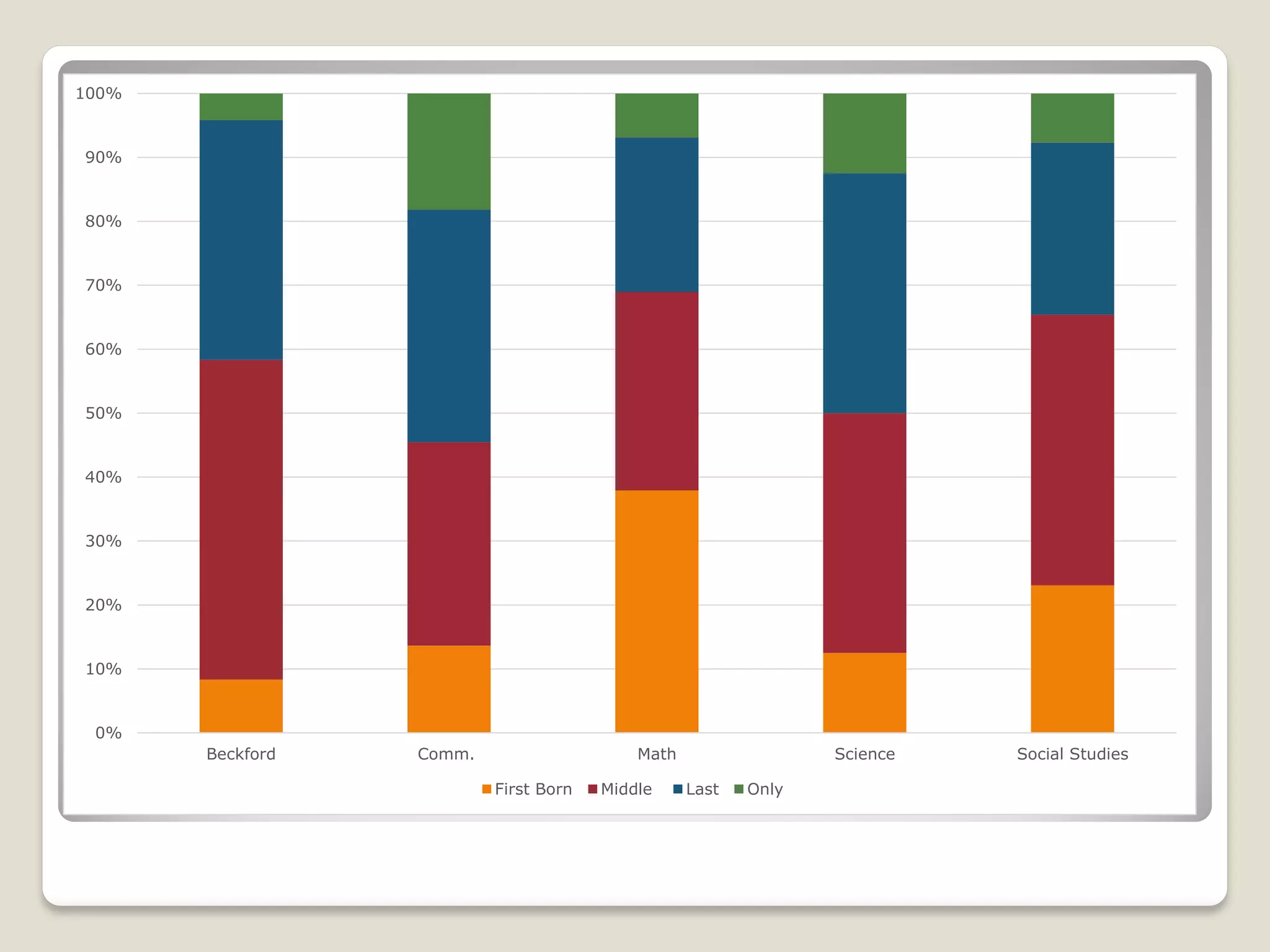
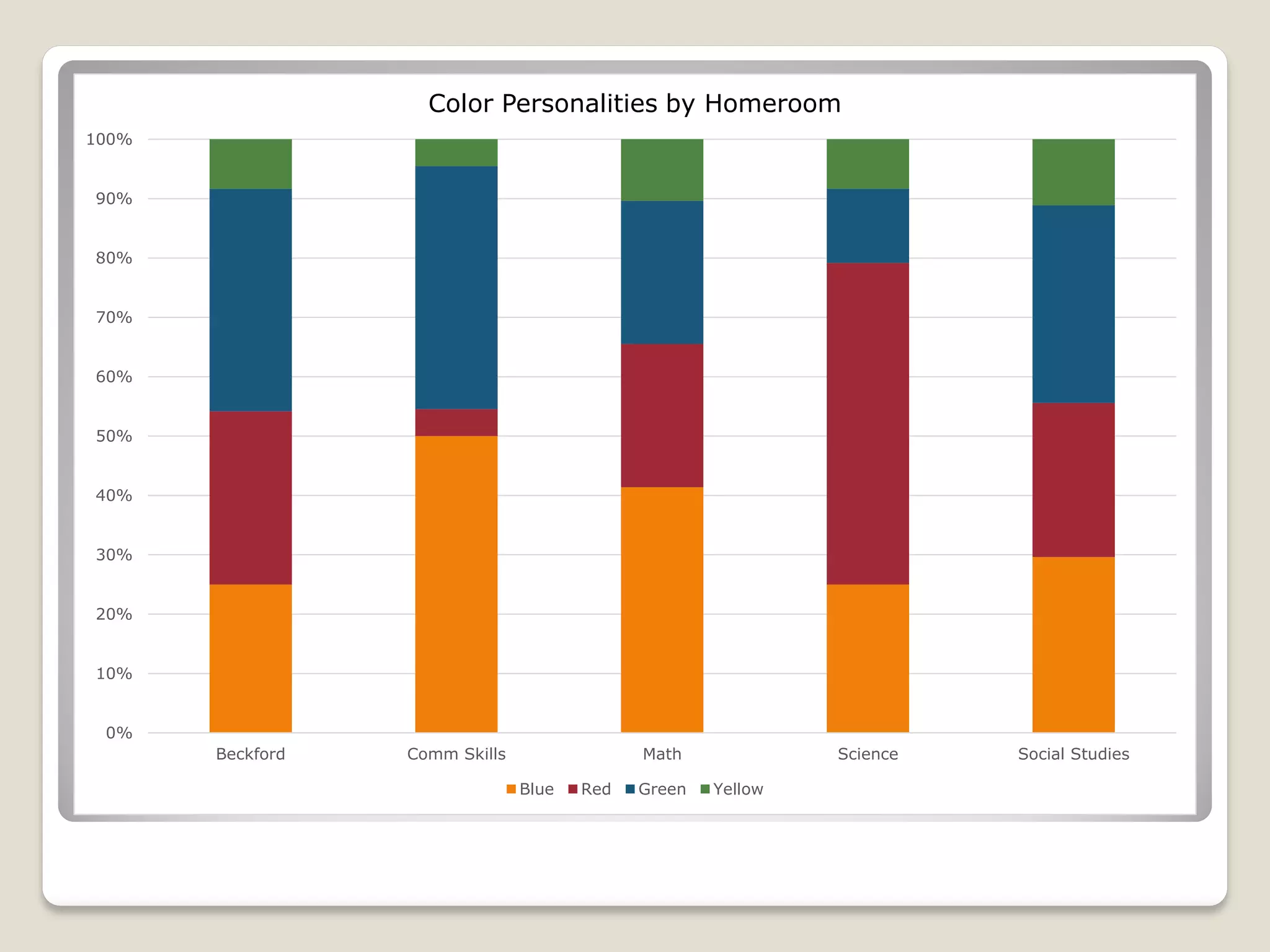
The document discusses the importance of creating student learning profiles to tailor educational approaches based on individual learning styles, multiple intelligences, and socio-economic factors. It emphasizes the need for teachers to collect relevant data and develop strategies for invitational learning that recognize students' potential. Additionally, it includes a student learning profile form and suggestions for data sharing and collaboration among educators.