The document discusses various white box testing techniques:
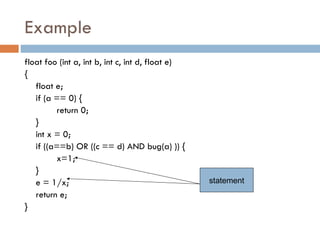
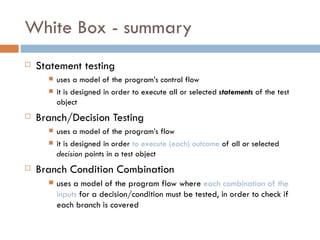
1. Statement testing executes all statements in the code.
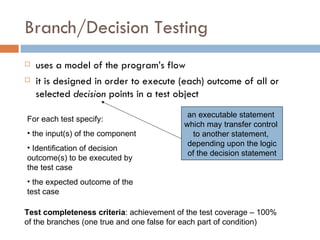
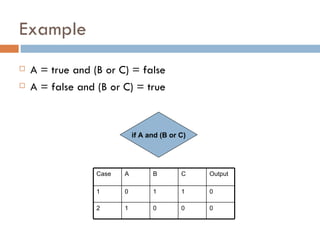
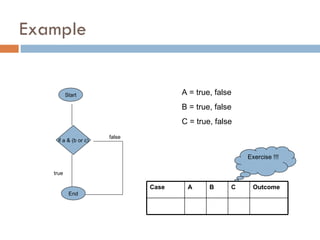
2. Branch/Decision Testing executes all outcomes (true/false) of decision points.
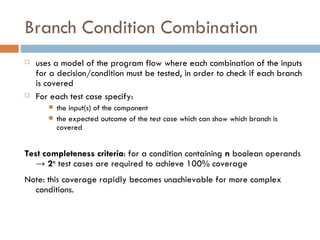
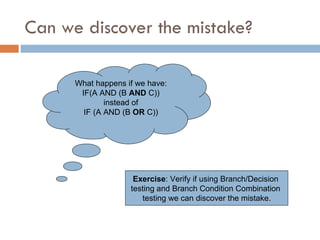
3. Branch Condition Combination Testing checks that each combination of inputs for a condition is tested to cover all branches.
4. Modified Condition Combination Testing independently tests each atomic condition to check its effect on the decision outcome.