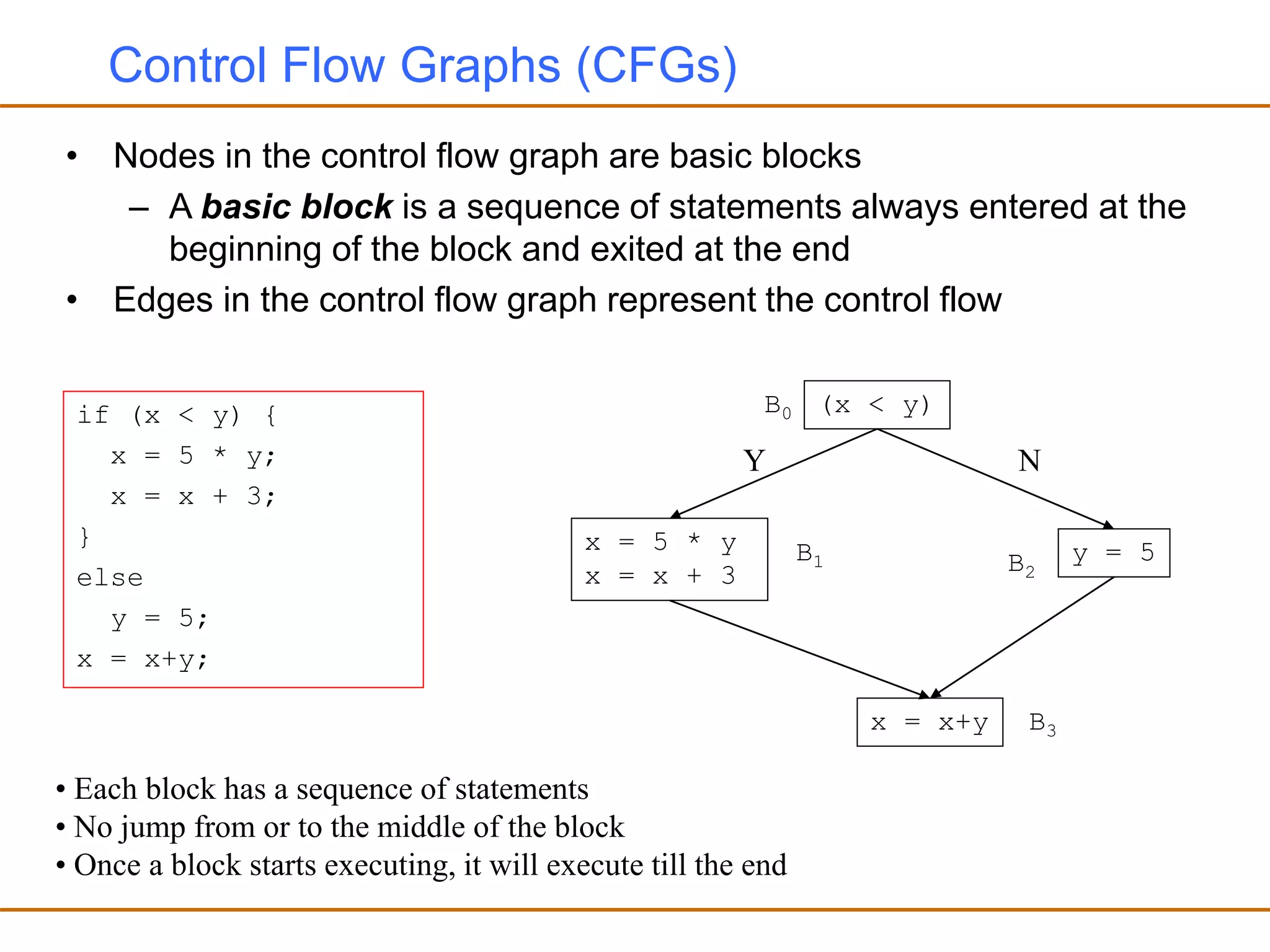
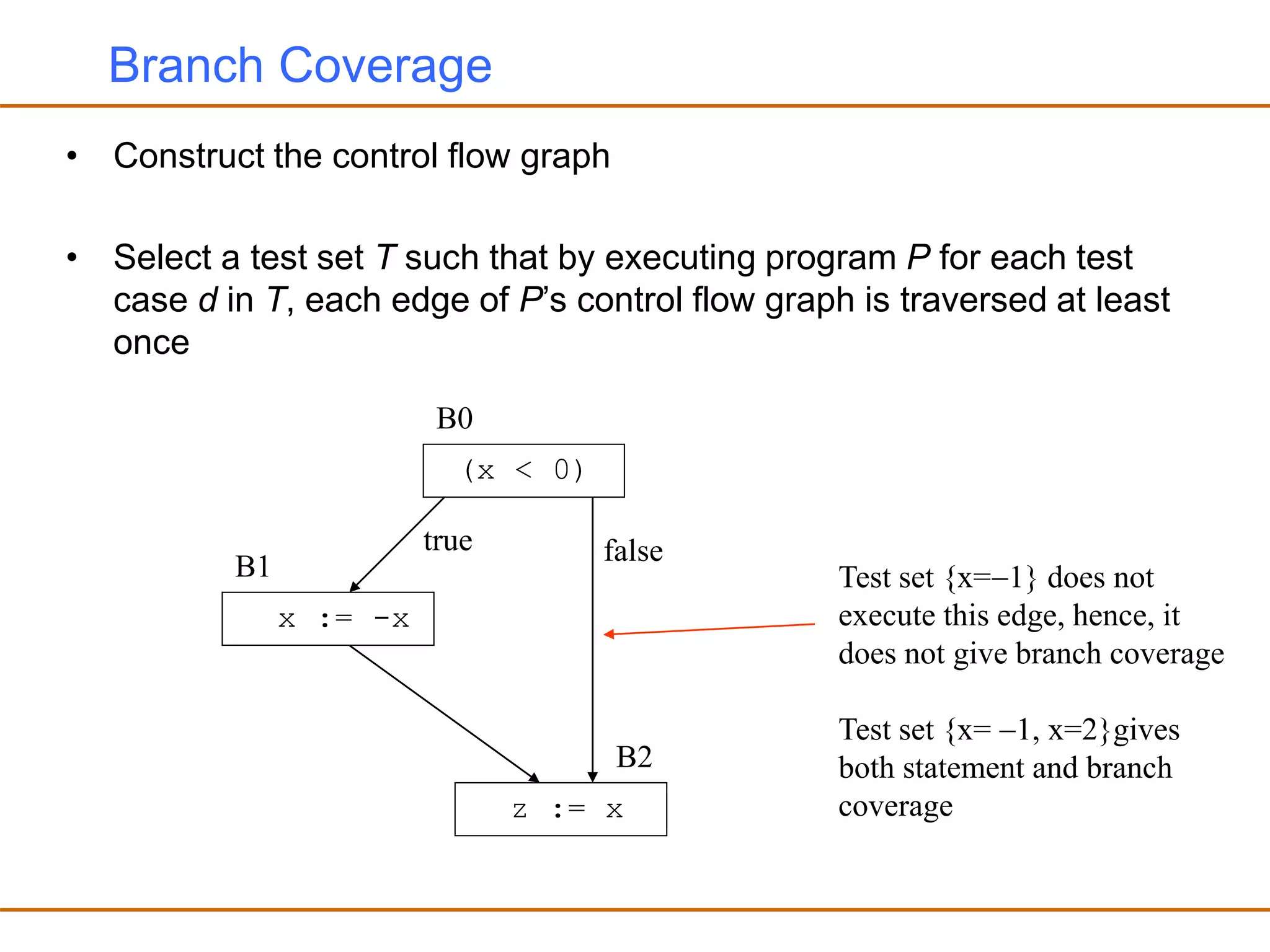
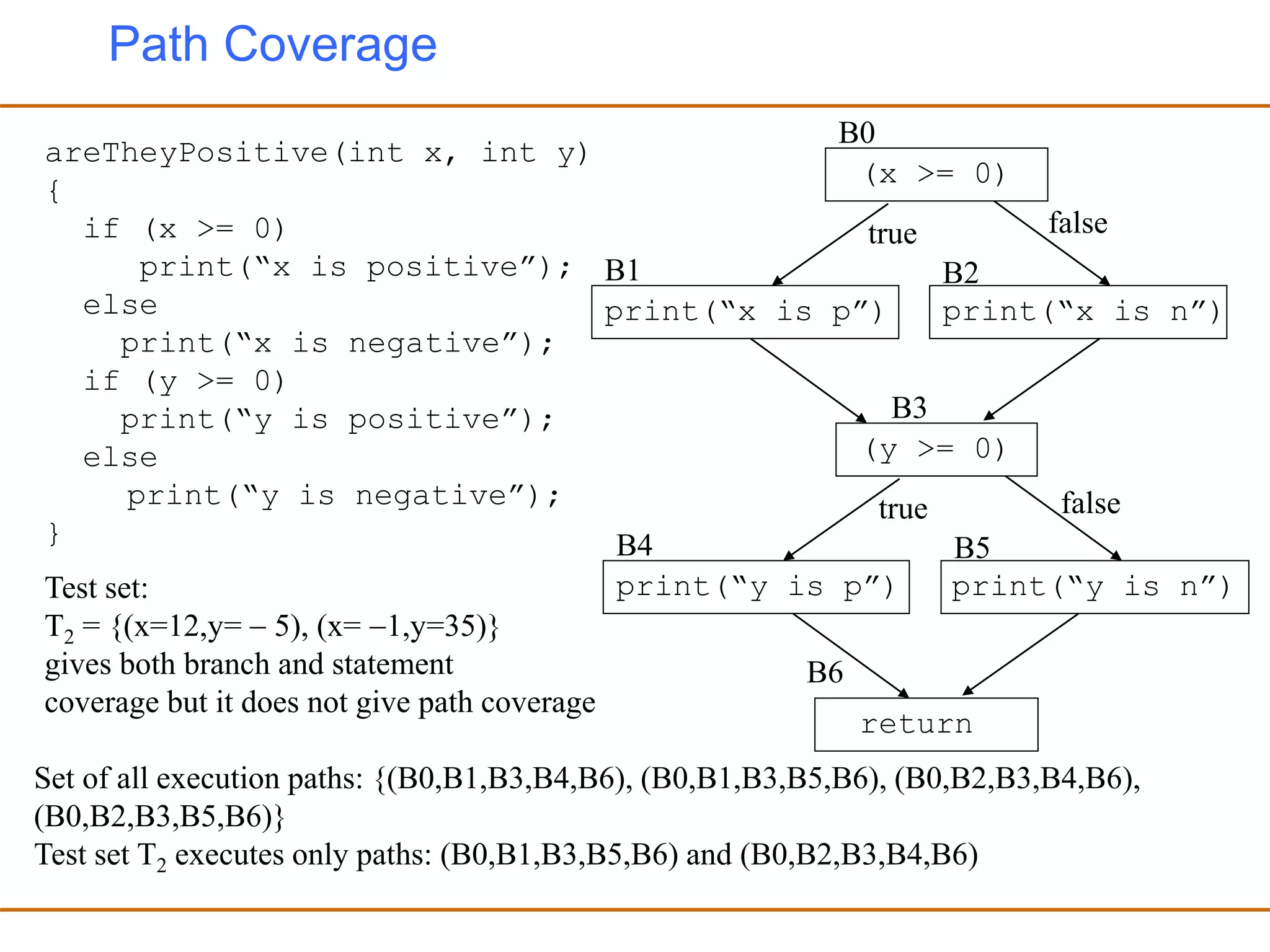
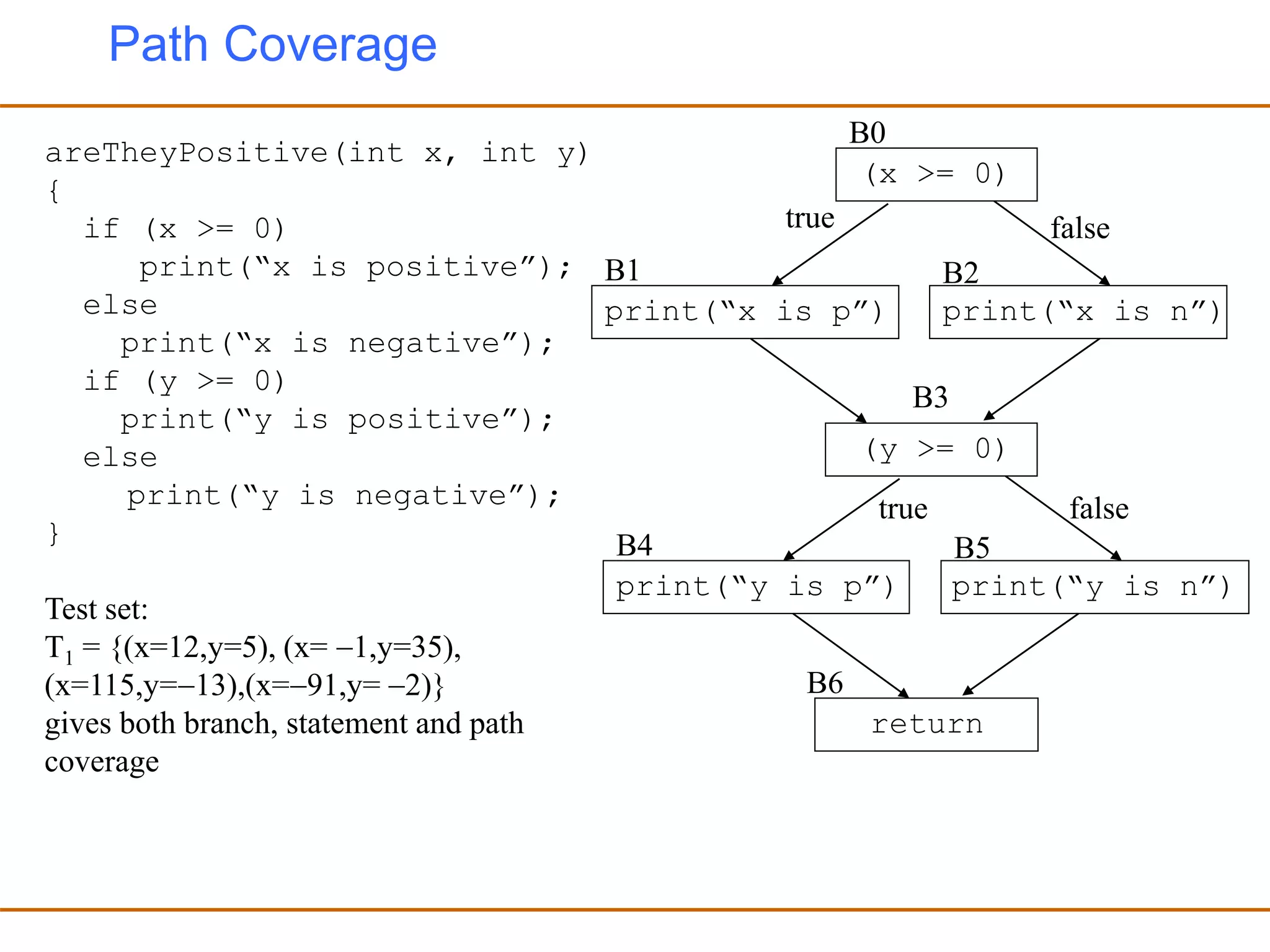
Testing software is difficult because exhaustively testing all possible inputs is infeasible due to the huge number of potential test cases. Common techniques for testing include:
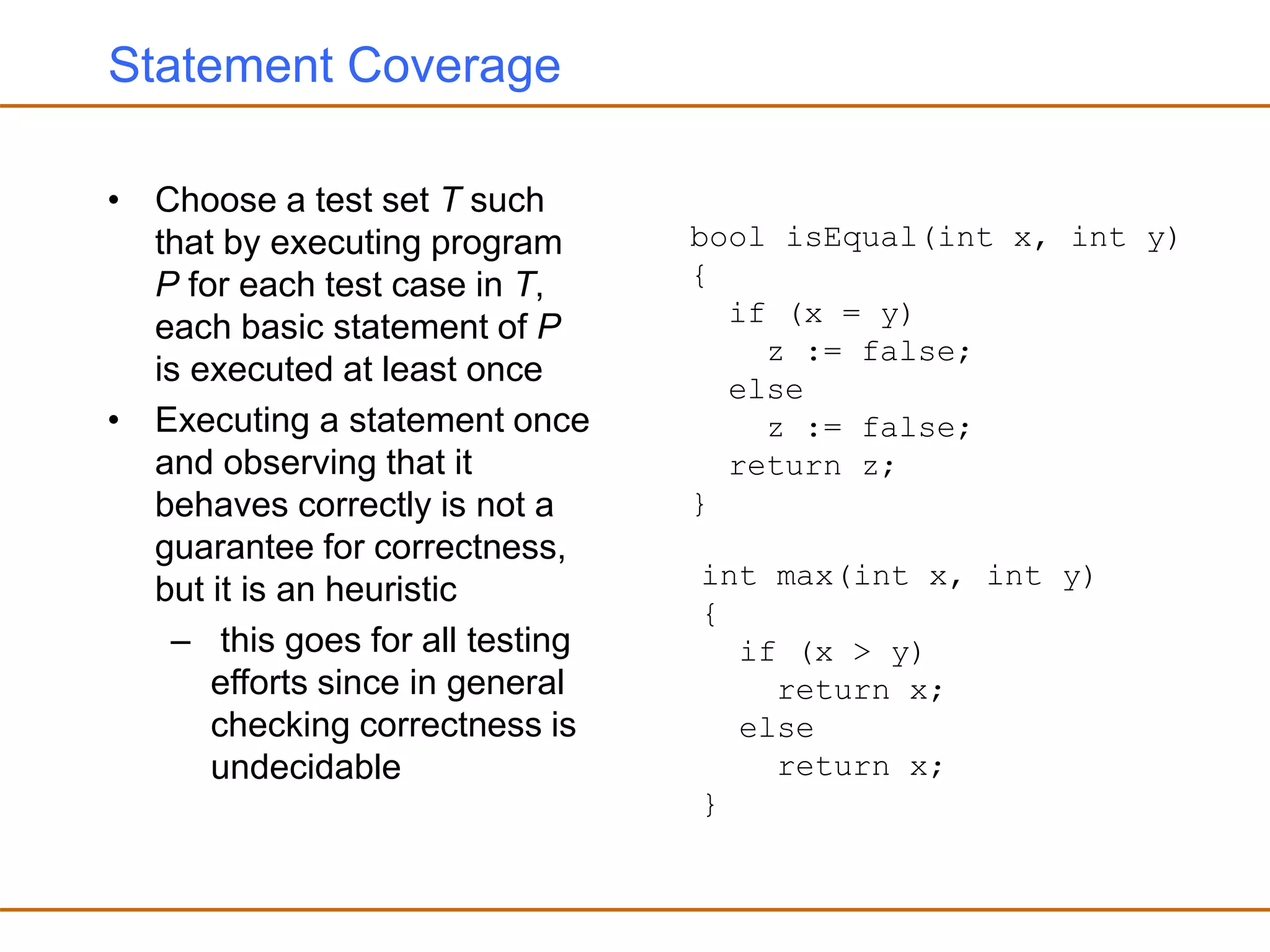
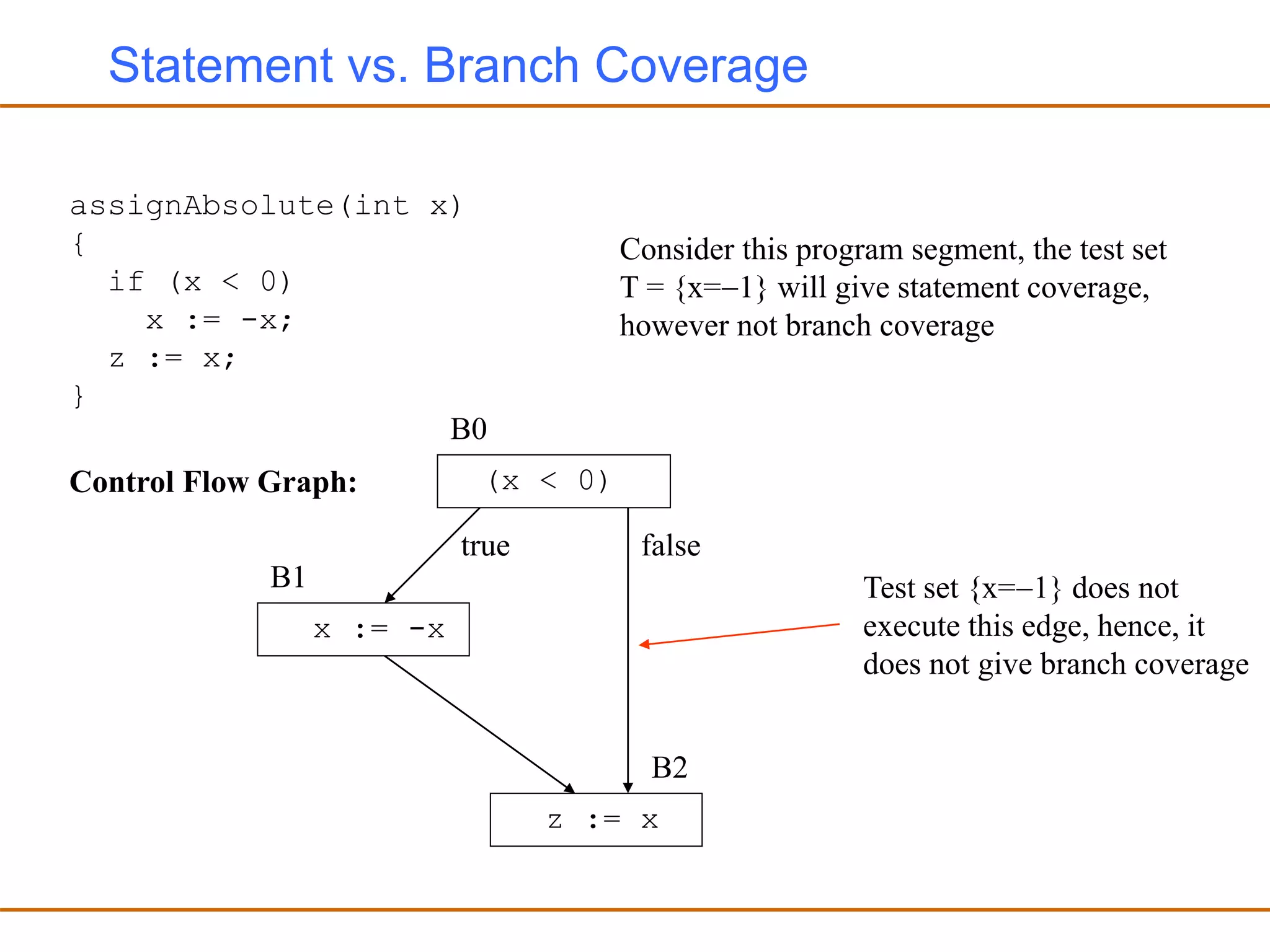
- Generating test cases that cover different parts of the program structure through techniques like statement coverage and branch coverage.
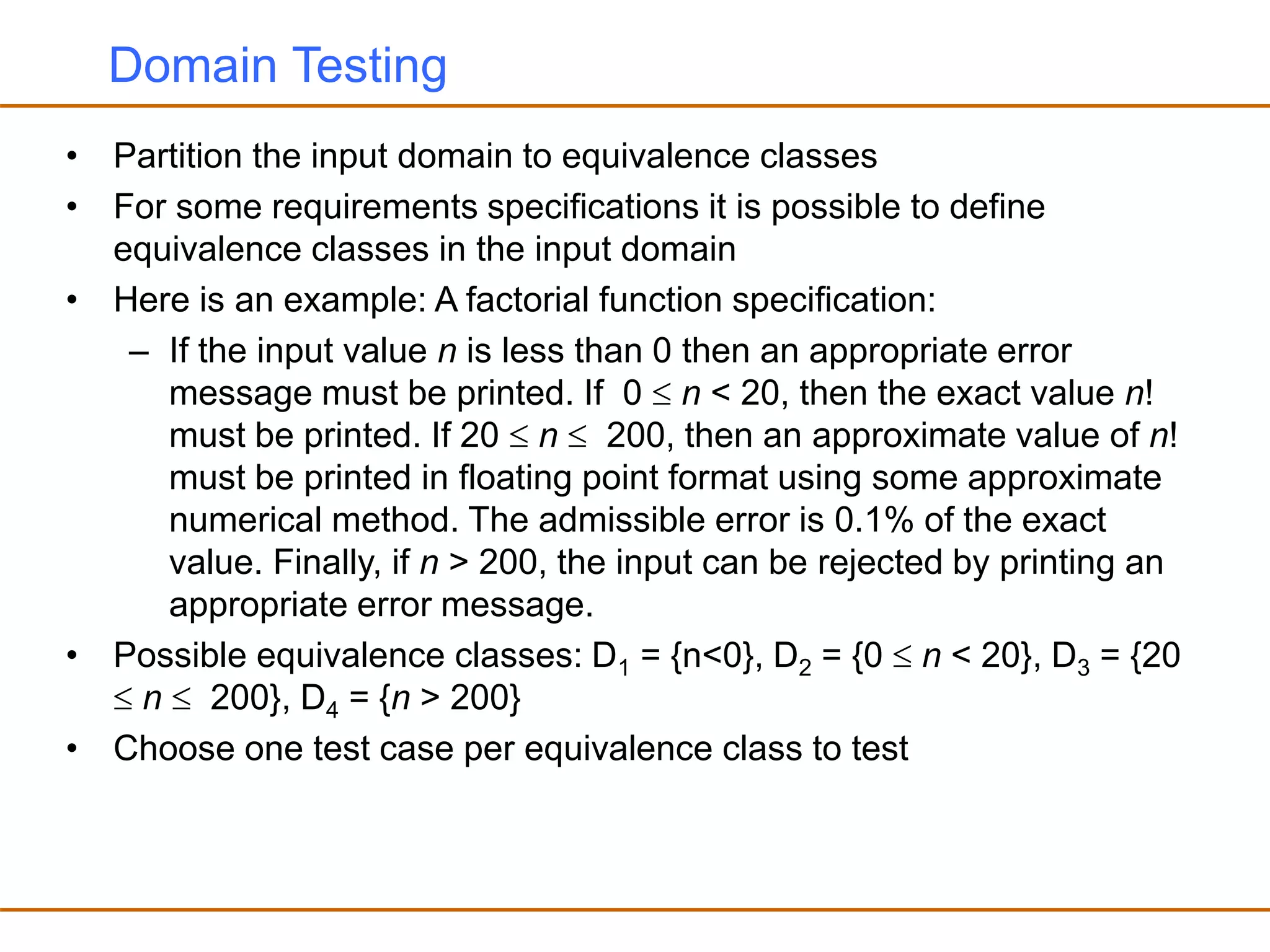
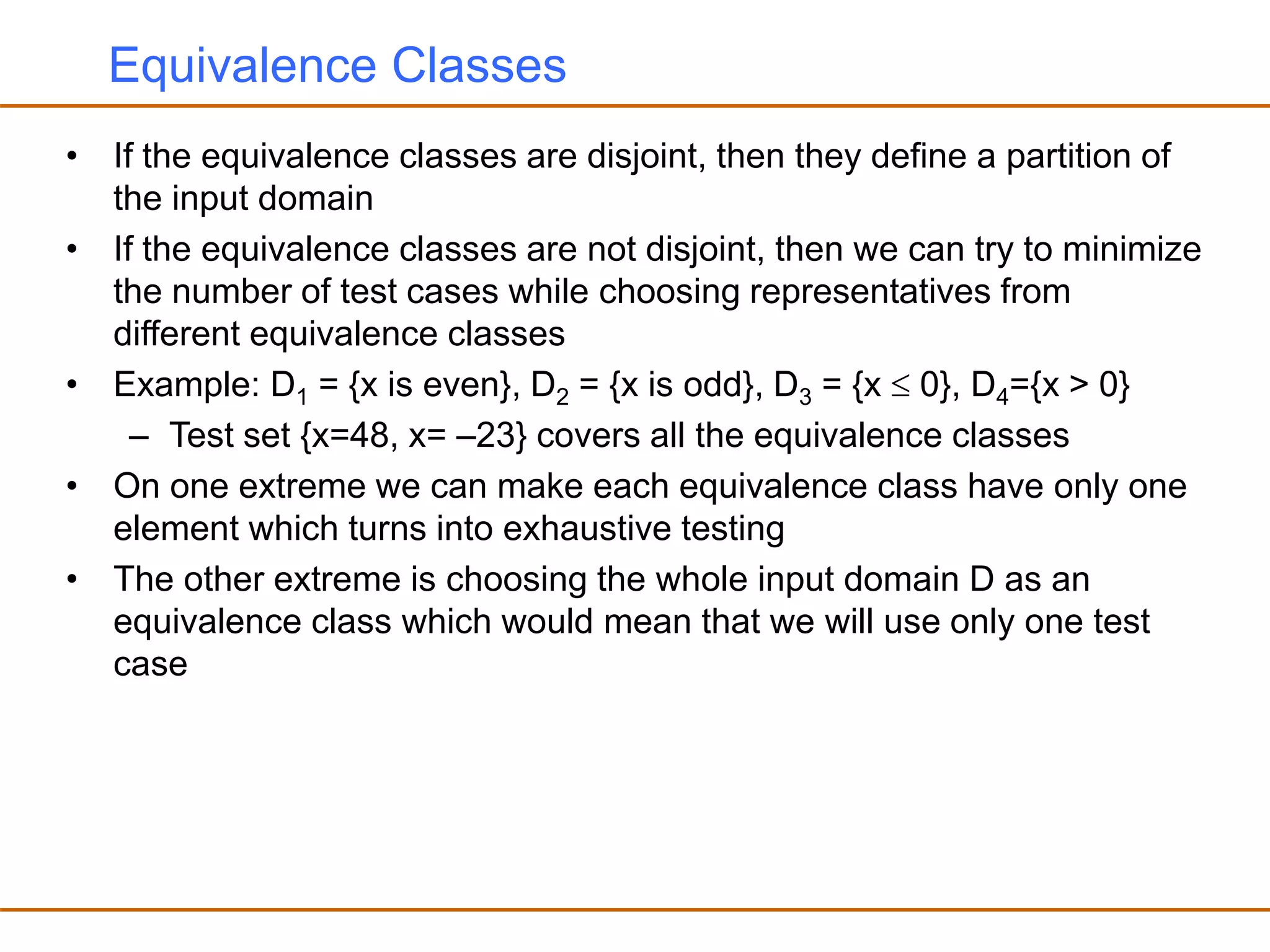
- Partitioning the input domain into equivalence classes and selecting representative test cases from each class.
- Testing boundary conditions and edge cases like values at the limits of input ranges.
- Using coverage metrics to guide test case selection and determine when sufficient coverage has been achieved, though testing can never prove a program completely correct. Random and exhaustive testing alone are not effective approaches.








![Testing Boundary Conditions
• For each range [R1, R2] listed in either the input or output
specifications, choose five cases:
– Values less than R1
– Values equal to R1
– Values greater than R1 but less than R2
– Values equal to R2
– Values greater than R2
• For unordered sets select two values
– 1) in, 2) not in
• For equality select 2 values
– 1) equal, 2) not equal
• For sets, lists select two cases
– 1) empty, 2) not empty
R1 R2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/autotest-230705051219-88557a17/75/AutoTest-ppt-14-2048.jpg)
![Testing Boundary Conditions
• For the factorial example, ranges for variable n are:
– [, 0], [0,20], [20,200], [200, ]
– A possible test set:
• {n = -5, n=0, n=11, n=20, n= 25, n=200, n= 3000}
– If we know the maximum and minimum values that n can take we
can also add those n=MIN, n=MAX to the test set.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/autotest-230705051219-88557a17/75/AutoTest-ppt-15-2048.jpg)



























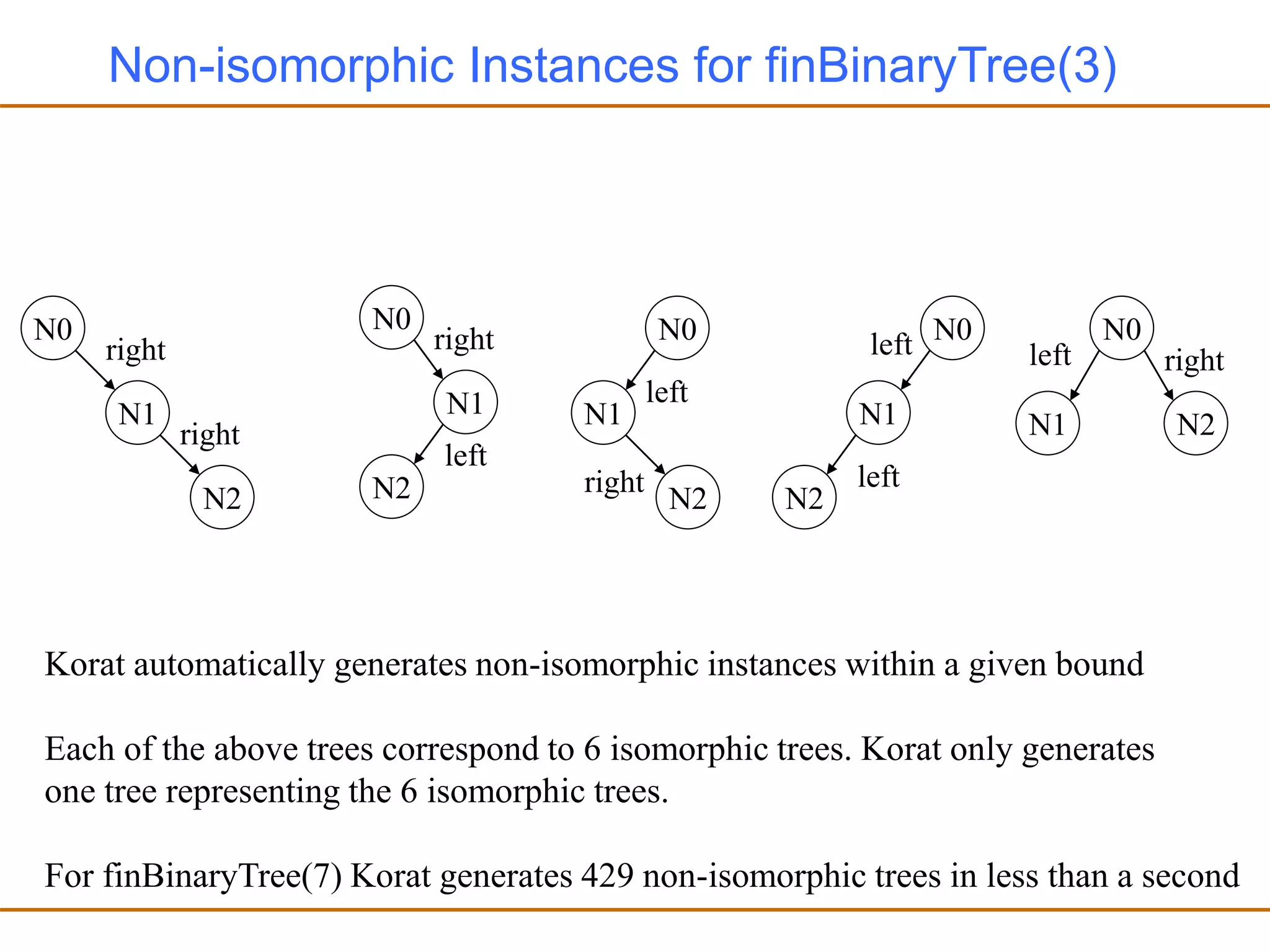
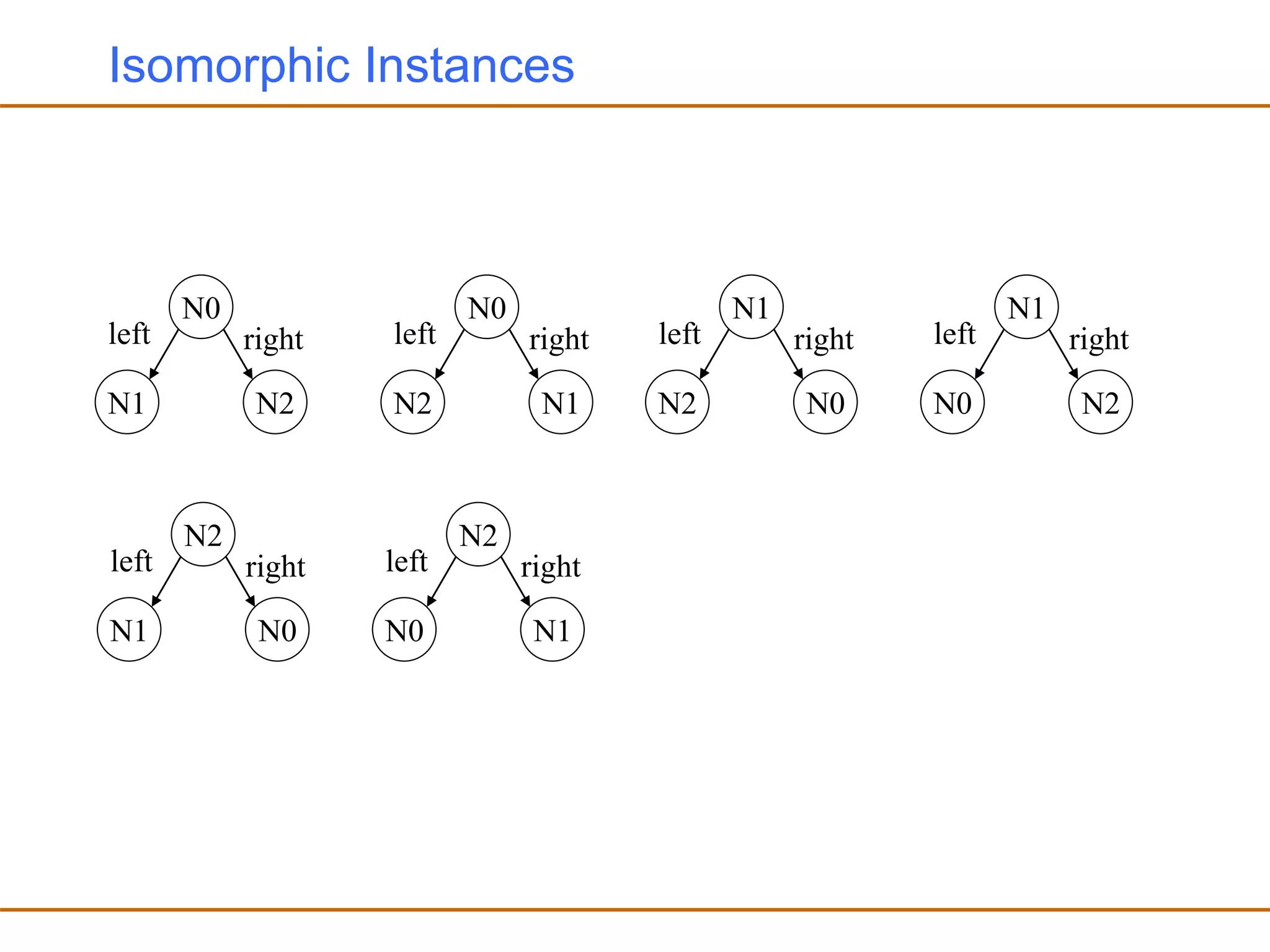
![Generating Test Cases
• Korat orders all the elements in every class domain and every field
domain
• Each test case is represented as a vector of indices into the
corresponding field domains
N0
N1 N2
right
left
size=3
[1,0,2,3,0,0,0,0,]
Test Case Corresponding Vector
For the Binary Tree example assume that
The class domain is ordered as N0 < N1 < N2
The field domains for root, left and right are ordered as null < N0 < N1 < N2
The size domain has one element which is 3
[1,0,2,3,0,0,0,0,]
fields of the
Binary tree object
fields of the Node object N0
fields of the
Node object N1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/autotest-230705051219-88557a17/75/AutoTest-ppt-75-2048.jpg)