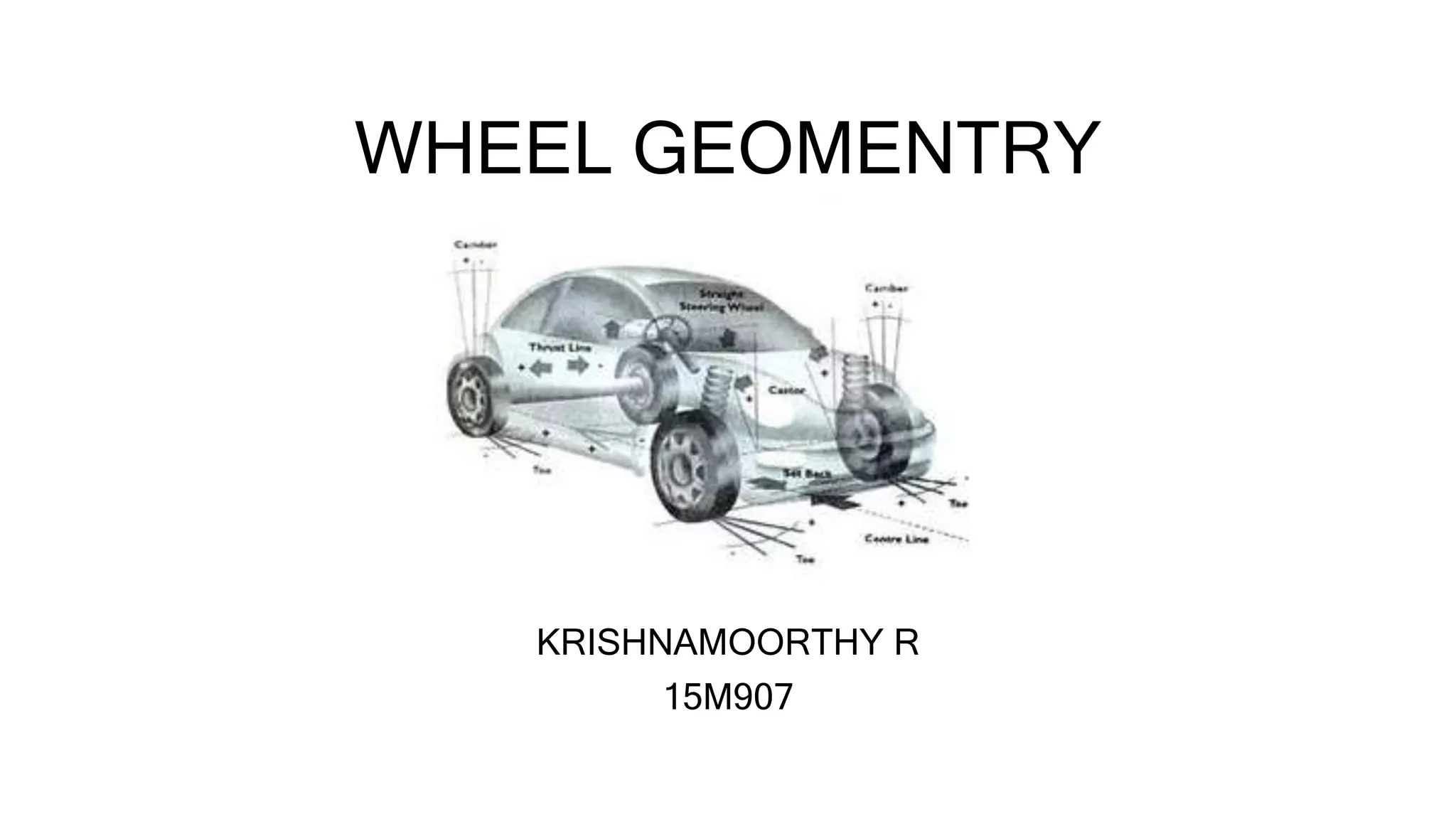
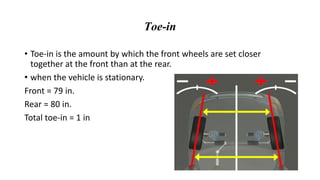
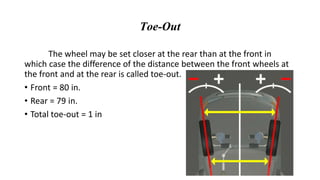
This document discusses wheel geometry and the steering system requirements. It describes camber as the tilt of the car wheel from vertical, with most manufacturers specifying a small positive camber of 2-3 degrees for front wheels and negative camber for rear wheels to increase cornering ability. Caster is defined as the angle between the kingpin centerline and vertical plane of the wheel, typically about 3 degrees, which helps steering effort and recovery. Toe-in and toe-out refer to the front wheels being set closer together or farther apart at the front than the rear while stationary.