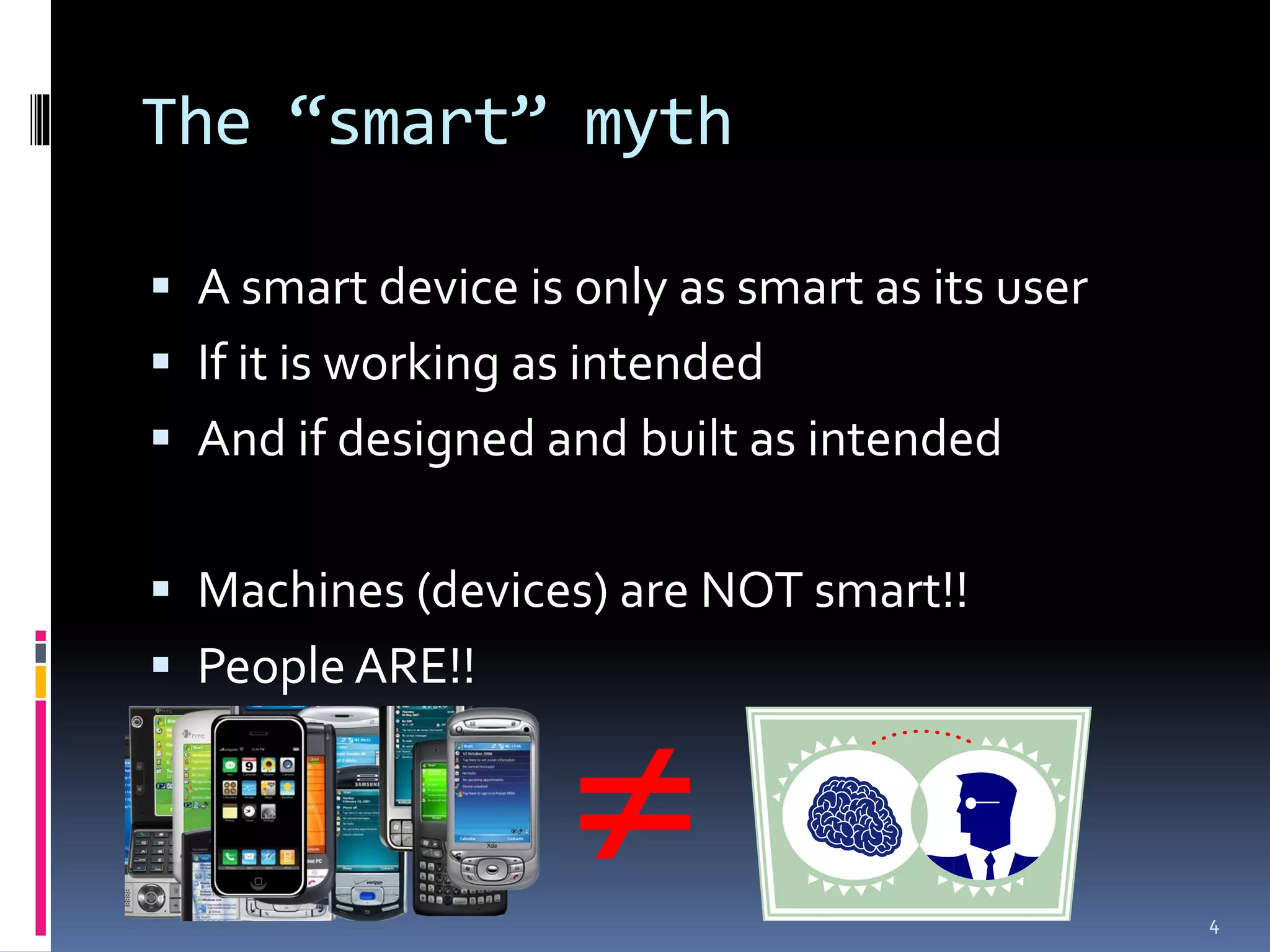
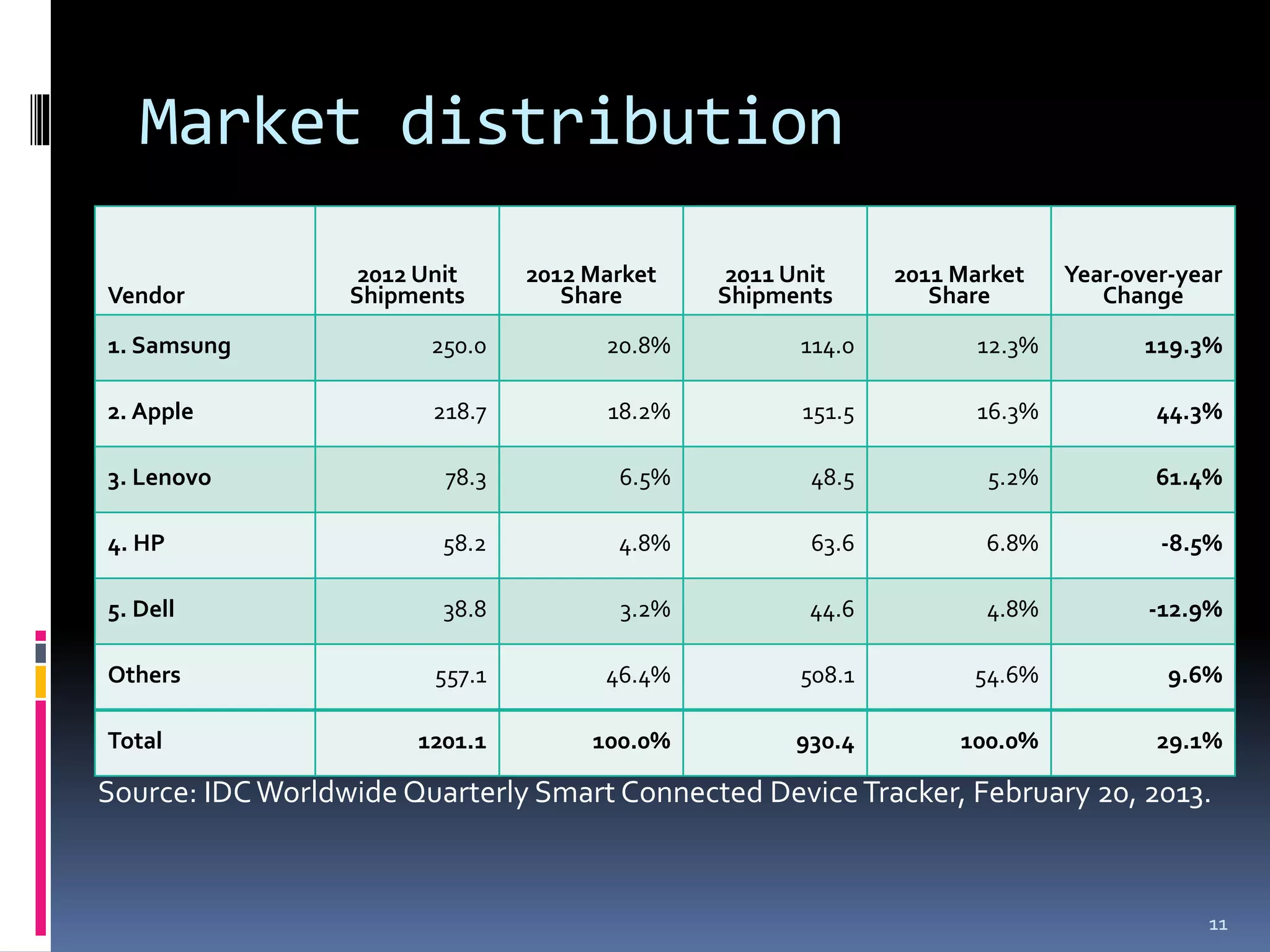
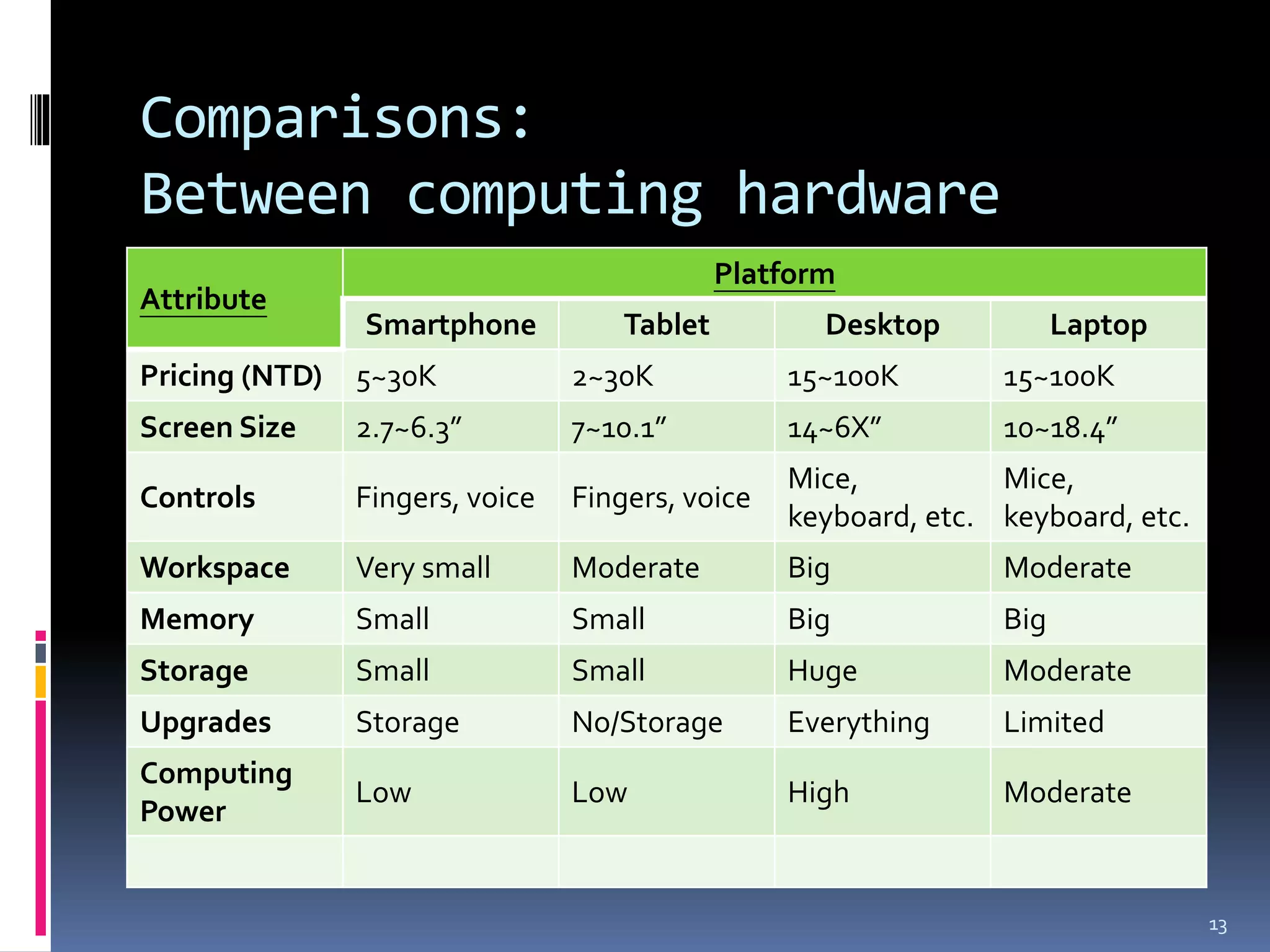
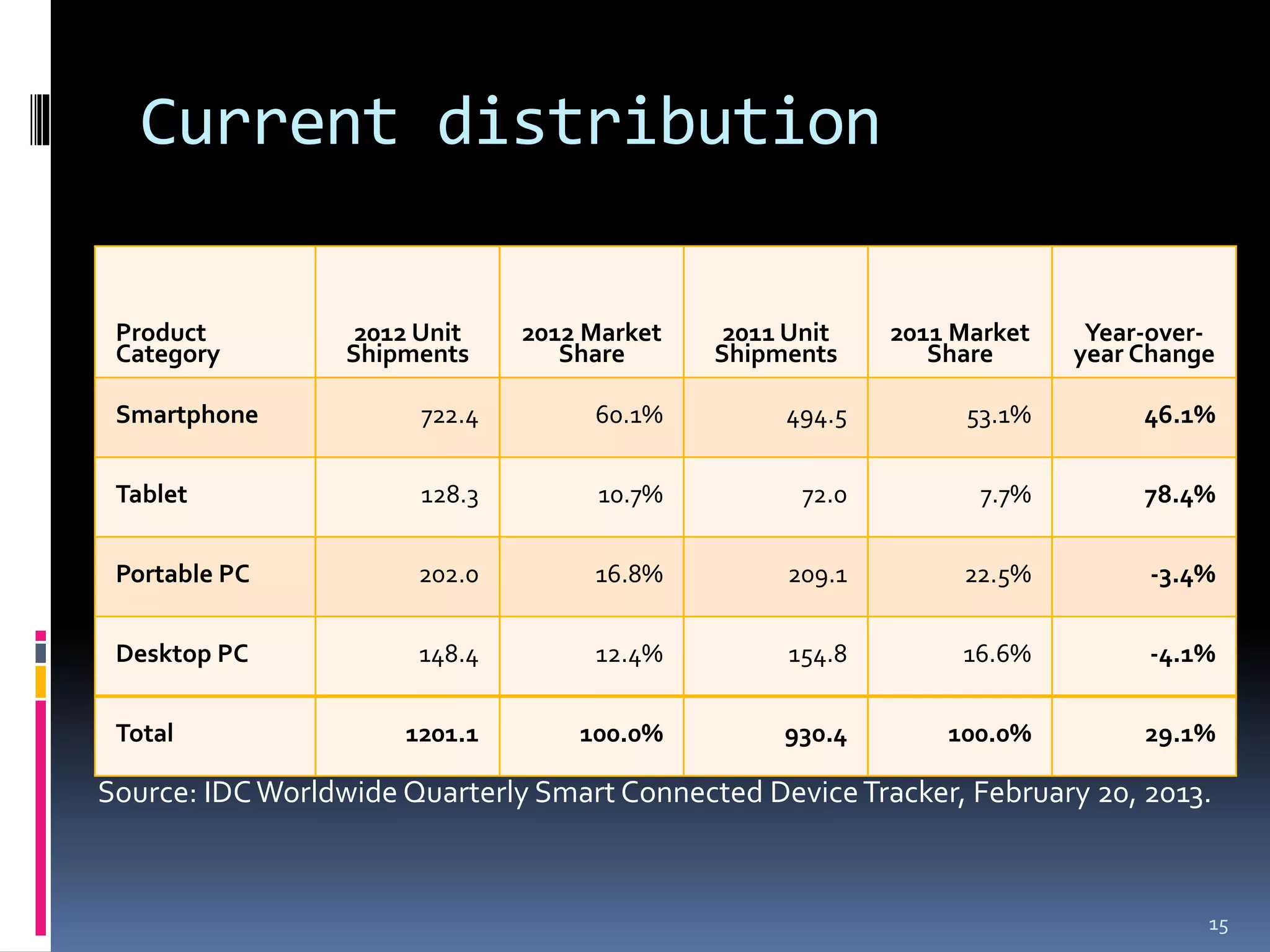
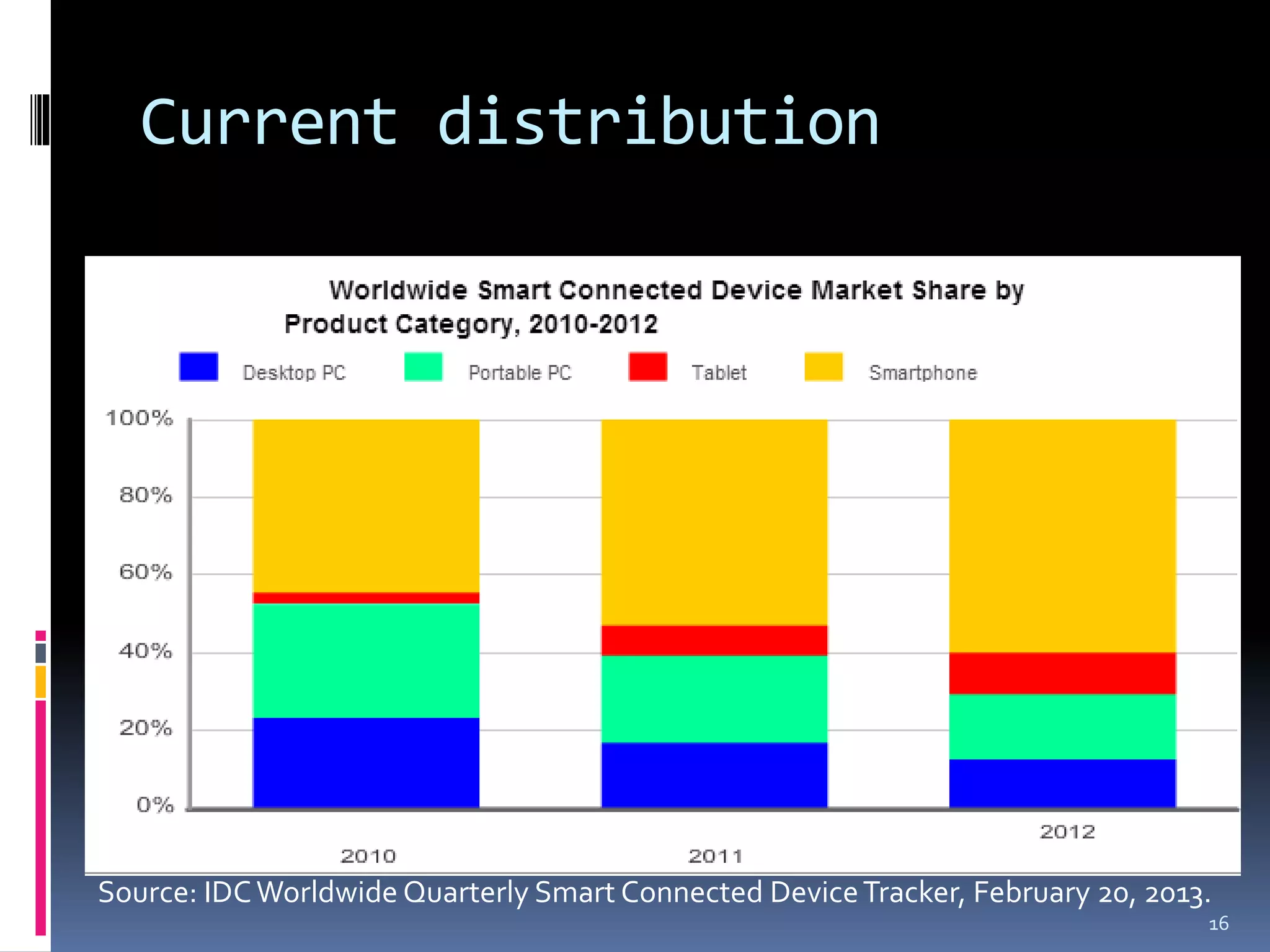
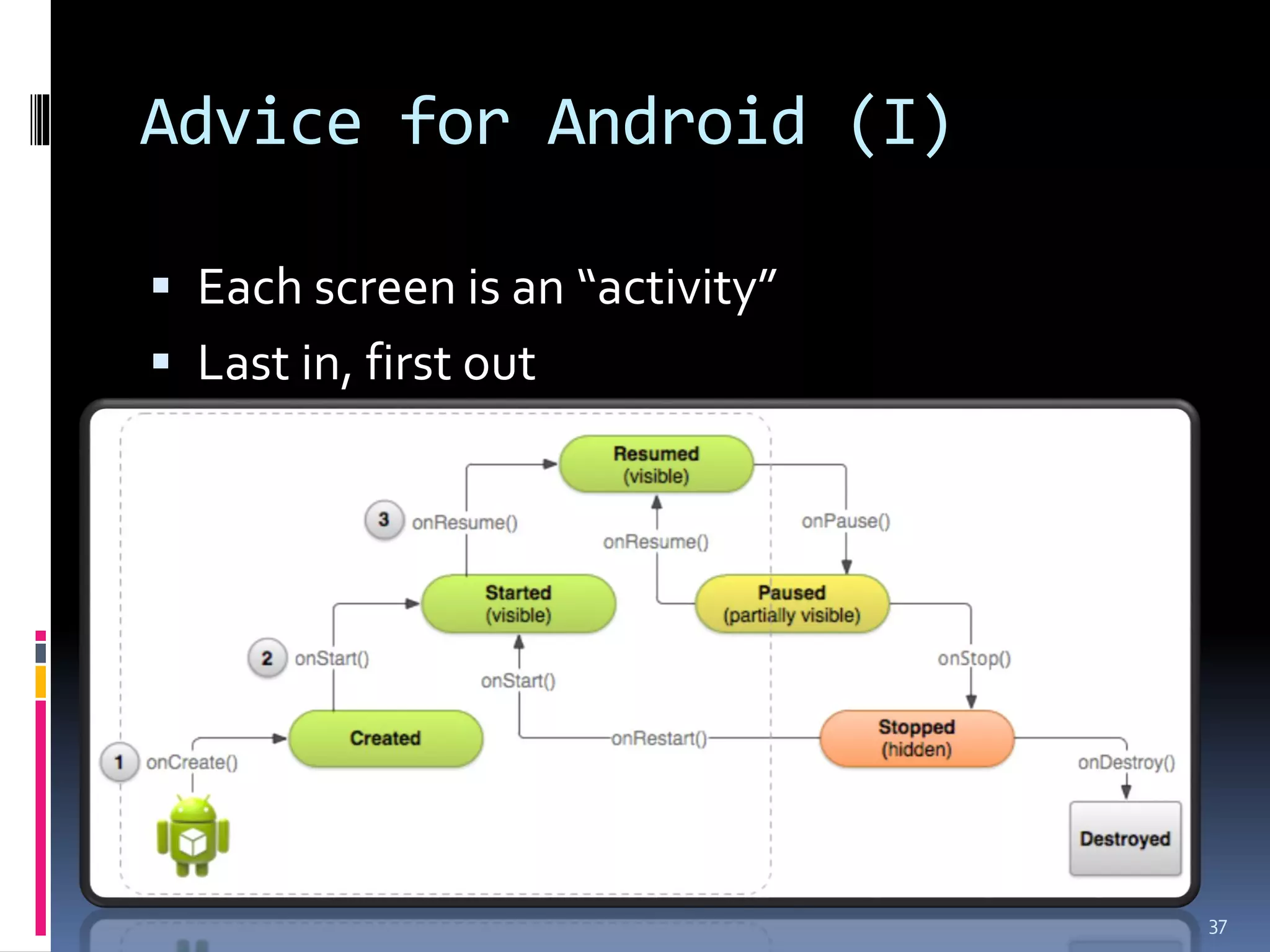
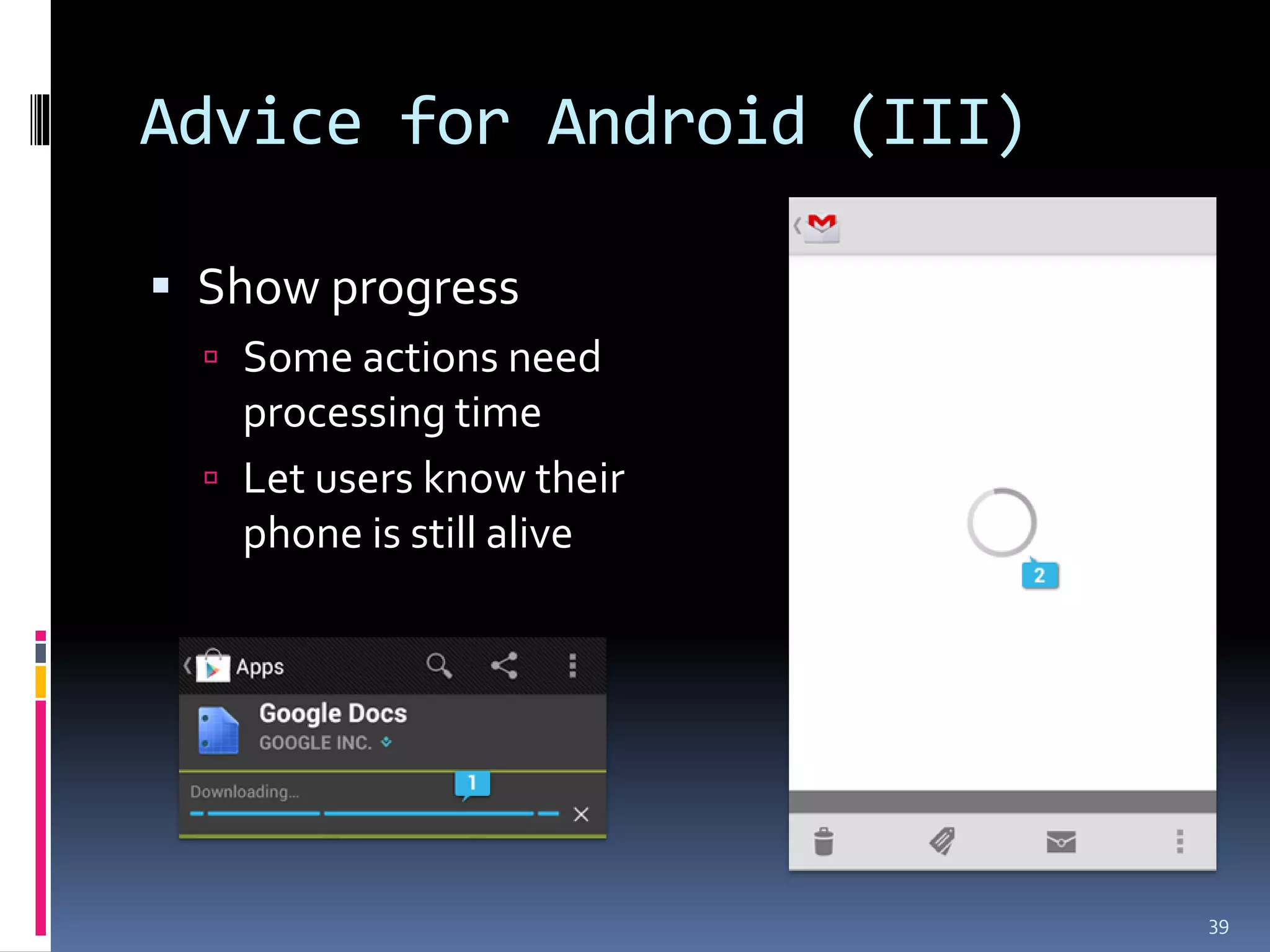
The document discusses smart platforms and provides advice for developing applications for them. It begins by debunking the myth that devices themselves are smart, noting that it is people who are smart. It then covers the history and evolution of smart platforms from early feature phones to today's smartphones and tablets. Market analysis shows smartphones now comprise over 60% of the market. Examples are given of education, health, and AR applications. General design advice includes keeping things simple, clear, and concise. Specific Android development tips include treating each screen as an activity and supporting different resolutions and orientations. In conclusion, smart platforms are powerful if used well but have limitations around resources, adoption, fragmentation, and monetization.