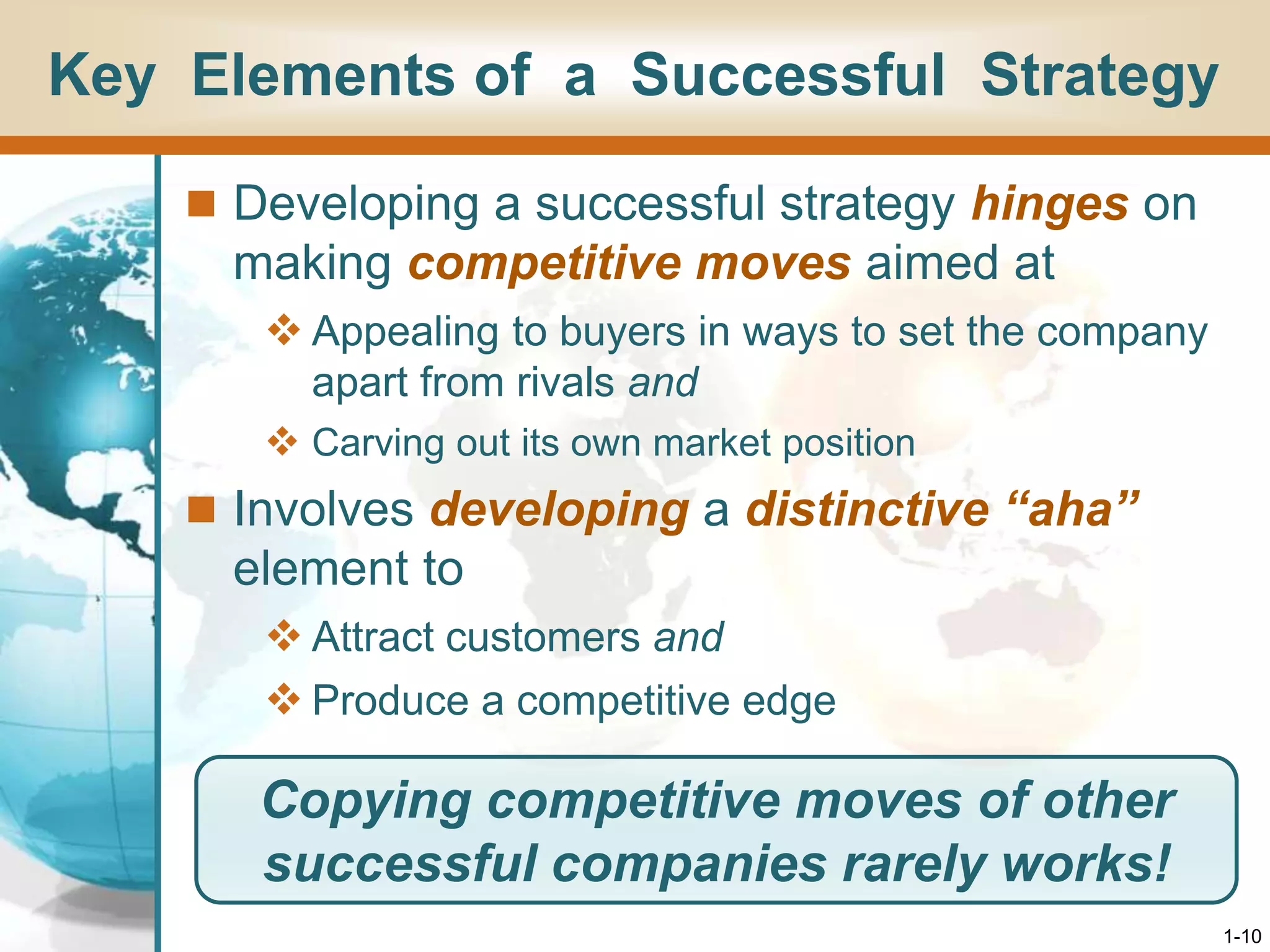
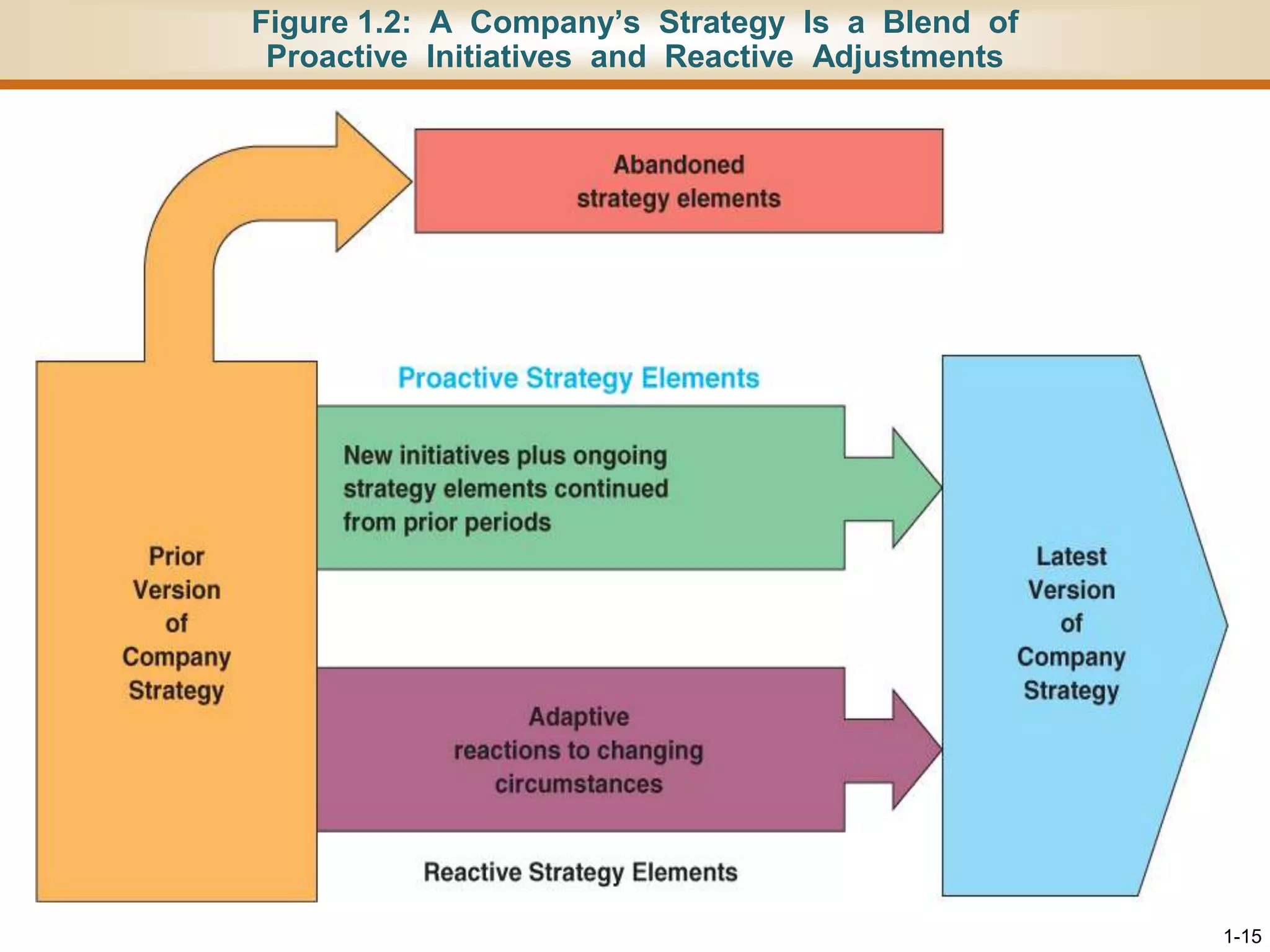
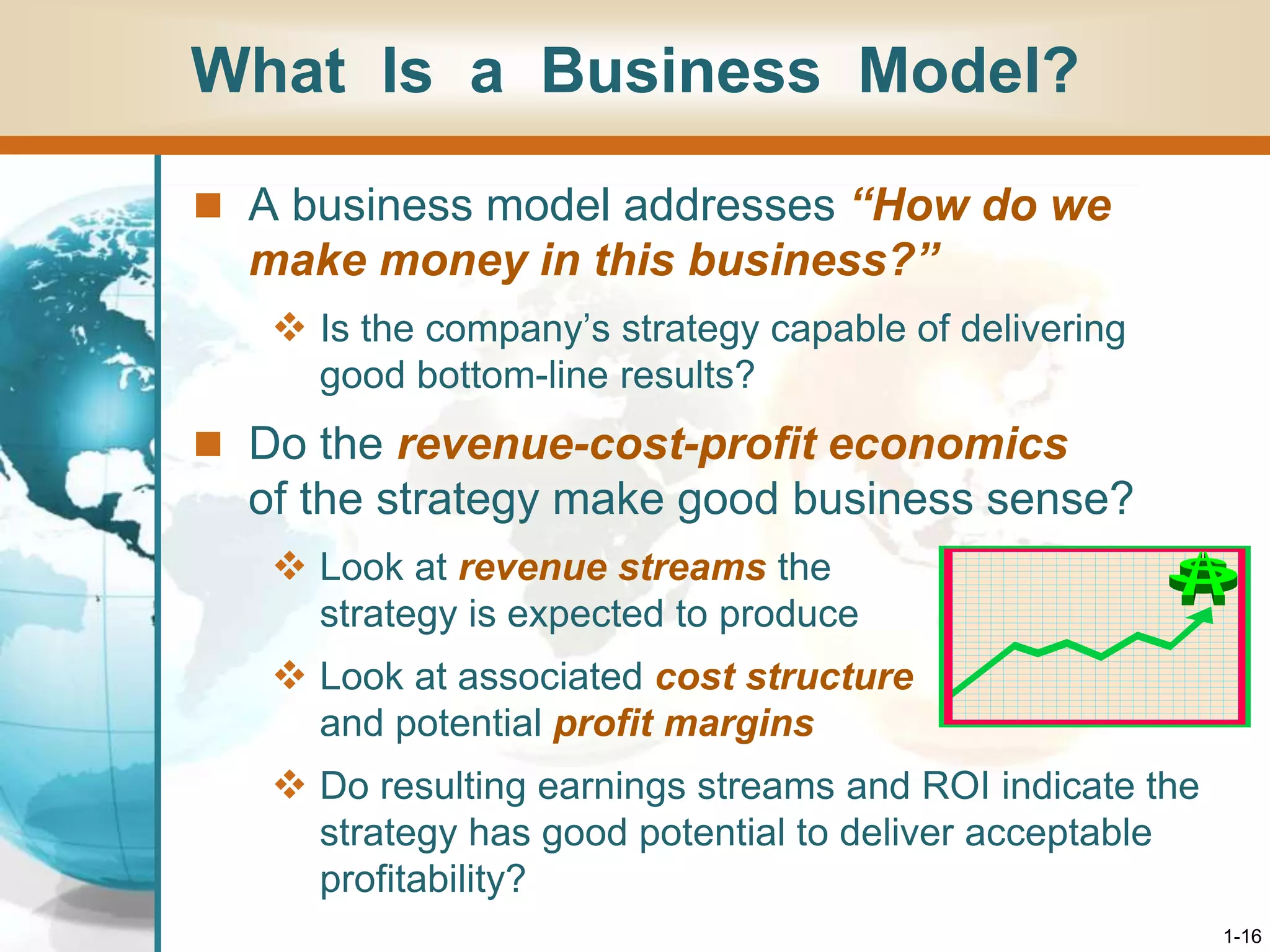
This document provides an overview of strategy and its importance for companies. It defines strategy as the set of actions managers take to outperform competitors and achieve superior profitability. Developing a successful strategy hinges on appealing to buyers in unique ways to gain a sustainable competitive advantage. A company's strategy evolves over time in response to changes in its environment or efforts to improve. For a strategy to be successful, it must fit the company's situation, provide a competitive advantage, and improve performance based on the business model's ability to be profitable. Good strategy development and execution are the most important management tasks and key signs of effective leadership.