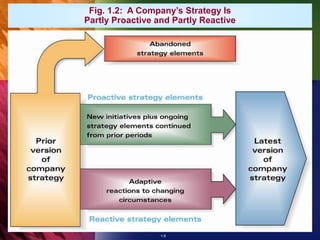
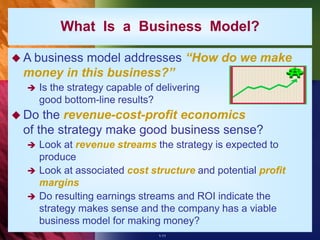
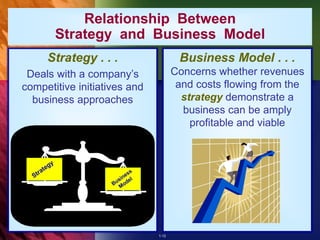
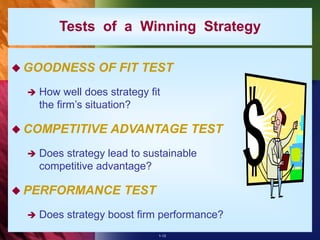
The document outlines the importance of strategy in a business context, defining strategy as a company's action plan to achieve competitive advantage and organizational performance. It emphasizes that effective strategies should evolve to respond to market changes and should align with ethical standards. Additionally, it notes the relationship between a business model and strategy, highlighting the necessity for strategies to be financially viable and to provide a sustainable competitive edge.