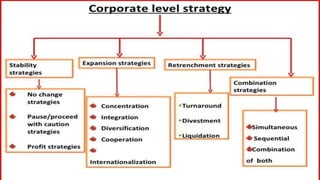
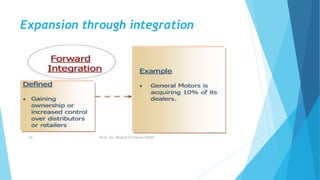
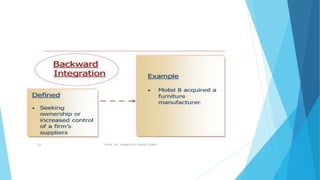
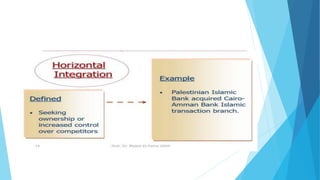
The document outlines various corporate-level strategies that organizations can employ, focusing on maximizing profitability and competitive advantage. It discusses different types of strategies, including stability, expansion, retrenchment, and combination strategies, detailing their subcategories and applications. It emphasizes the significance of conducting SWOT analyses to inform strategy formulation and make informed decisions in varying market conditions.