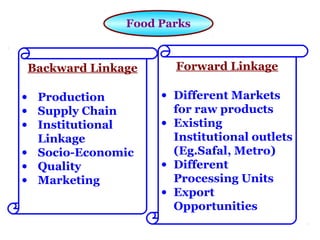
The document discusses food parks and related concepts:
1. Food parks are promoted by the Ministry of Food Processing Industries to encourage corporations to establish common facilities like cold storage and warehouses for small and medium food processing units.
2. They must be a minimum of 30 acres with at least 20 processing units. Grants of 25-33% of the project cost are provided. 20-25% of losses can be minimized through food parks.
3. The concept of backward and forward linkages in food supply chains is introduced.