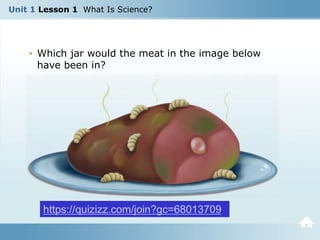
This document provides an introduction to the field of science. It explains that science involves making careful observations of the natural world and conducting investigations to understand natural phenomena. Scientists observe using their senses, compare similarities and differences, think critically about their results, and collect evidence to explain their observations. An example is given of Francesco Redi's experiment which showed that flies, not spontaneous generation, caused maggots to form. The document stresses that scientists draw conclusions based on evidence from repeated experiments, not opinions, and that scientific knowledge advances as findings are shared and built upon.