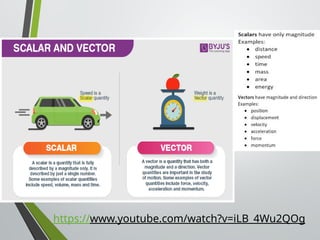
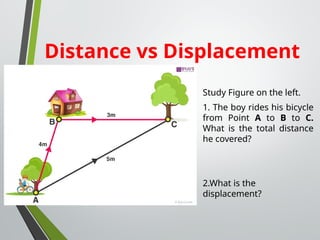
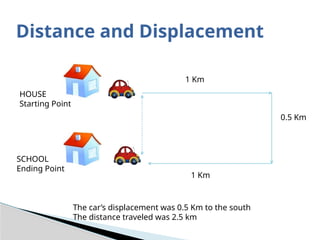
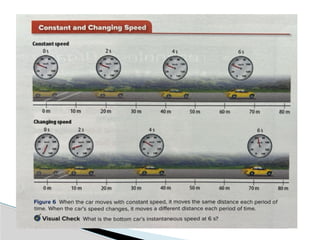
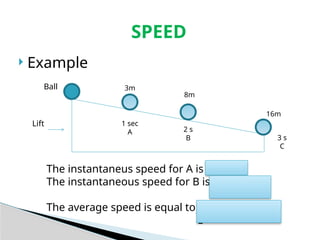
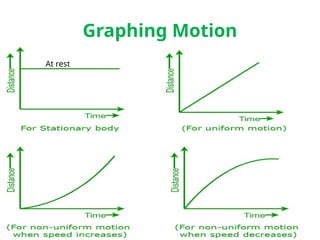
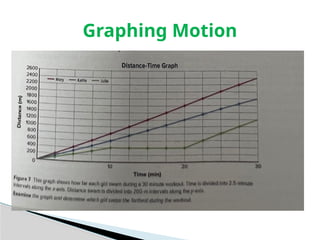
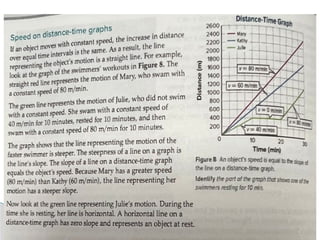
The document outlines concepts of motion, including position, reference points, distance, and displacement. It defines motion as a change in position relative to a reference point and distinguishes between distance as a scalar quantity and displacement as a vector quantity. Additionally, it discusses speed, including average and instantaneous speed, with examples to illustrate the calculations involved.