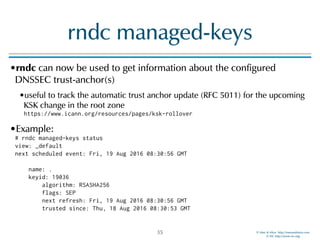
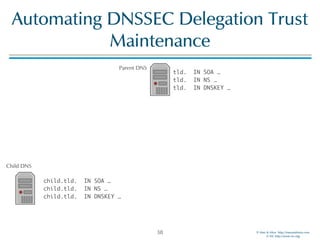
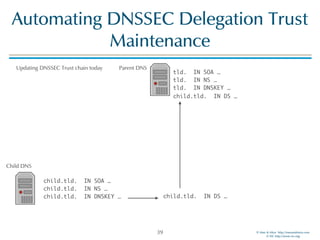
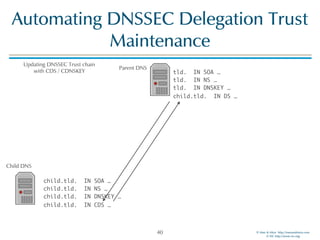
The document discusses updates in BIND 9.11, including licensing changes and new features like catalog zones, which allow DNS zones to be provisioned and maintained efficiently. It describes how catalog zones work by controlling metadata for secondary servers and integrates new functionalities for managing DNSSEC keys. Additionally, it highlights enhancements in configuration management using the rndc tool, enabling dynamic adjustments and secure operations.





![© Men & Mice http://menandmice.com
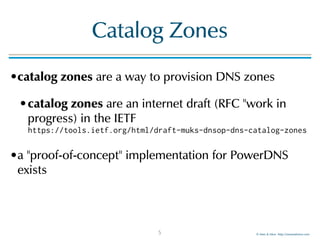
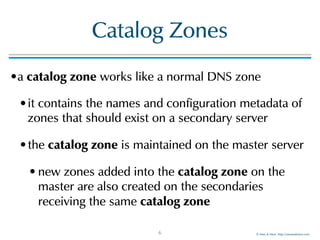
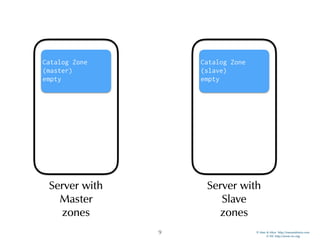
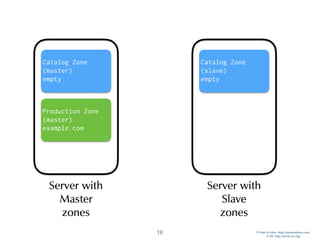
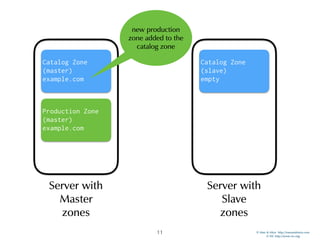
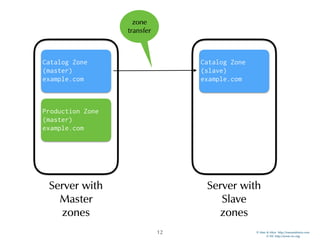
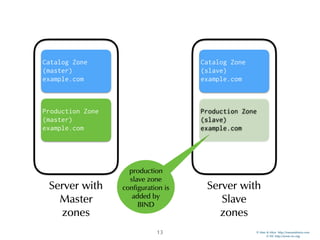
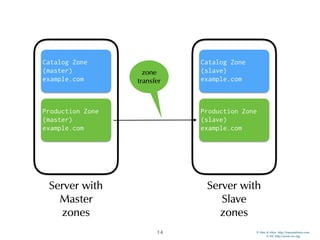
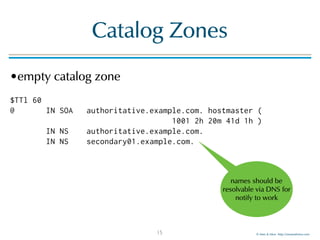
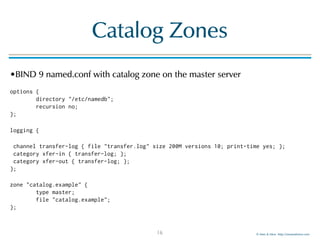
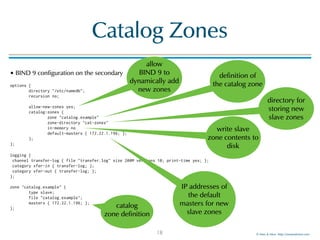
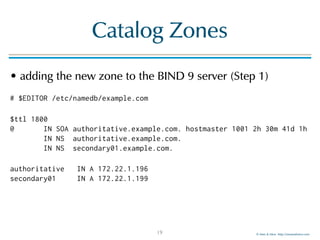
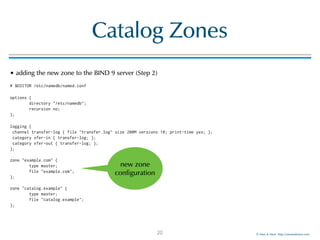
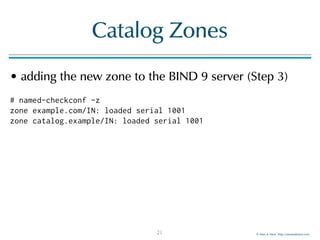
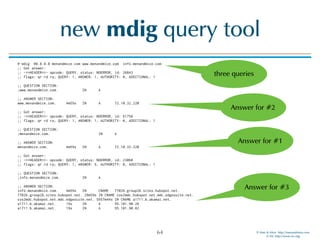
Catalog Zones
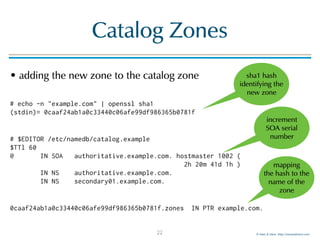
• BIND 9 log information shows the update of the
catalog zone followed by an transfer of the new zone:
named[157]: client 172.22.1.196#60914: received notify for zone 'catalog.example'
named[157]: zone catalog.example/IN: notify from 172.22.1.196#60914: serial 1002
named[157]: zone catalog.example/IN: Transfer started.
named[157]: catz: updating catalog zone 'catalog.example' with serial 1002
named[157]: zone catalog.example/IN: transferred serial 1002
named[157]: zone catalog.example/IN: sending notifies (serial 1002)
named[157]: catz: adding zone 'example.com' from catalog 'catalog.example' - success
named[157]: zone example.com/IN: Transfer started.
named[157]: zone example.com/IN: transferred serial 1001
named[157]: zone example.com/IN: sending notifies (serial 1001)
23
new
zone is now
available on the
secondary](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bind911-160830041205/85/What-is-new-in-BIND-9-11-23-320.jpg)

















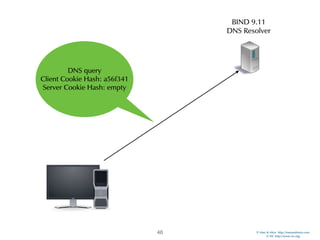
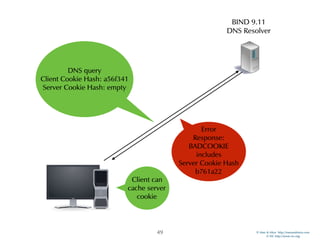
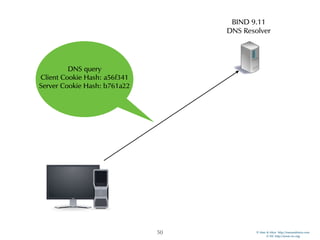
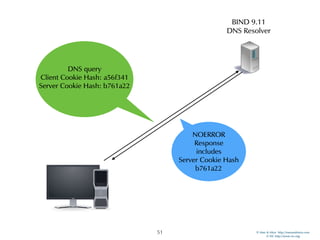




![© Men & Mice http://menandmice.com
© ISC http://www.isc.org
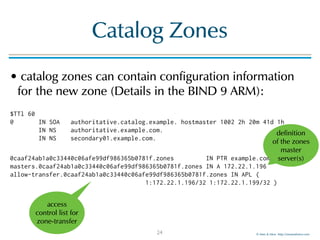
Minimal ANY
•a BIND 9 server getting an query with type ANY
(QTYPE 255) will answer with all records matching
the requested domain name and class
•this can create large UDP DNS answer packets
;; QUESTION SECTION:
;menandmice.com. IN ANY
;; ANSWER SECTION:
menandmice.com. 86400 IN SOA dns1.menandmice.com. hostmaster.menandmice.com. 2016052701 900 300 604800 900
menandmice.com. 3600 IN TXT "HhnTdT3K"
menandmice.com. 3600 IN TXT "MS=ms81797768"
menandmice.com. 3600 IN TXT "v=spf1 include:spf.protection.outlook.com a:smtp.menandmice.is a:support.menandmice.com a:otrs.menandmice.com
a:imap2.skyrr.is a:mx.hysing.is ~all"
ns2.c.is. 84985 IN A 213.176.143.102
dns1.menandmice.com. 171385 IN A 217.151.171.7
dns2.menandmice.com. 171385 IN A 217.151.171.21
dns3.menandmice.com. 171385 IN A 45.79.153.125
[…]
;; Query time: 97 msec
;; SERVER: 127.0.0.1#53(127.0.0.1)
;; WHEN: Mon Aug 15 10:49:15 CEST 2016
;; MSG SIZE rcvd: 719
57
DNS
answer
size](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bind911-160830041205/85/What-is-new-in-BIND-9-11-57-320.jpg)






![© Men & Mice http://menandmice.com
© ISC http://www.isc.org
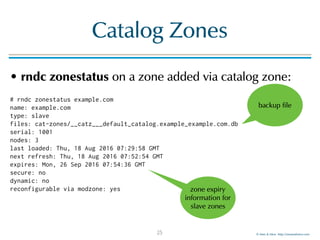
dig switches
dig +ttlunits causes dig to print TTL values with time-unit suffixes: w, d, h, m, s for weeks, days, hours,
minutes, and seconds:
# dig +ttlunits menandmice.com
; <<>> DiG 9.11.0b3 <<>> +ttlunits menandmice.com
;; global options: +cmd
;; Got answer:
[…]
;; ANSWER SECTION:
menandmice.com. 4m54s IN A 72.10.32.220
;; AUTHORITY SECTION:
menandmice.com. 20h52m59s IN NS ns2.c.is.
menandmice.com. 20h52m59s IN NS dns1.menandmice.com.
menandmice.com. 20h52m59s IN NS ns0.c.is.
menandmice.com. 20h52m59s IN NS dns3.menandmice.com.
menandmice.com. 20h52m59s IN NS ns1.c.is.
menandmice.com. 20h52m59s IN NS dns2.menandmice.com.
;; ADDITIONAL SECTION:
dns1.menandmice.com. 21h9m22s IN A 217.151.171.7
dns2.menandmice.com. 20h52m59s IN A 217.151.171.21
dns3.menandmice.com. 1h29m39s IN A 45.79.153.125
65](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bind911-160830041205/85/What-is-new-in-BIND-9-11-65-320.jpg)
![© Men & Mice http://menandmice.com
© ISC http://www.isc.org
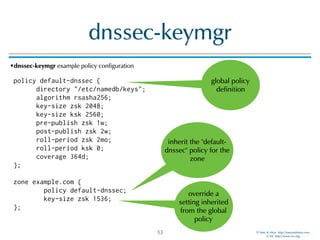
multiple named processes
# named -g
18-Aug-2016 13:31:16.929 starting BIND 9.11.0b3 <id:a23f742>
18-Aug-2016 13:31:16.929 running on Linux x86_64 4.6.6-300.fc24.x86_64 #1 SMP Wed Aug 10 21:07:35 UTC 2016
18-Aug-2016 13:31:16.929 built with '--sysconfdir=/etc/namedb'
18-Aug-2016 13:31:16.929 running as: named -g
18-Aug-2016 13:31:16.929 ----------------------------------------------------
18-Aug-2016 13:31:16.929 BIND 9 is maintained by Internet Systems Consortium,
18-Aug-2016 13:31:16.929 Inc. (ISC), a non-profit 501(c)(3) public-benefit
18-Aug-2016 13:31:16.929 corporation. Support and training for BIND 9 are
18-Aug-2016 13:31:16.929 available at https://www.isc.org/support
18-Aug-2016 13:31:16.929 ----------------------------------------------------
18-Aug-2016 13:31:16.929 adjusted limit on open files from 65536 to 1048576
18-Aug-2016 13:31:16.929 found 4 CPUs, using 4 worker threads
18-Aug-2016 13:31:16.929 using 3 UDP listeners per interface
18-Aug-2016 13:31:16.929 using up to 4096 sockets
18-Aug-2016 13:31:16.938 loading configuration from '/etc/namedb/named.conf'
18-Aug-2016 13:31:16.939 reading built-in trusted keys from file '/etc/namedb/bind.keys'
18-Aug-2016 13:31:16.939 using default UDP/IPv4 port range: [32768, 60999]
18-Aug-2016 13:31:16.939 using default UDP/IPv6 port range: [32768, 60999]
18-Aug-2016 13:31:16.941 listening on IPv6 interfaces, port 53
18-Aug-2016 13:31:16.948 binding TCP socket: address in use
18-Aug-2016 13:31:16.948 listening on IPv4 interface lo, 127.0.0.1#53
18-Aug-2016 13:31:16.949 binding TCP socket: address in use
18-Aug-2016 13:31:16.949 listening on IPv4 interface mv-p3p1, 172.22.1.129#53
18-Aug-2016 13:31:16.950 binding TCP socket: address in use
18-Aug-2016 13:31:16.950 unable to listen on any configured interfaces
18-Aug-2016 13:31:16.950 loading configuration: failure
18-Aug-2016 13:31:16.950 exiting (due to fatal error)
67](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bind911-160830041205/85/What-is-new-in-BIND-9-11-67-320.jpg)




