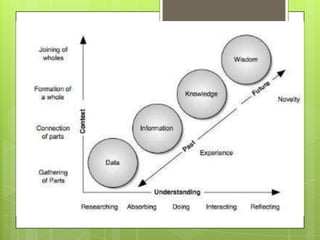
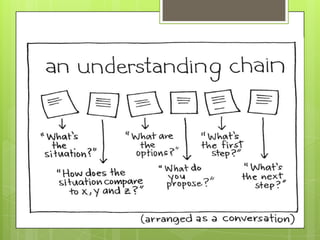
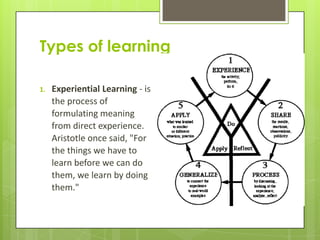
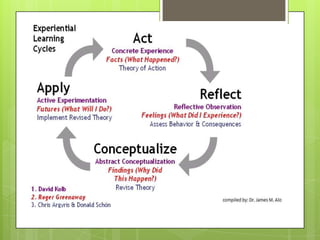
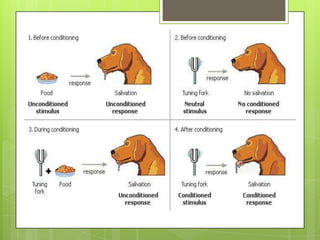
Learning involves acquiring new knowledge, behaviors, skills, values, and understanding through various methods. There are many types of learning including experiential learning through direct experience, associative learning by forming connections between elements, observational learning through imitation, and informal learning from everyday situations. Learning also involves different domains such as cognitive learning of facts, psychomotor learning of physical skills, and affective learning of values and preferences.