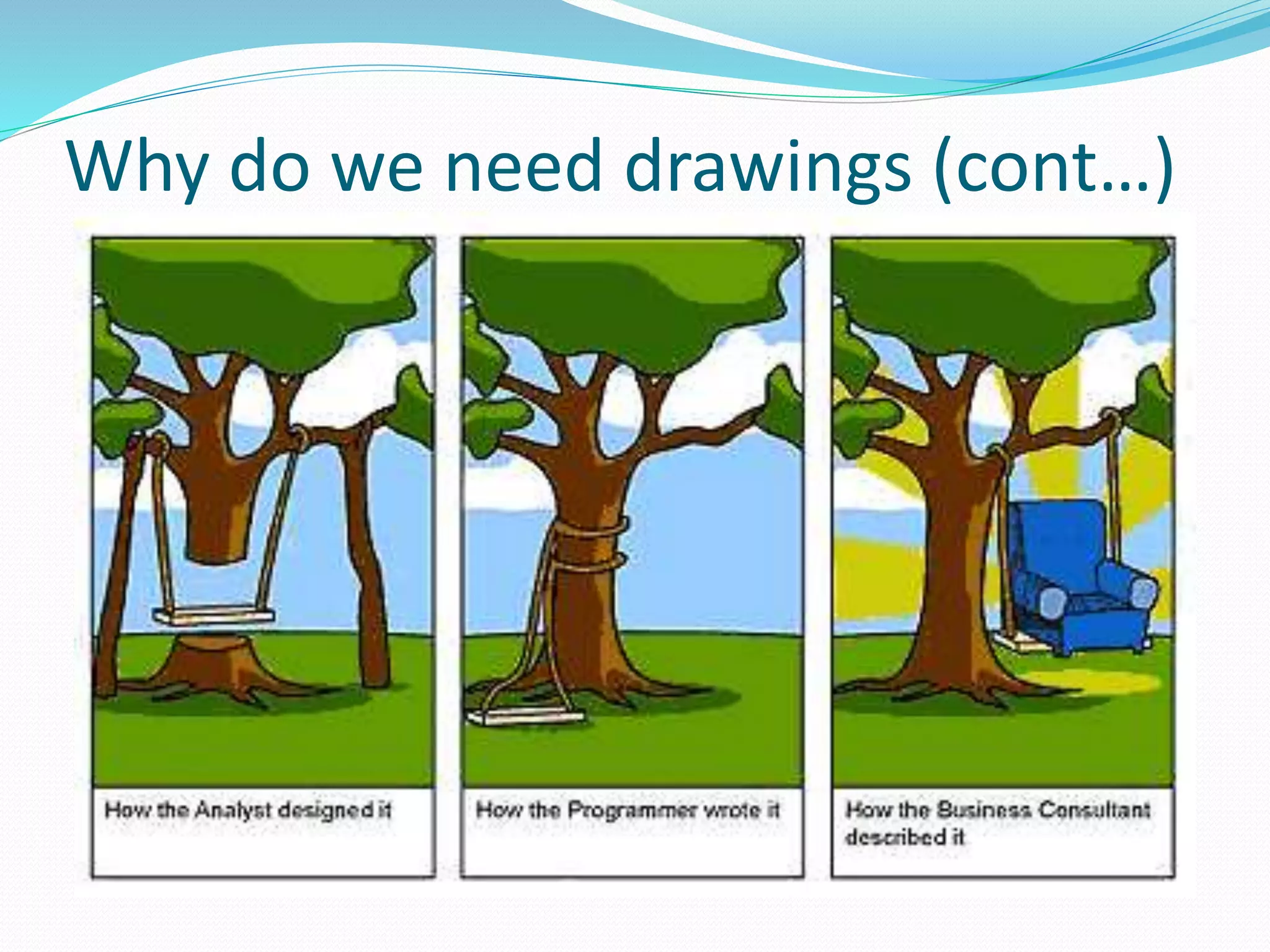
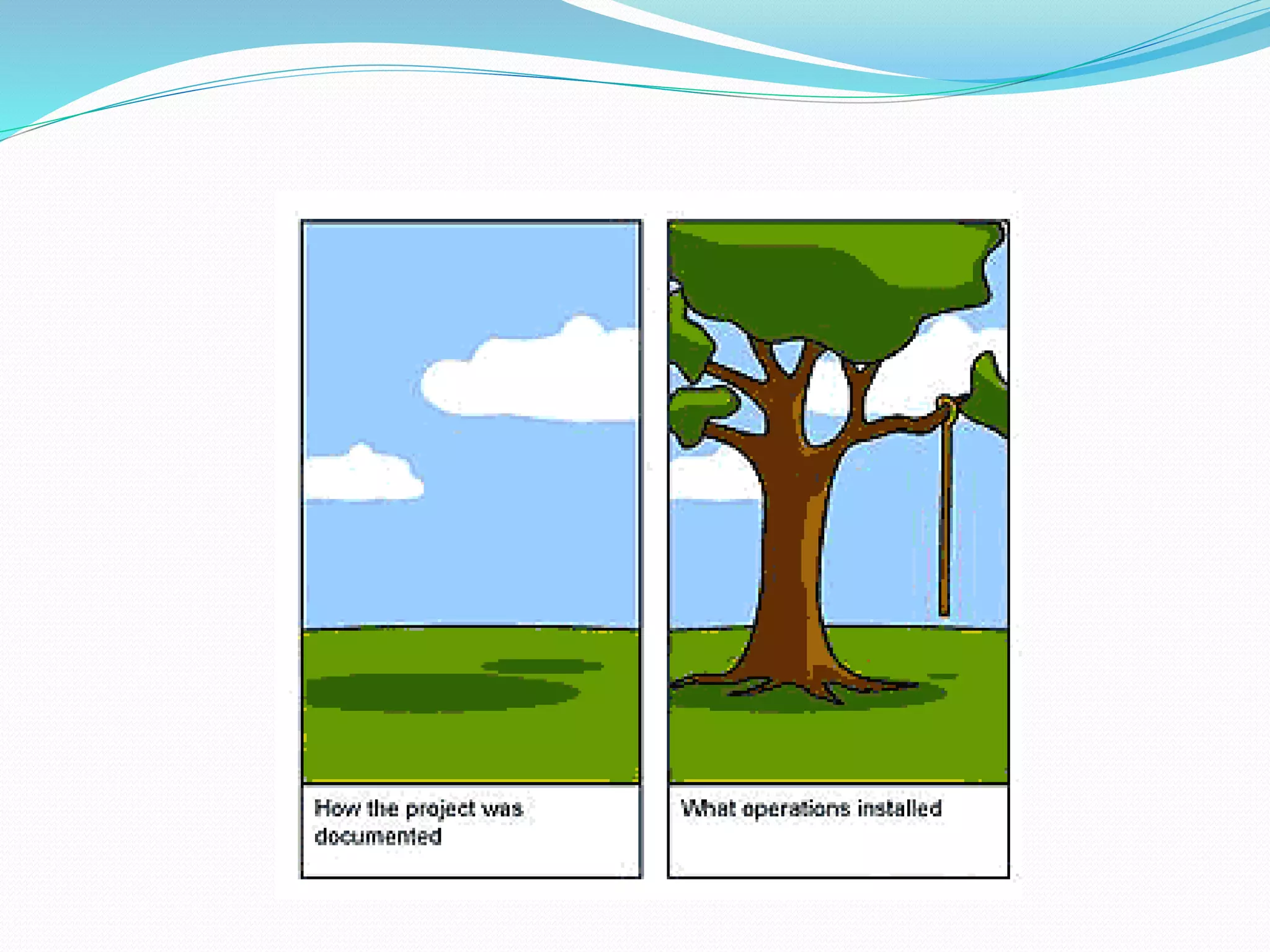
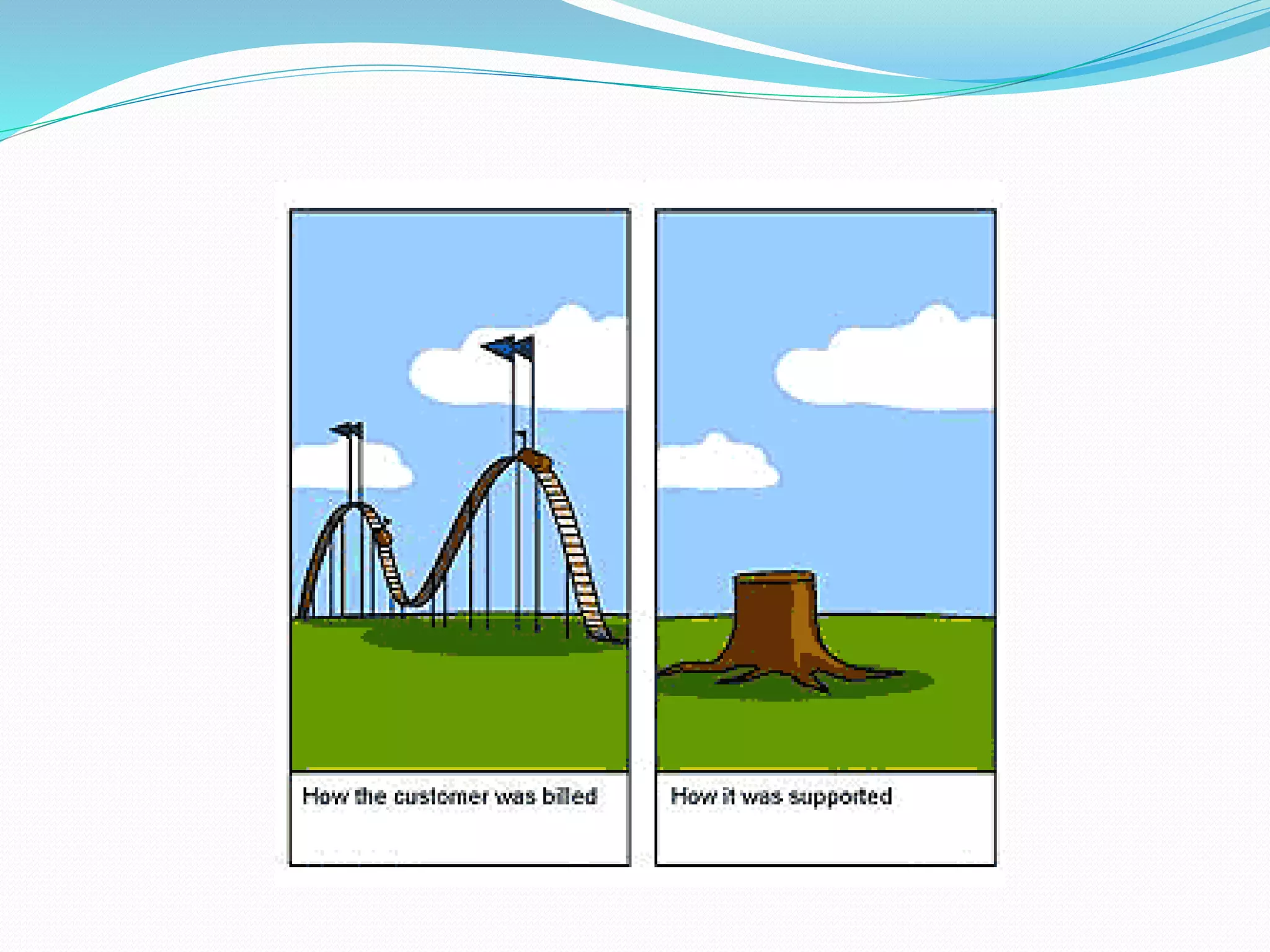
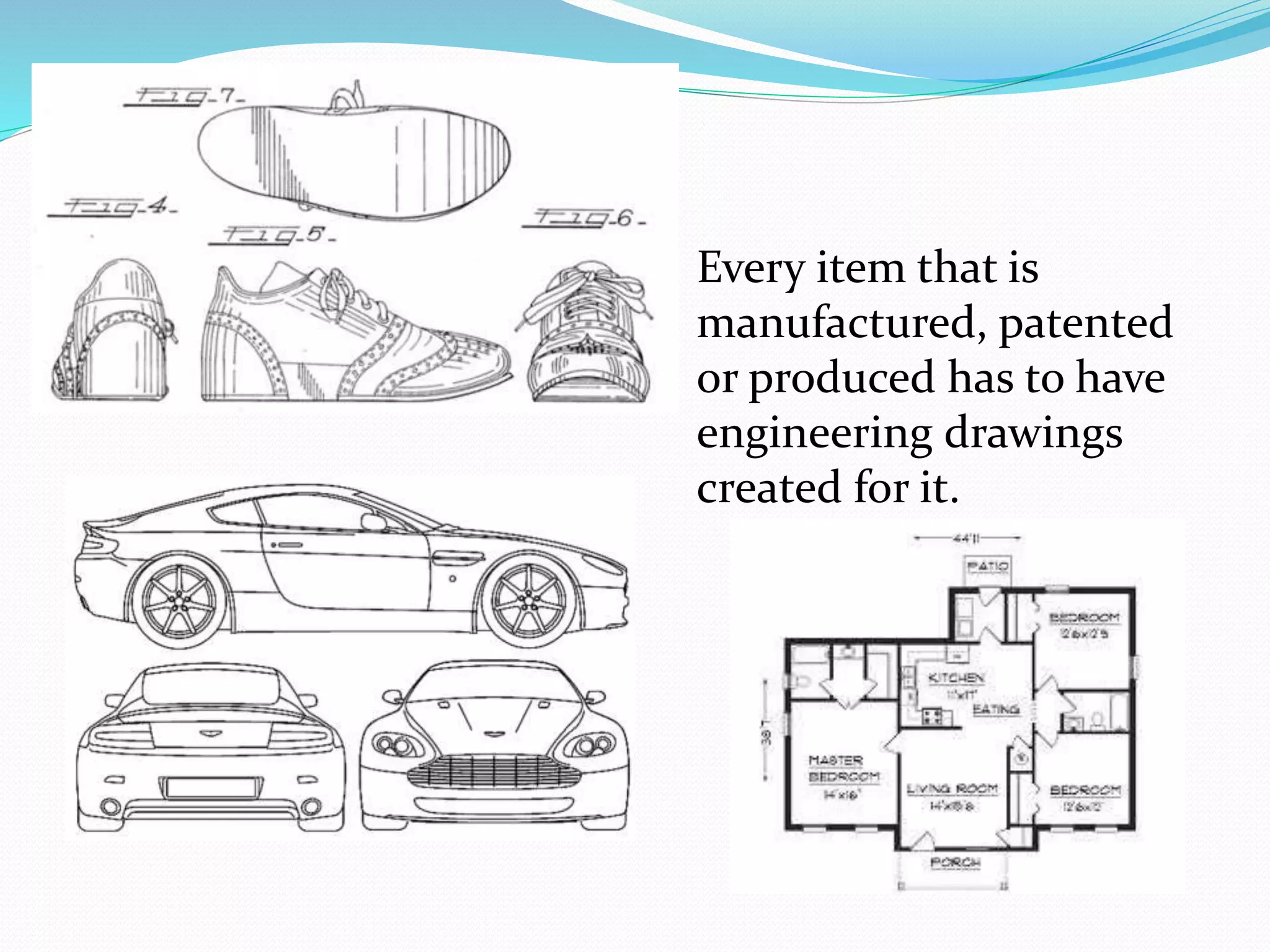
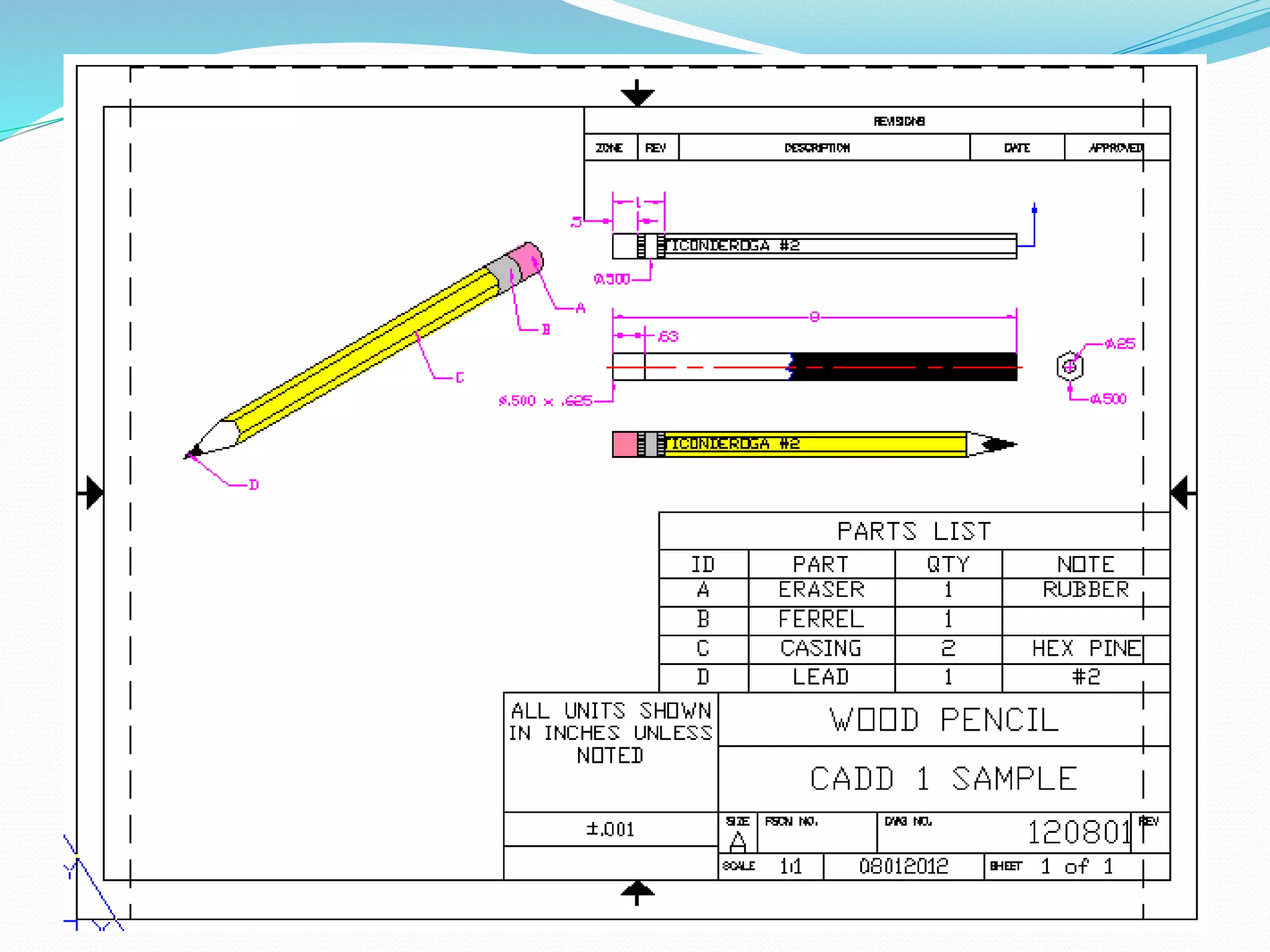
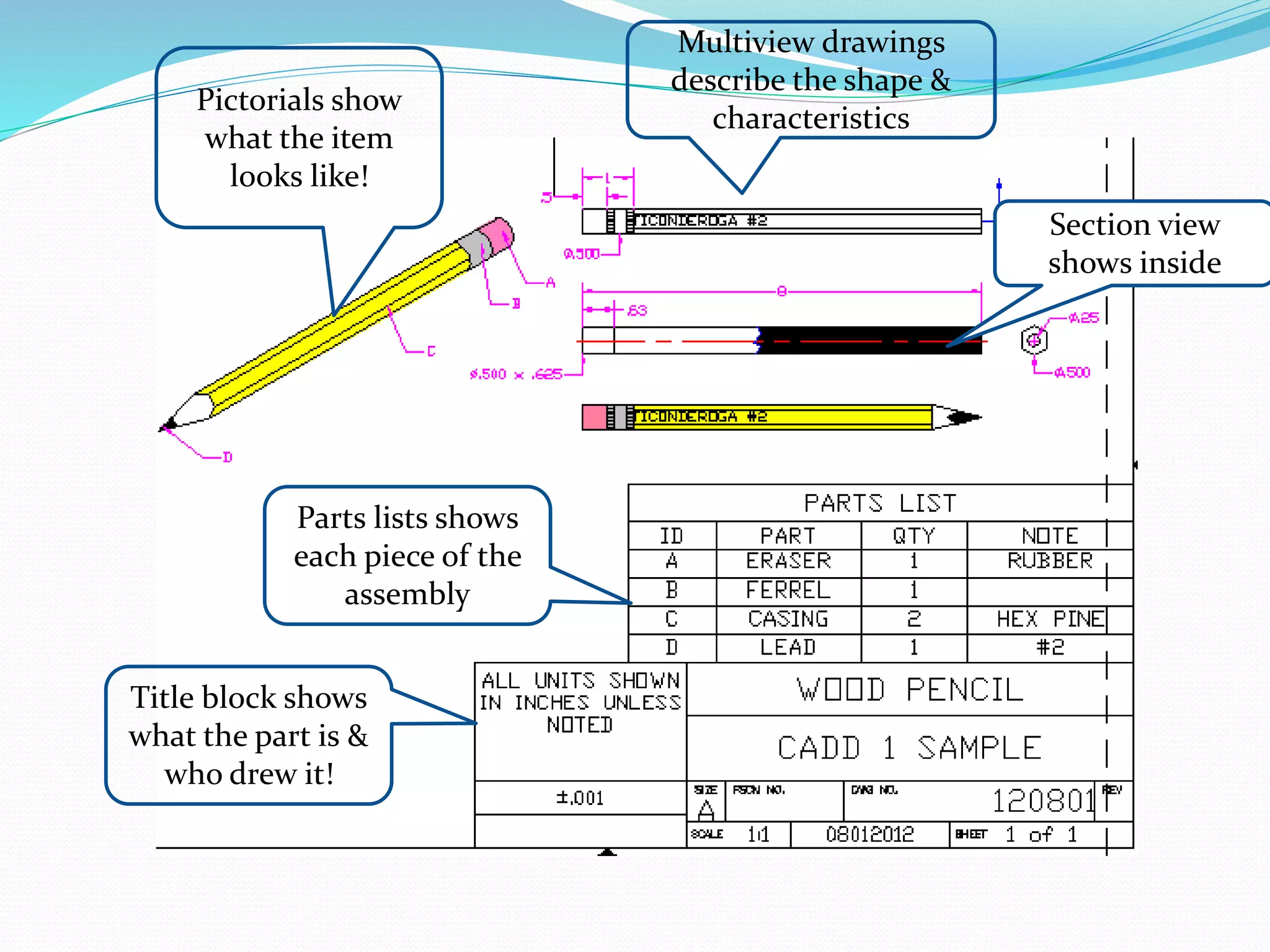
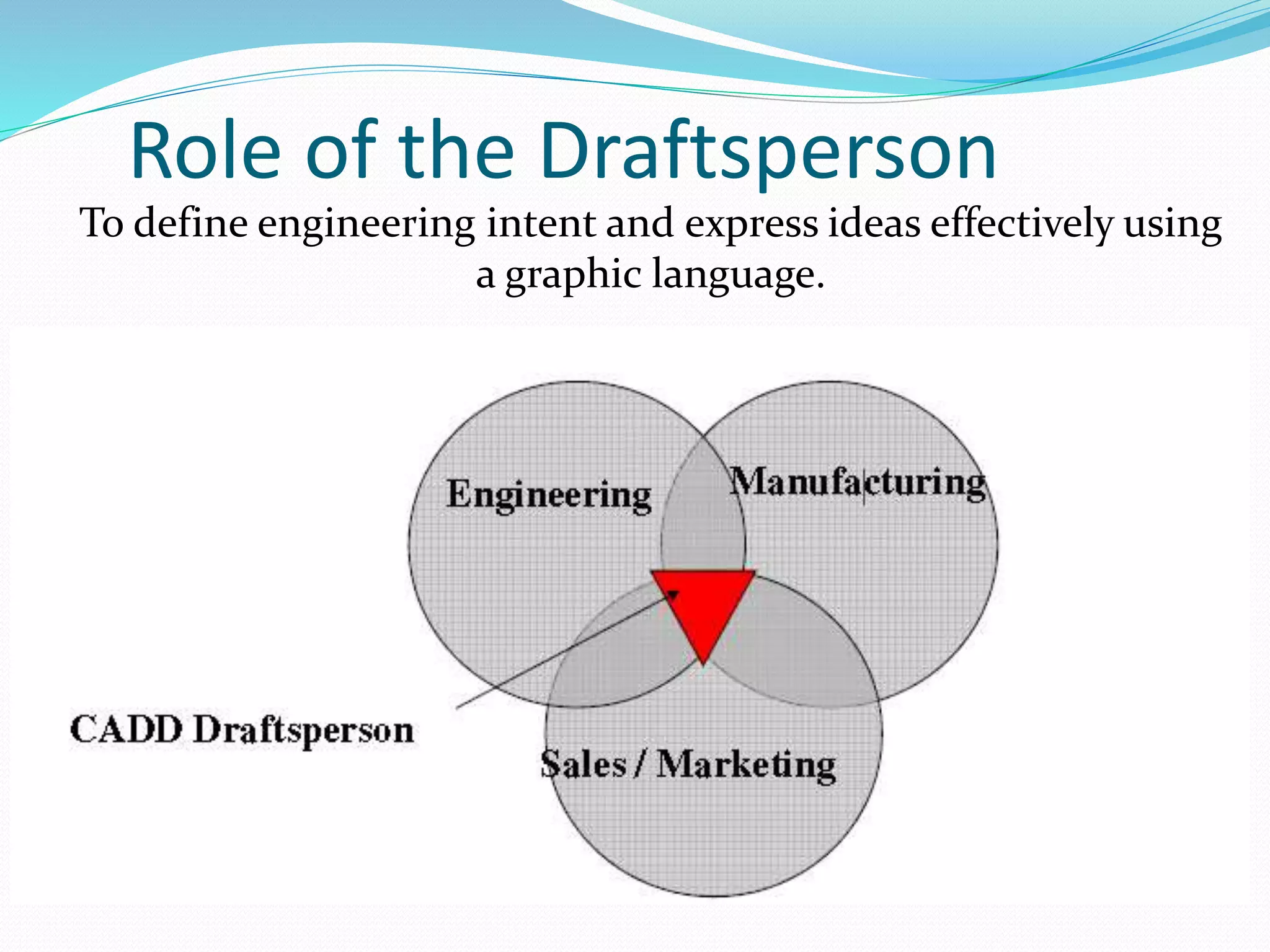
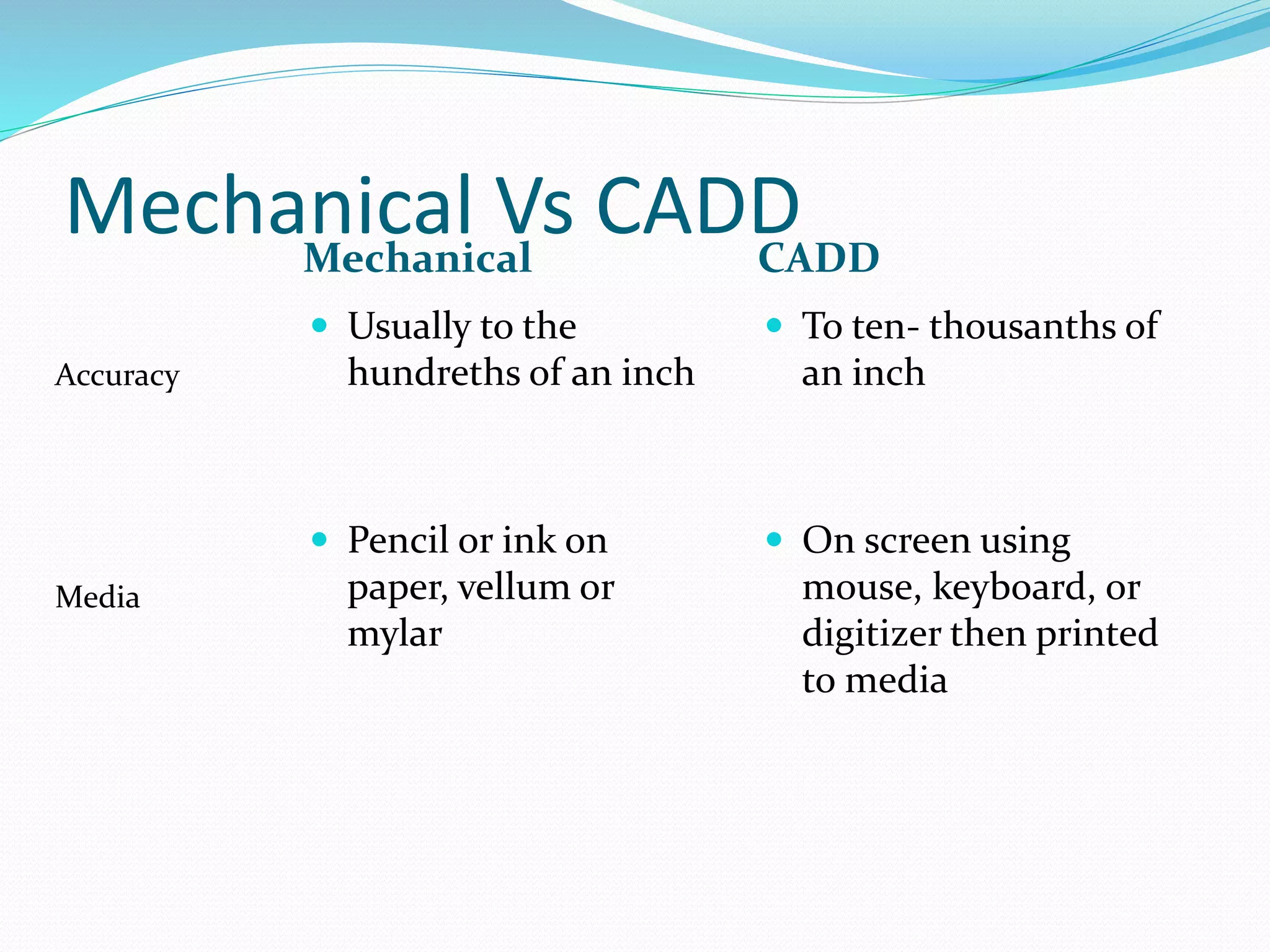
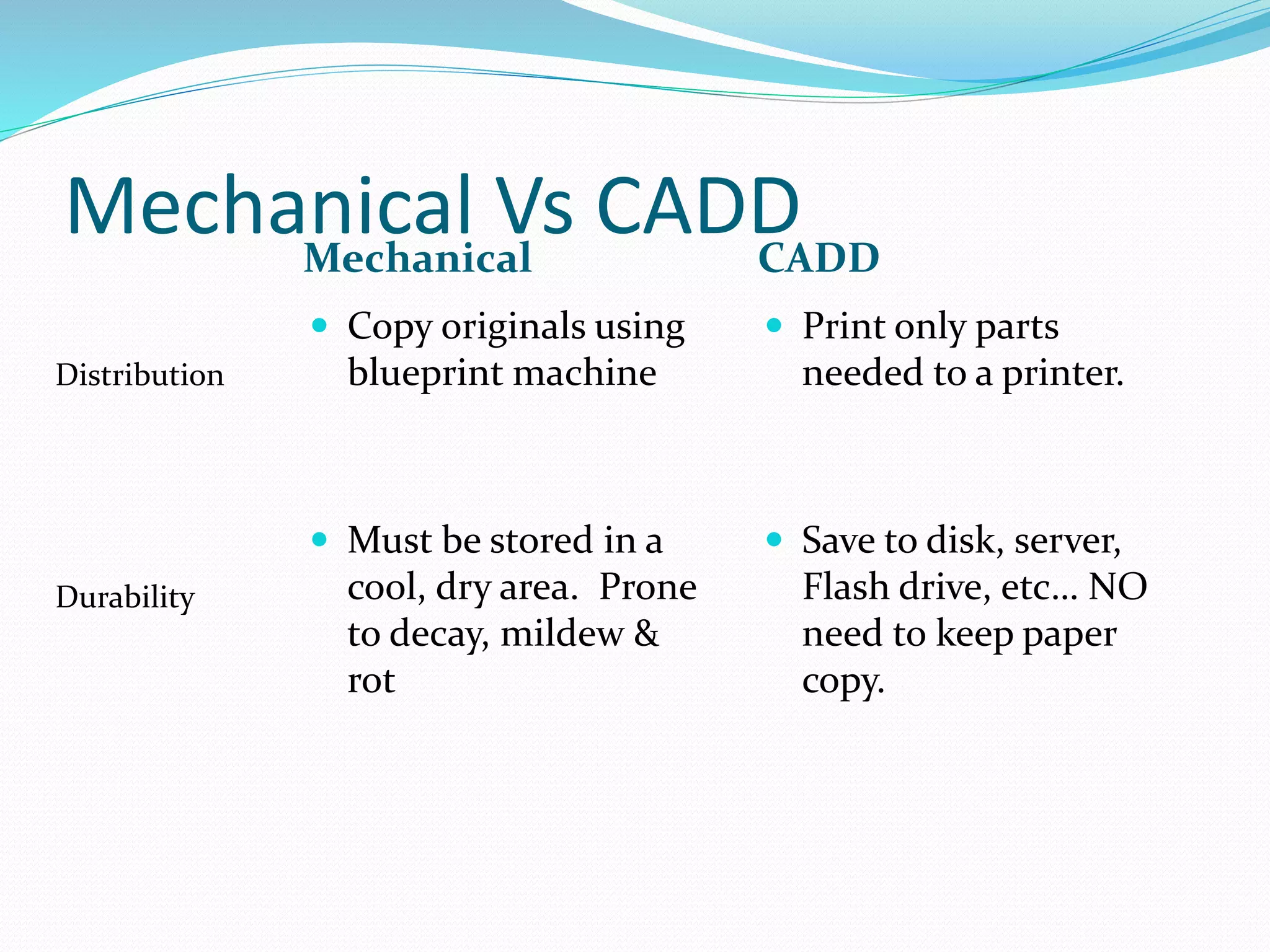
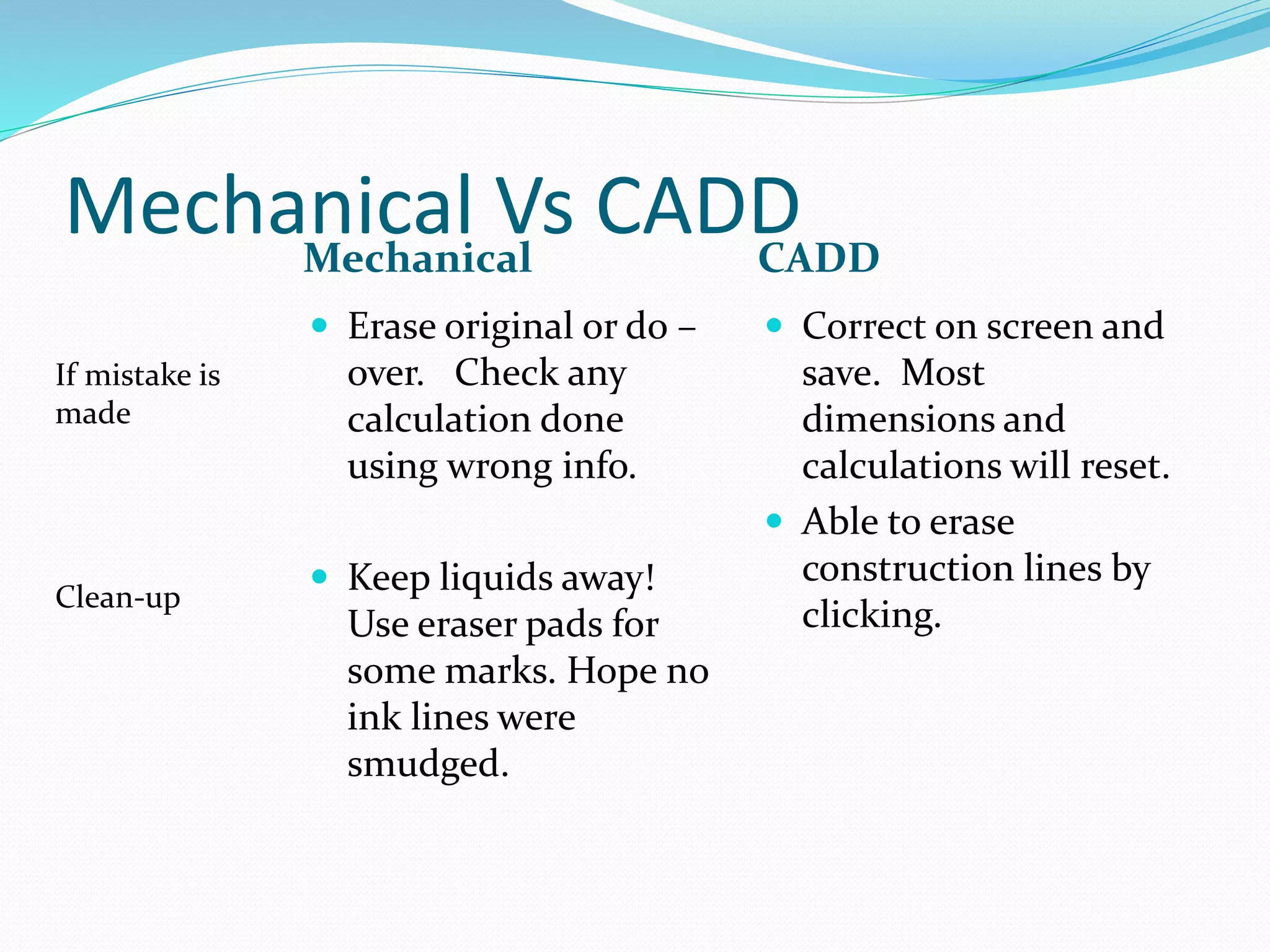
This document discusses the importance and uses of technical drawings. It explains that drawings are used to represent manufactured items and are a universal language for conveying design information. The document outlines different types of drawings, including multiview, pictorial, and section drawings. It also compares manual and computer-aided drafting, noting advantages like speed and accuracy with CAD. Key applications of drawings in fields like construction, manufacturing, and engineering are also highlighted. Finally, it emphasizes that drawings must be detailed, annotated, and drawn clearly to effectively communicate design specifications.