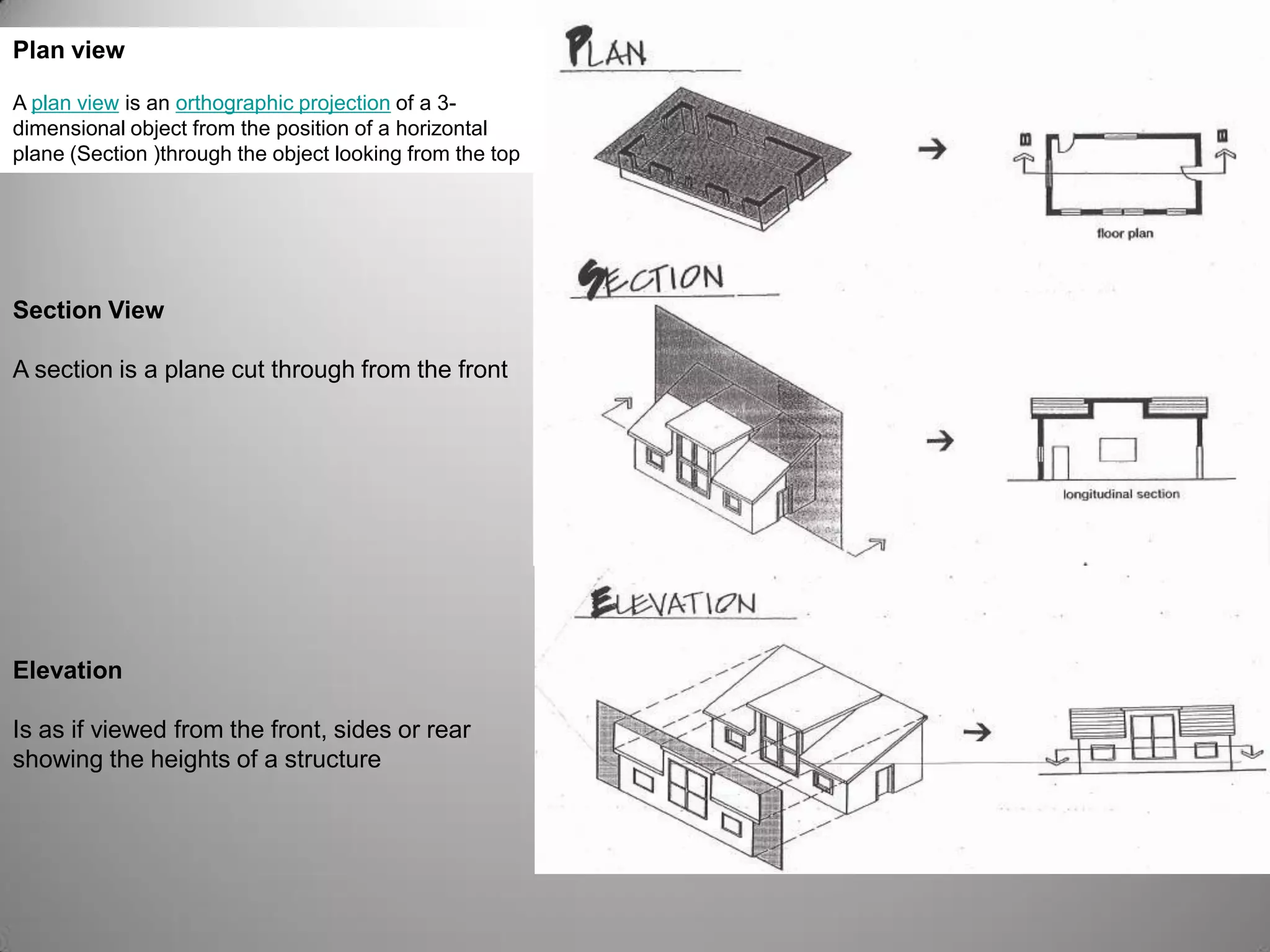
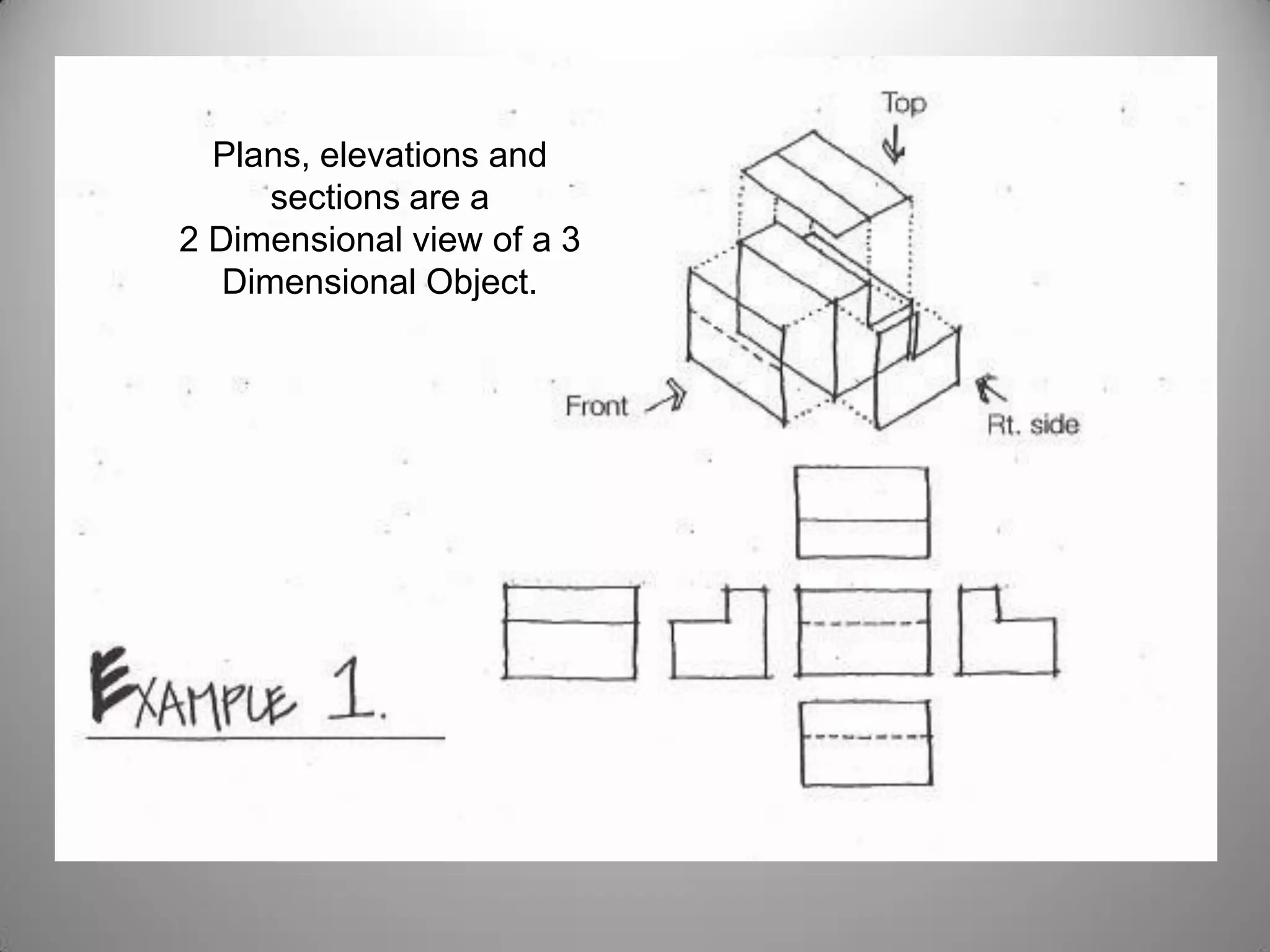
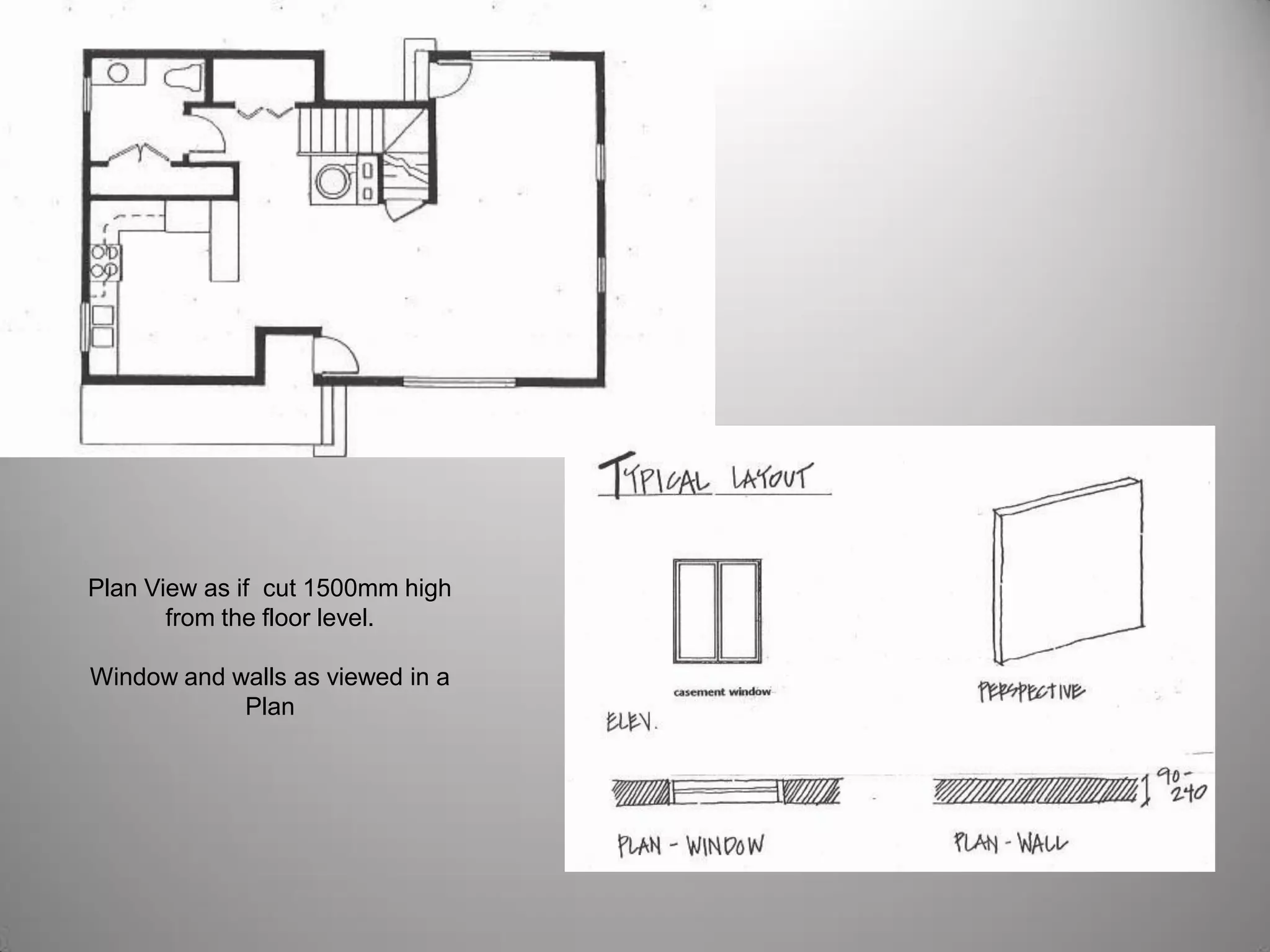
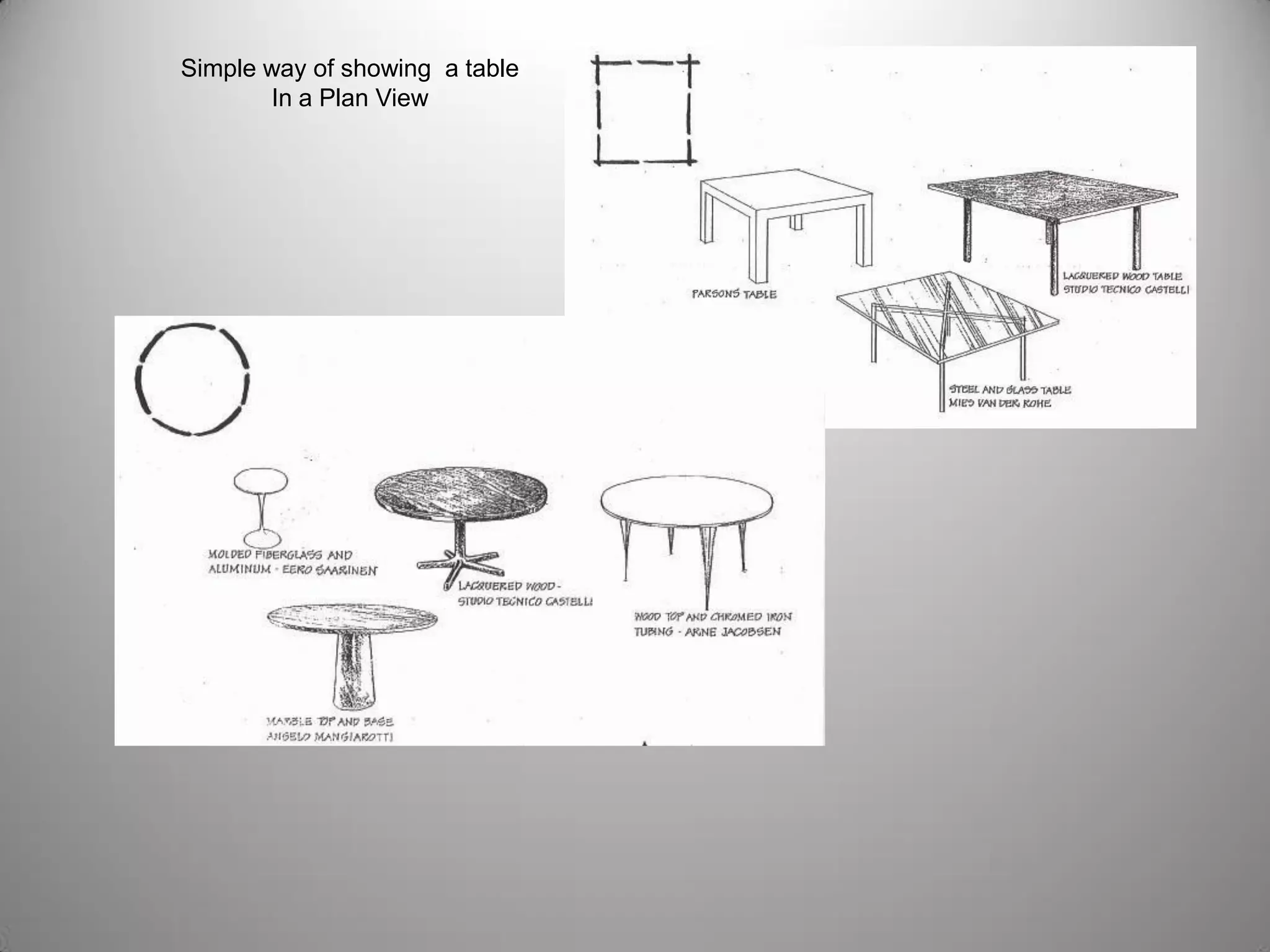
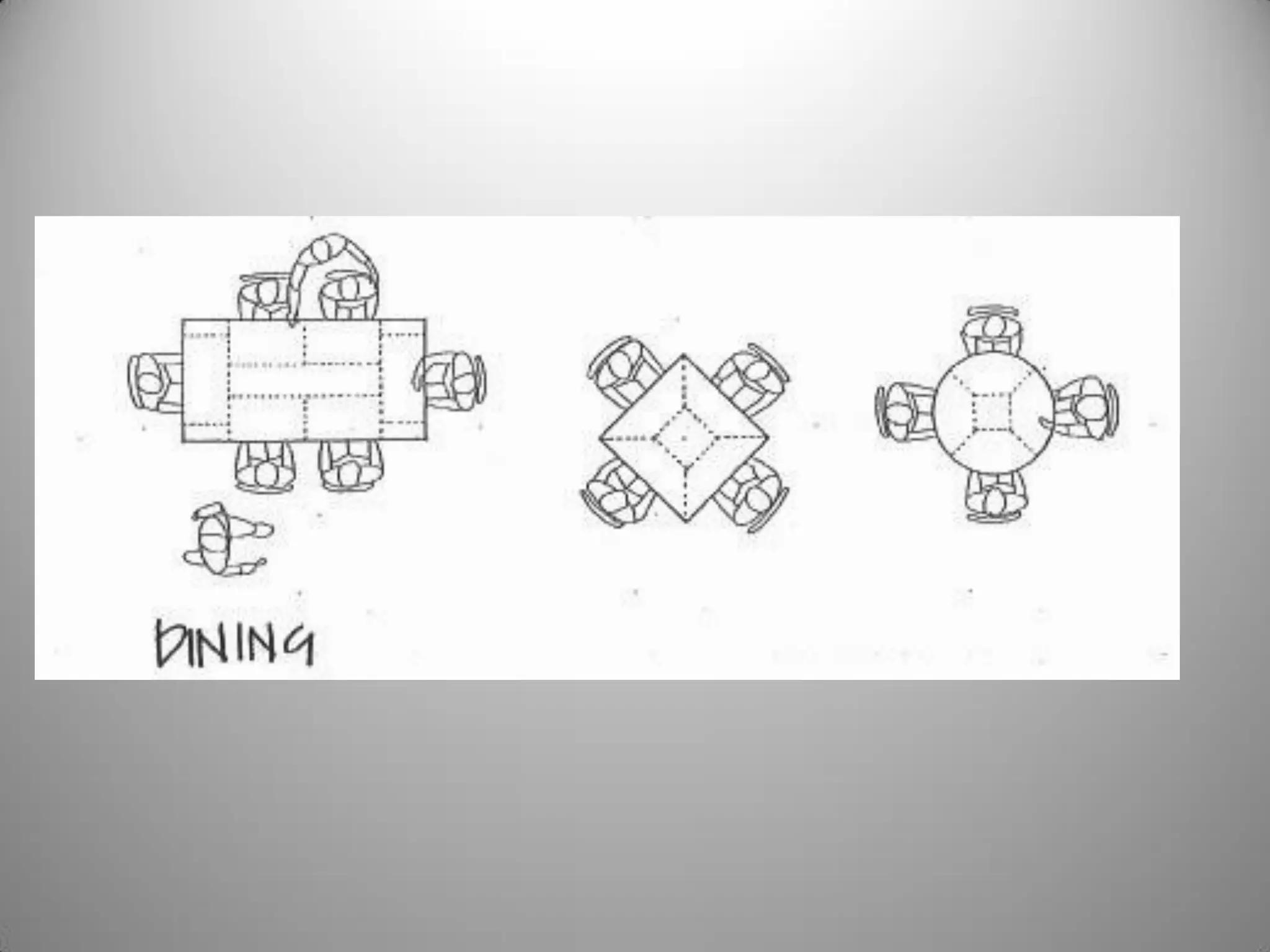
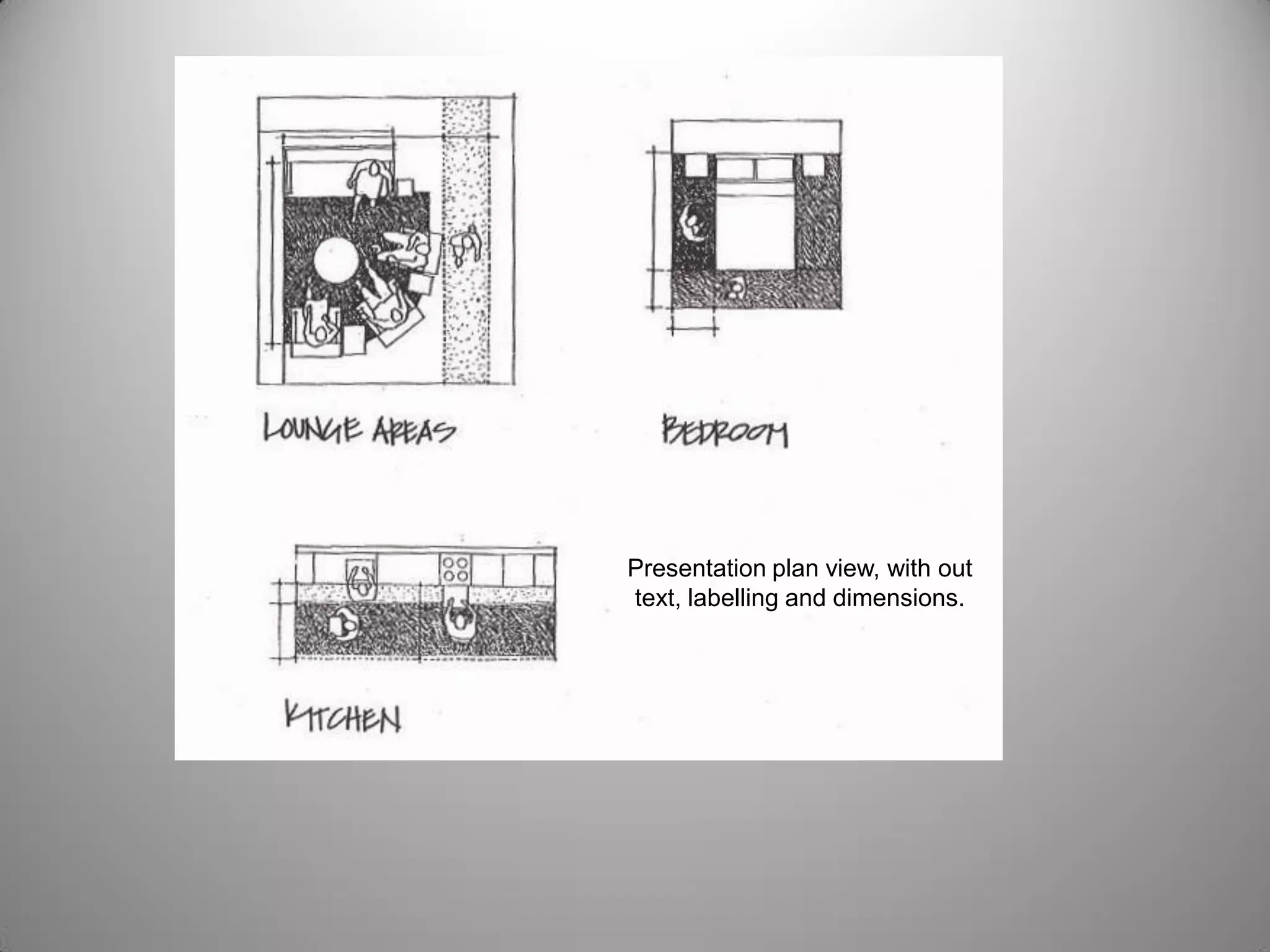
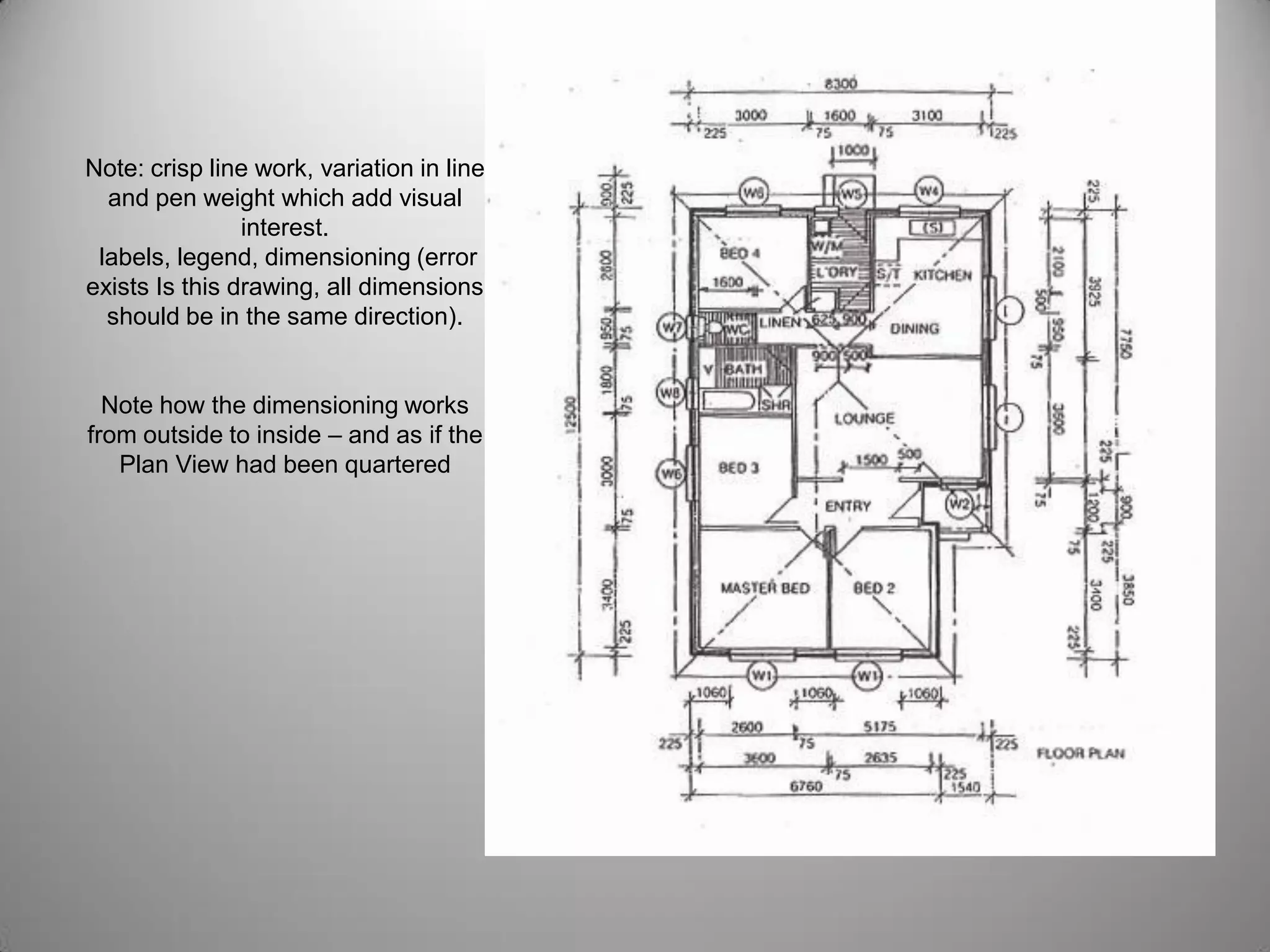
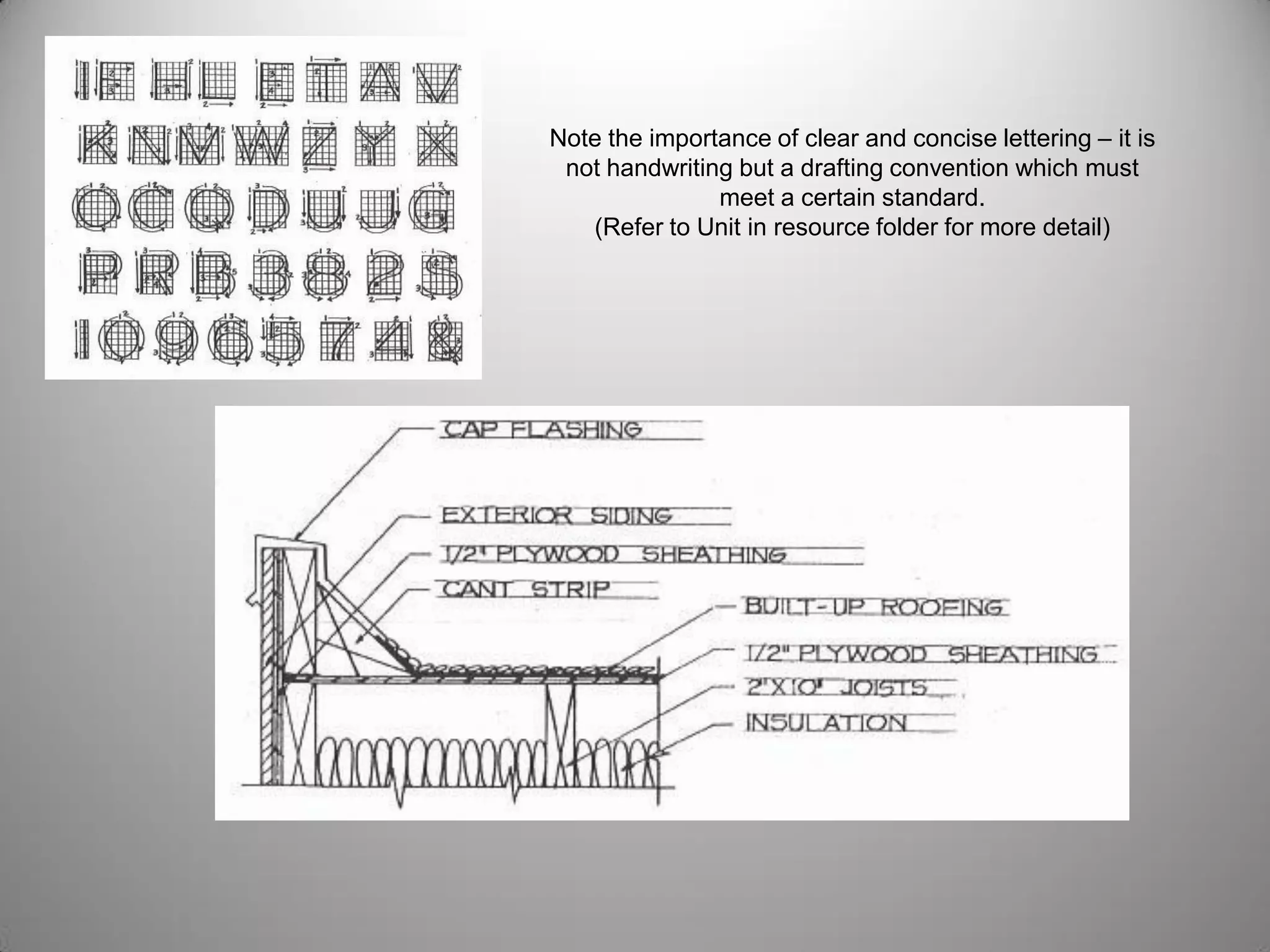
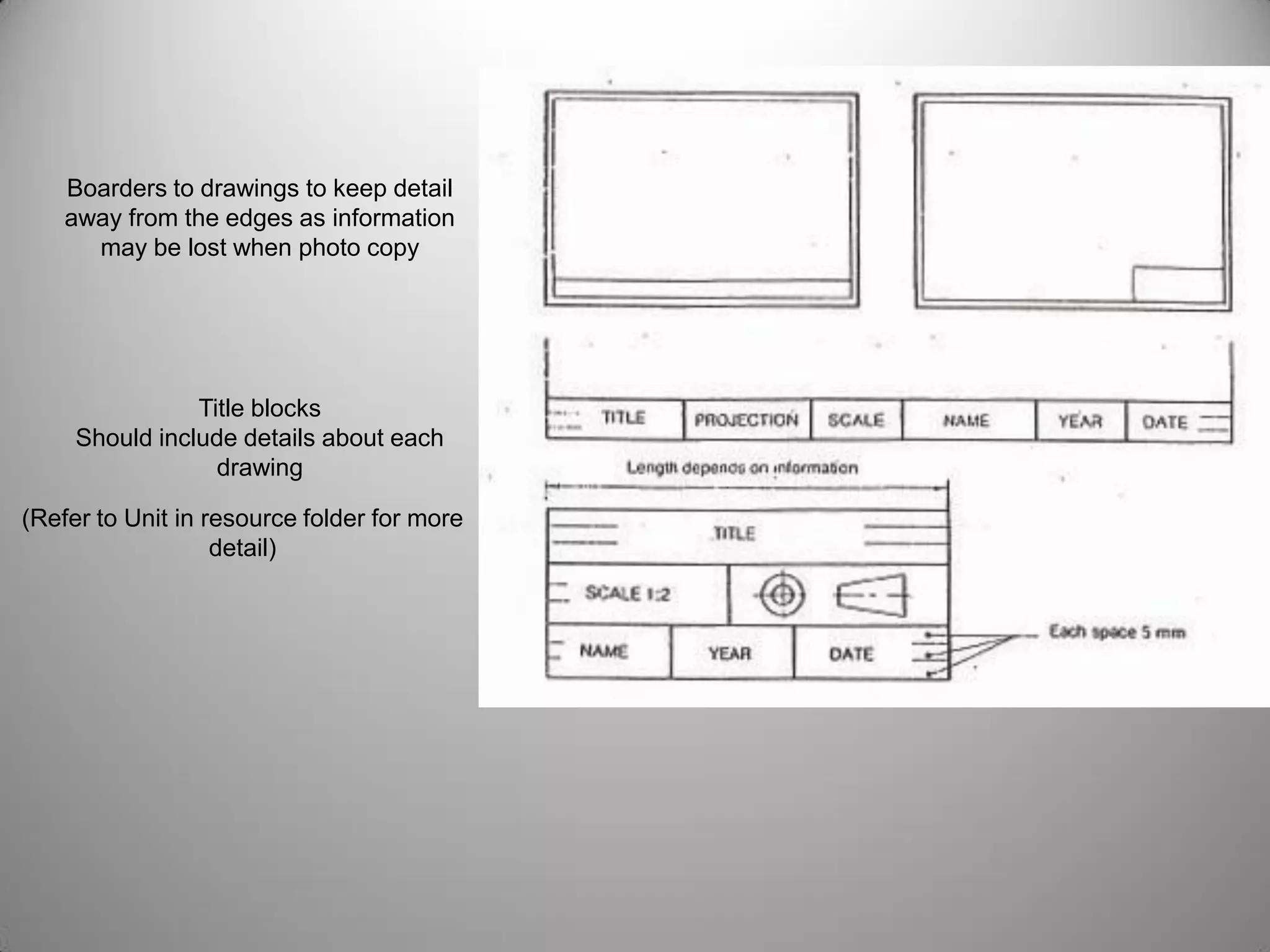
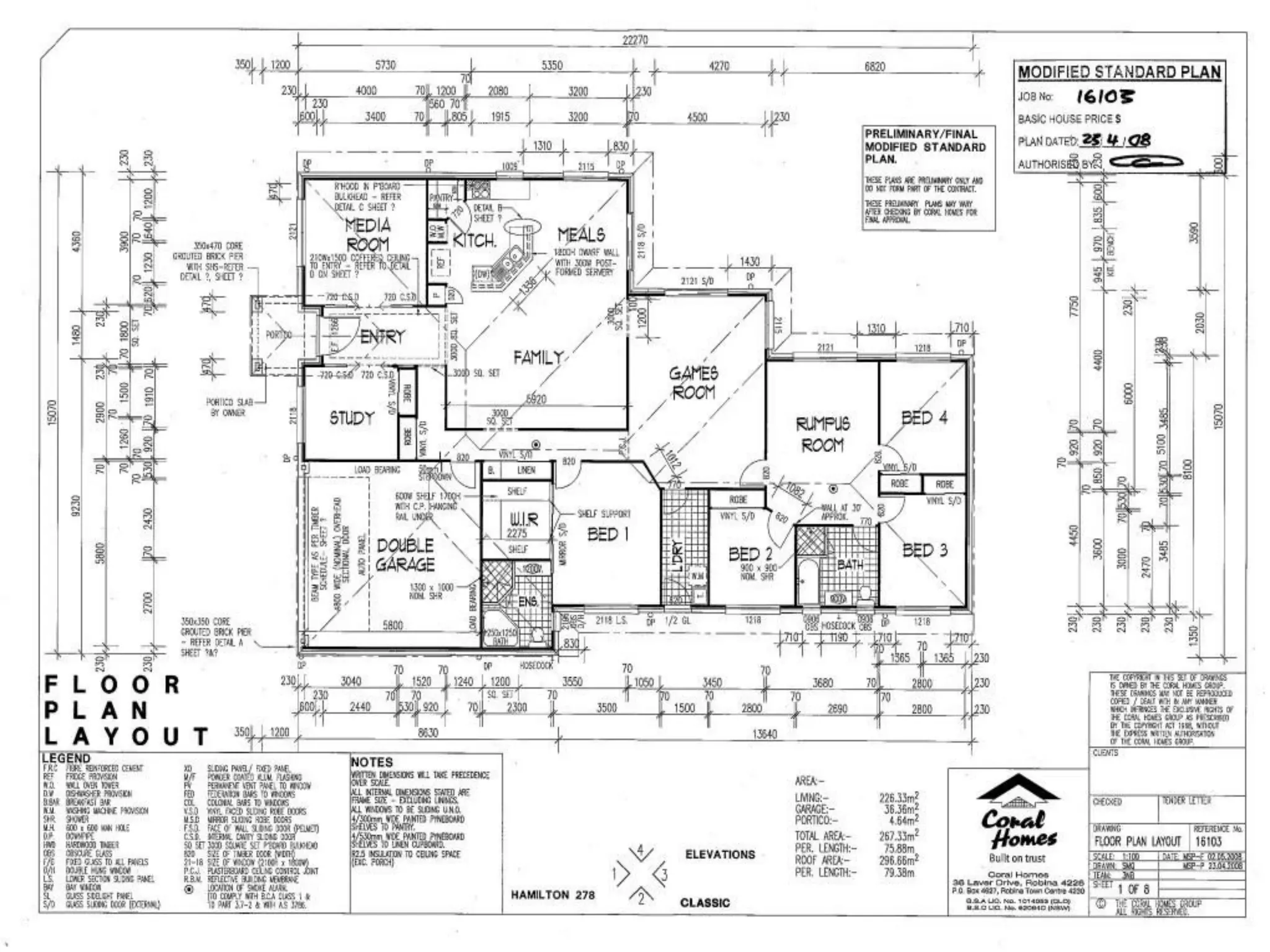
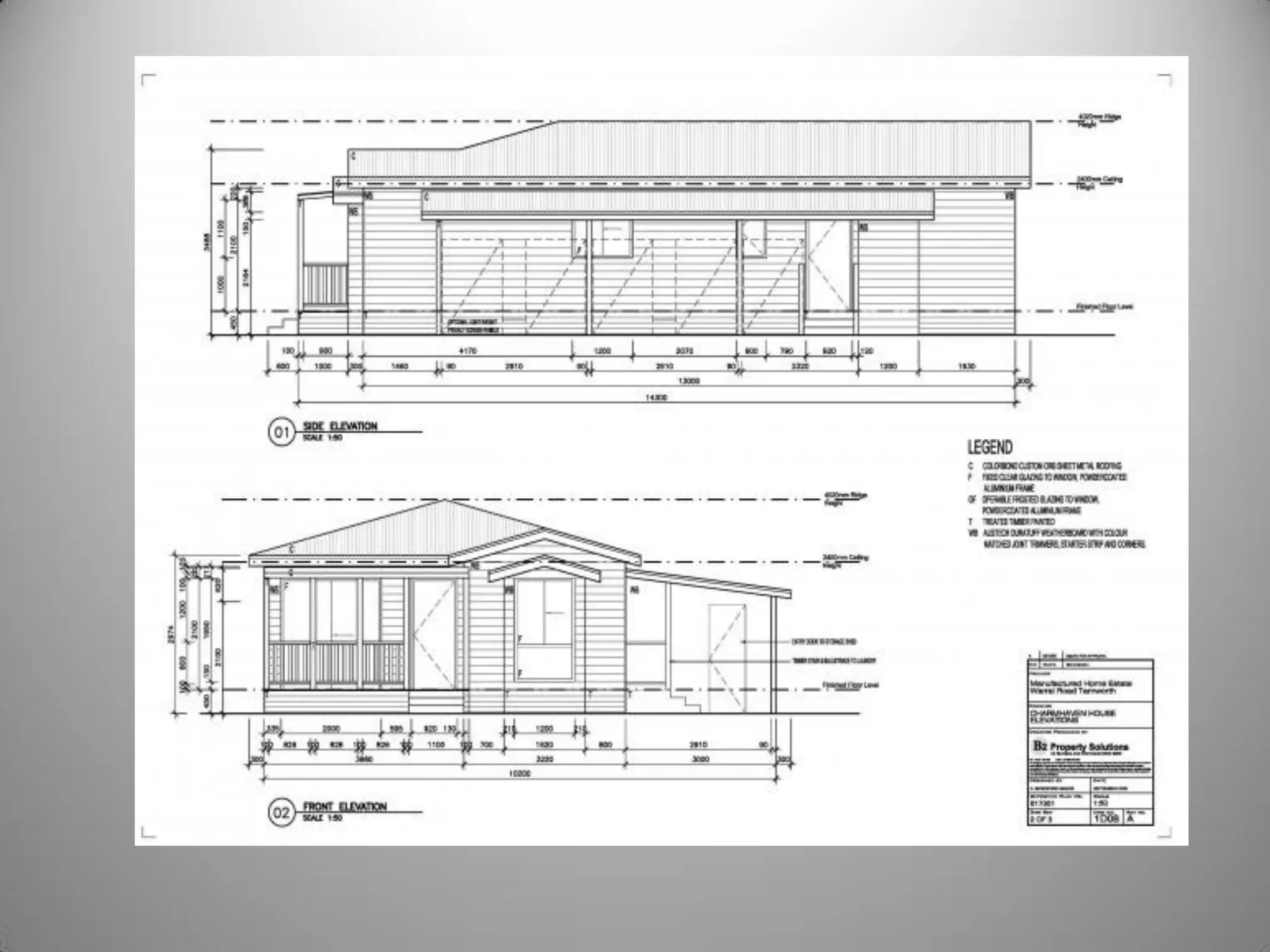
Drafting involves representing 3D structures in 2D drawings through the use of plans, elevations, and sections. Plans show a top view, elevations show front, side, or rear views, and sections show cuts through the structure. These drawings communicate design intentions to clients and tradesmen and allow people to understand if a design will fit and function in a space. Drafting requires accuracy in linework, dimensioning, lettering, and presentation as well as speed and legibility to clearly convey all necessary information to readers.