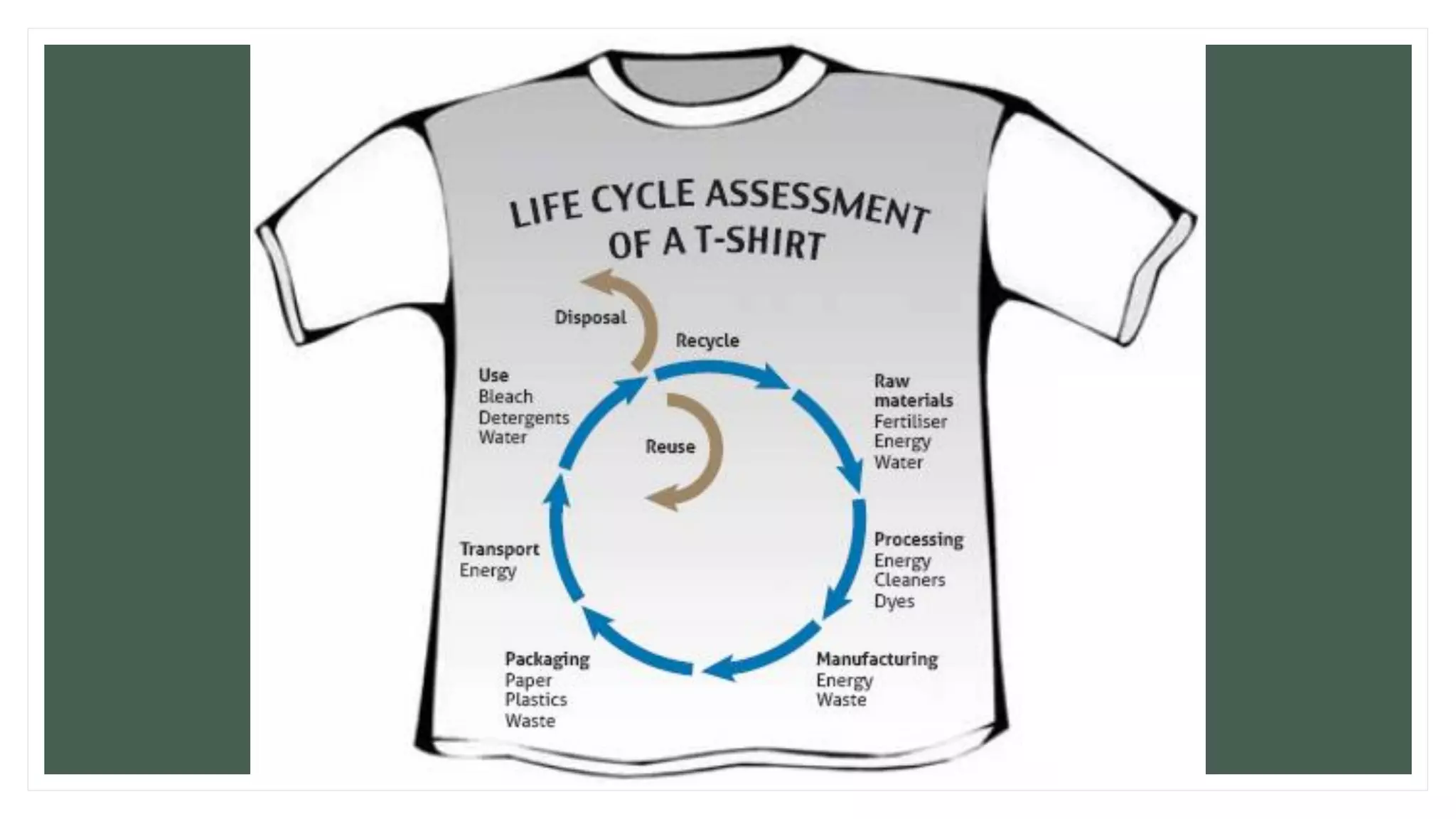
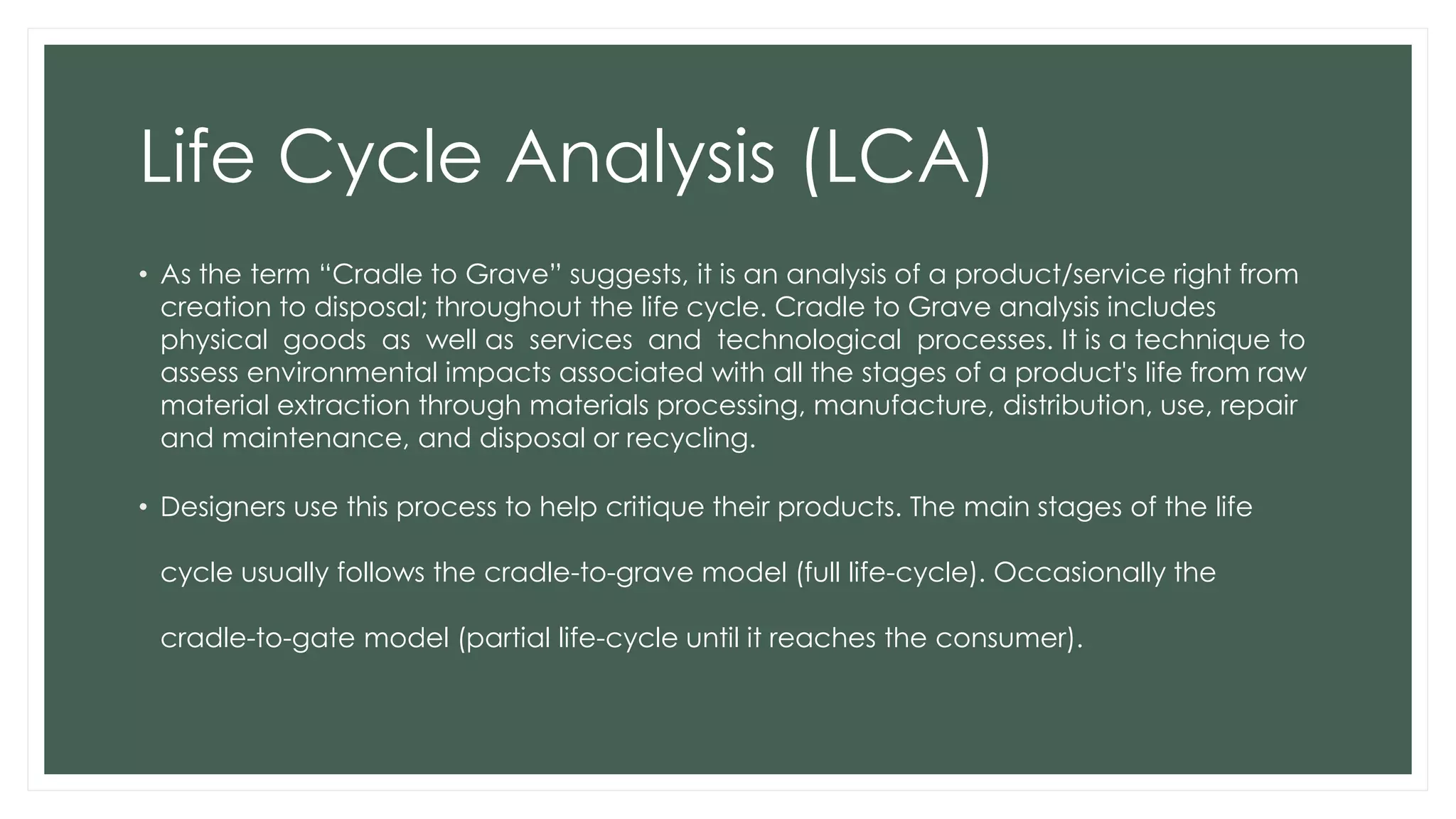
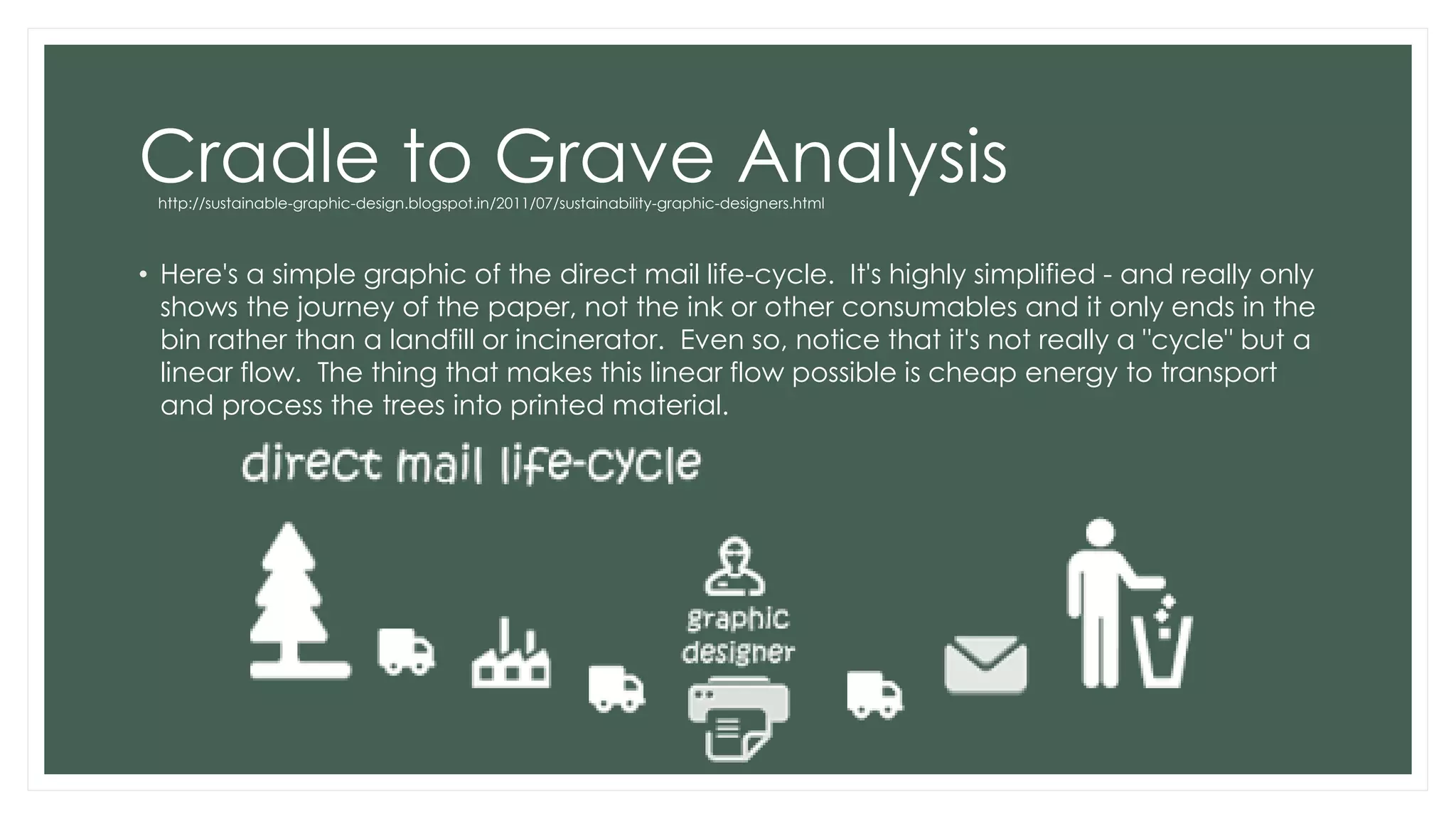
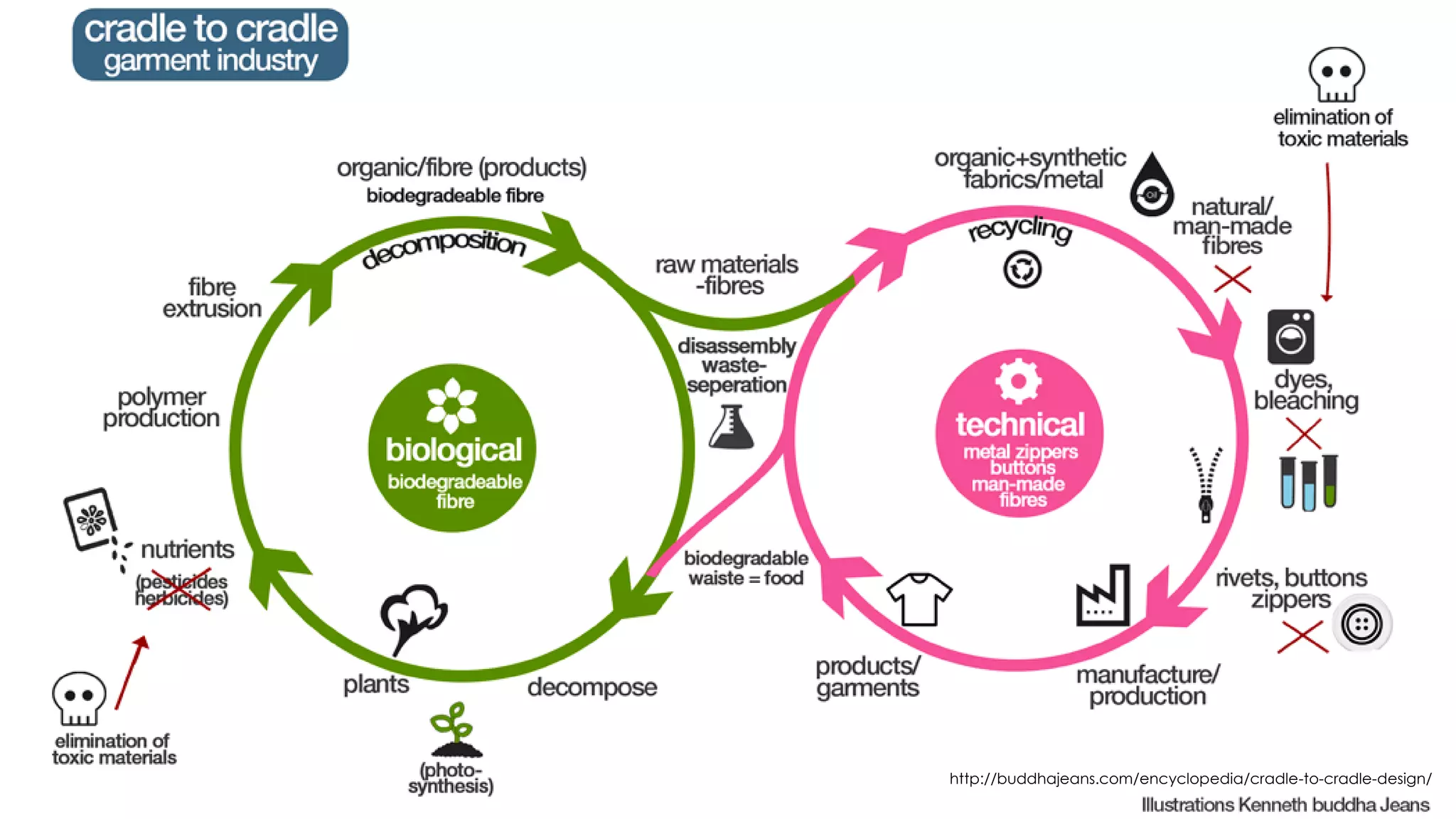
The document discusses design and the environment. It notes that climate change poses threats like rising sea levels and food shortages. Designers can play a major role in developing sustainable solutions by understanding a product's full life cycle from cradle to grave. This includes analyzing raw material extraction, production, distribution, use, and disposal, and their environmental impacts. Conducting a life cycle analysis allows designers to assess a product's environmental footprint and find ways to reduce impacts and create more sustainable designs. Cradle to cradle is introduced as a framework that aims to create waste-free production by designing products to be recycled or composted as technical or biological nutrients.