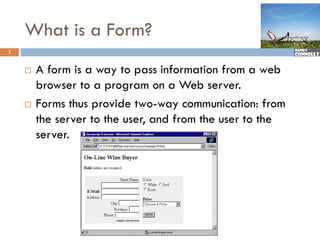
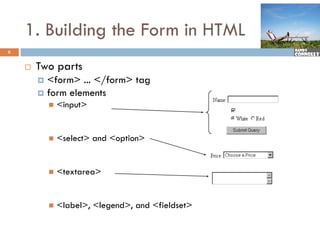
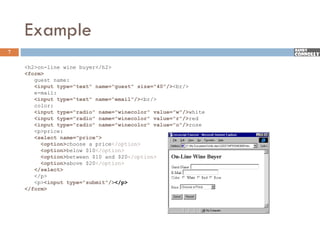
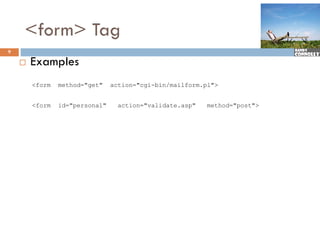
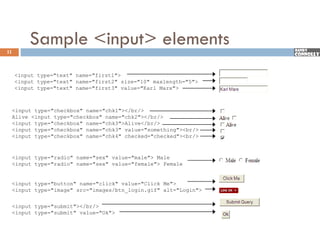
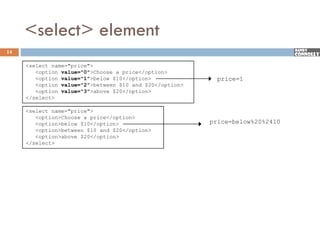
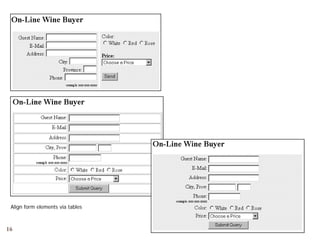
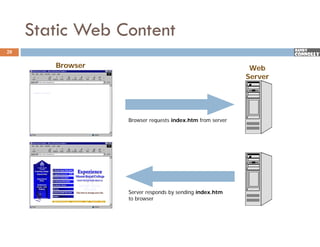
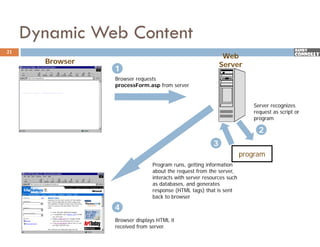
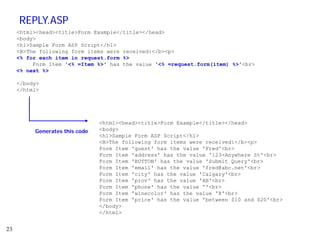
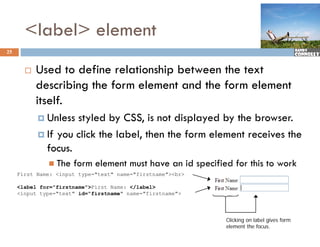
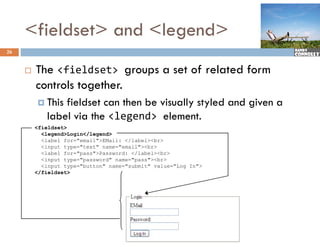
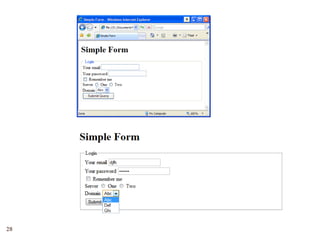
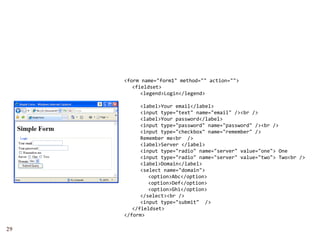
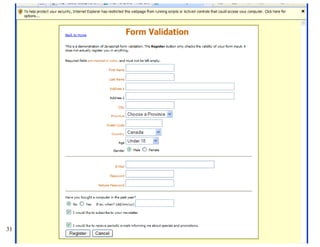
The document provides a comprehensive overview of web forms, detailing their structure, components, and the data flow between users and servers. It covers the construction of forms using HTML, including tags like <form>, <input>, <select>, and the use of client-side scripting for validation. Additionally, it highlights the importance of server-side processing for handling user inputs and improving form accessibility.